首先介绍一下BroadCastRecieve有几种:
1.无序广播(普通广播):sendBroadcast()方式
2.有序广播:sendOrderedBroadcast()方式
3.粘性广播:sendStickyBroadcast()方式
生命周期比较简单:
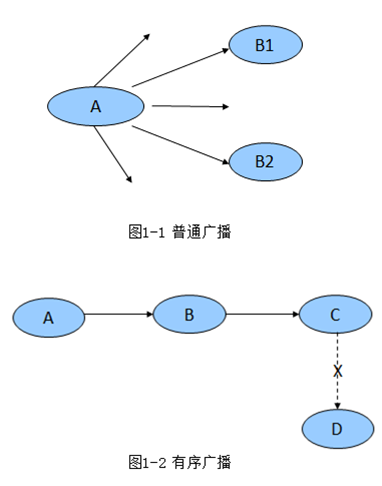
下面是无序广播与有序广播的区别:
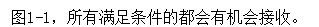
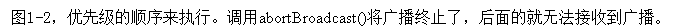
下面是普通广播(无序广播,有序广播)与粘性广播的区别:
sendBroadcast(intent); 发送之前必须注册广播,否则无法接收到广播信息。
sendStickyBroadcast(intent);发送广播后,注册也可收到广播信息。
首先看下一个无序广播,有序广播的例子:
package com.example.demo_broadcast2; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; public class MainActivity extends Activity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } /** * 发送无序广播 * * @param view */ public void send1(View view) { Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setAction("com.itheima.broadcasttest.songwennuan"); intent.putExtra("msg", "发1万块"); intent.putExtra("isUnordered", true); // 无序广播,不可被拦截,不可终止 sendBroadcast(intent); } public void send2(View view) { Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setAction("com.itheima.broadcasttest.songwennuan"); // 有序广播,可被拦截,可终止,可以修改数据 sendOrderedBroadcast(intent, null, null, null, 0, "给农民兄弟发10000块钱", null); } }
send1,send2分别为点击事件触发时调用的函数分别为发送无序广播按钮,发送有序广播按钮。
activity_main.xml文件
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <Button android:onClick="send1" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="发送无序广播" /> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_marginTop="51dp" android:onClick="send2" android:text="发送有序广播" /> </RelativeLayout>
下面依次是多个广播的实例(为了体现有序广播)
package com.example.demo_broadcast2; import android.content.BroadcastReceiver; import android.content.Context; import android.content.Intent; import android.util.Log; public class Level1Receiver extends BroadcastReceiver { private static final String TAG = "Broadcasttest"; @Override public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { boolean isUnordered = intent.getBooleanExtra("isUnordered", false); if (isUnordered) { String message = intent.getStringExtra("msg"); Log.i(TAG, "省级部门得到中央的消息:" + message); } else { String message = getResultData(); Log.i(TAG, "省级部门得到中央的消息:" + message); abortBroadcast(); // 这里是终止了消息,可以关闭或者取消这里查看LogCat中打印的效果。 setResultData("给农民兄弟发5000块钱"); // setResultData()方法,就是为了在有序广播中修改传到下一个广播中的值而存在的,且只能存储一个String. } } }
package com.example.demo_broadcast2; import android.content.BroadcastReceiver; import android.content.Context; import android.content.Intent; import android.util.Log; public class Level2Receiver extends BroadcastReceiver { private static final String TAG = "Broadcasttest"; @Override public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { boolean isUnordered = intent.getBooleanExtra("isUnordered", false); if (isUnordered) { String message = intent.getStringExtra("msg"); Log.i(TAG, "市级部门得到省级的消息" + message); } else { String message = getResultData(); Log.i(TAG, "市级部门得到省级的消息" + message); setResultData("给农民兄弟发2000块钱"); } } }
package com.example.demo_broadcast2; import android.content.BroadcastReceiver; import android.content.Context; import android.content.Intent; import android.util.Log; public class Level3Receiver extends BroadcastReceiver { private static final String TAG = "Broadcasttest"; @Override public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { boolean isUnordered = intent.getBooleanExtra("isUnordered", false); if (isUnordered) { String message = intent.getStringExtra("msg"); Log.i(TAG, "乡级部门得到市的消息:" + message); } else { String message = getResultData(); Log.i(TAG, "乡级部门得到市的消息:" + message); setResultData("给农民兄弟发两大大米"); } } }
package com.example.demo_broadcast2; import android.content.BroadcastReceiver; import android.content.Context; import android.content.Intent; import android.util.Log; public class FinalReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver { private static final String TAG = "Broadcasttest"; @Override public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { boolean isUnordered = intent.getBooleanExtra("isUnordered", false); if (isUnordered) { String message = intent.getStringExtra("msg"); Log.i(TAG, "农民兄弟得到乡的消息:" + message); } else { String message = getResultData(); Log.i(TAG, "农民兄弟得到乡的消息:" + message); } } }
首先我么线设置一下logcat如下:
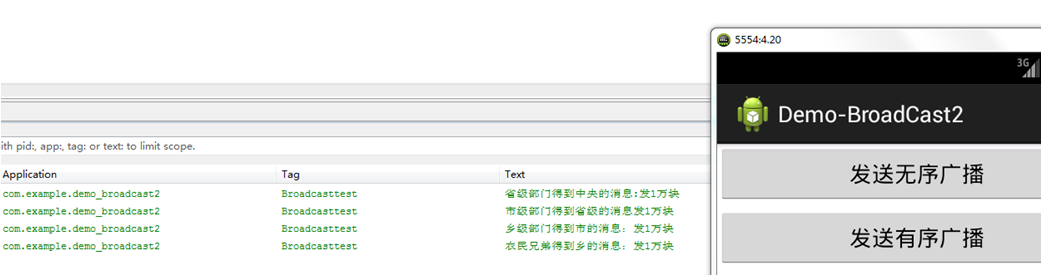
接下来我们看一下效果:
当我们点击“发送无序广播”的时候效果如下:
可见只要我们发送一个广播,注册此广播的都会搜到相同的信息。
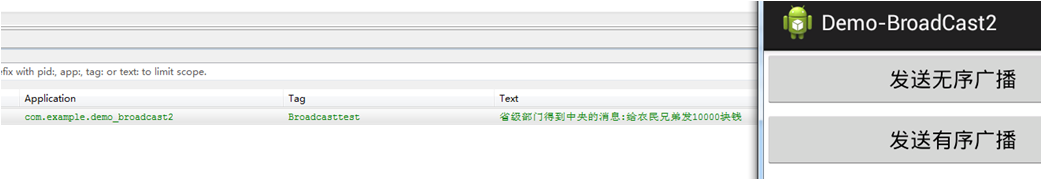
当我们点击“发送有序广播”的时候效果如下:
我们在Level1Receiver 中调用了一下方法截断了消息传输到下一个广播接收者。
abortBroadcast(); // 这里是终止了消息
如果我们把下面函数注释掉。
//abortBroadcast();
可见效果每个接收者接收到的数据都不一样这是因为我们通过一下函数向下发送了消息:
setResultData("给农民兄弟发2000块钱");
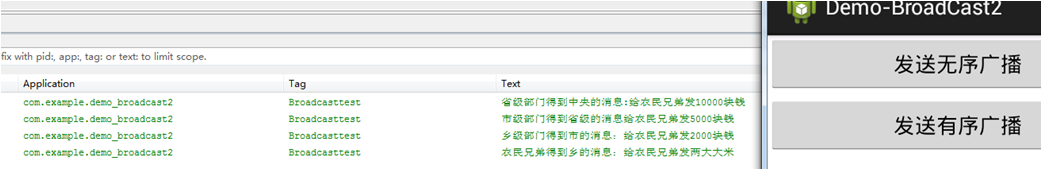
可见这是有顺序的,顺序是由广播接收者定义时可以设置优先级。代码可参考androidManifast.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.demo_broadcast2" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0" > <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" android:targetSdkVersion="17" /> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <activity android:name="com.example.demo_broadcast2.MainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> <receiver android:name=".Level1Receiver" > <intent-filter android:priority="1000" > <action android:name="com.itheima.broadcasttest.songwennuan" /> </intent-filter> </receiver> <receiver android:name=".Level2Receiver" > <intent-filter android:priority="500" > <action android:name="com.itheima.broadcasttest.songwennuan" /> </intent-filter> </receiver> <receiver android:name=".Level3Receiver" > <intent-filter android:priority="100" > <action android:name="com.itheima.broadcasttest.songwennuan" /> </intent-filter> </receiver> <receiver android:name=".FinalReceiver" > <intent-filter android:priority="-100" > <action android:name="com.itheima.broadcasttest.songwennuan" /> </intent-filter> </receiver> </application> </manifest>
还有一点我们要注意的是如果通过下面方法中指定final接收者时:
sendOrderedBroadcast(intent, null, new finalReceiver(), null, 0,"给农民兄弟发10000块钱", null);
同时调用 abortBroadcast(); // 这里是终止了消息
此时的效果如下:
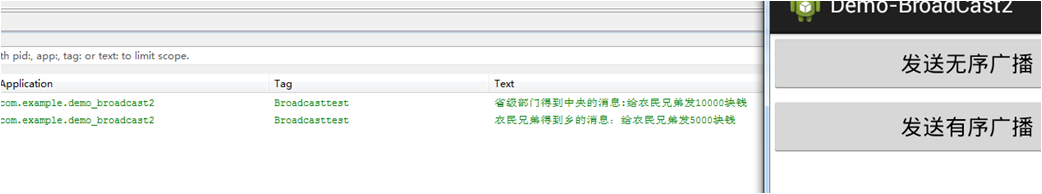
也就是说发送有序广播时可以指定一个final接收者来充当无序广播,即不管是中间截断了消息传递只要定义了final接收者那么久可以收到传递下来的消息。
接下来我么看一下粘性广播与普通广播有什么区别代码如下:
package com.example.demo_stickybroadcast; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Context; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.view.View.OnClickListener; import android.widget.Button; /* * sendBroadcast(intent); 发送之前必须注册广播,否则无法接收到广播信息。 * sendStickyBroadcast(intent);发送广播后,注册也可收到广播信息。 */ public class MainActivity extends Activity { Button btnSendi; Button btnSends; Button btnStart; Context mContext; /** Called when the activity is first created. */ @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); btnSendi = (Button) findViewById(R.id.broadcast); btnSends = (Button) findViewById(R.id.stickybroadcast); btnStart = (Button) findViewById(R.id.next_activity); mContext = getApplicationContext(); btnSendi.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setAction("com.android.my.action"); //指定意图Action mContext.sendBroadcast(intent); //普通广播发送 } }); btnStart.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, ReceiverActivity.class); startActivity(intent); //跳转到ReceiverActivity } }); btnSends.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setAction("com.android.my.action.sticky");//指定意图Action mContext.sendStickyBroadcast(intent);//sticky广播发送 } }); } }
package com.example.demo_stickybroadcast; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.BroadcastReceiver; import android.content.Context; import android.content.Intent; import android.content.IntentFilter; import android.os.Bundle; import android.widget.TextView; public class ReceiverActivity extends Activity { private IntentFilter mIntentFilter; private TextView text; /** Called when the activity is first created. */ @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_second); text = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.context); mIntentFilter = new IntentFilter(); //初始化intent过滤器 //添加action mIntentFilter.addAction("com.android.my.action"); mIntentFilter.addAction("com.android.my.action.sticky"); } private BroadcastReceiver mReceiver = new BroadcastReceiver() { @Override public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { final String action = intent.getAction(); text.setText("action: " + action); } }; @Override protected void onResume() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onResume(); registerReceiver(mReceiver, mIntentFilter); //註冊廣播 } @Override protected void onPause() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onPause(); unregisterReceiver(mReceiver); //註銷廣播 } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.demo_stickybroadcast" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0" > <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" android:targetSdkVersion="17" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BROADCAST_STICKY" /> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <activity android:name="com.example.demo_stickybroadcast.MainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> <activity android:name="com.example.demo_stickybroadcast.ReceiverActivity" > </activity> </application> </manifest>
运行应用后可以操作一下步骤:
1.点击“sendbroadcast”
2.点击进入“StartAcitivity”
此时你会发现没有显示任何信息这说明,在ReceiverActivity中注册的广播没有收到任何信息。
这是因为普通广播发送以后即通过sendbroadcast() 或 sendOrderedbroadcast(),只有已经注册相应的广播的接受者可以接到信息,而后注册此广播的广播接收者是无法接受到的。
也就是说要接收普通广播发出的广播时,需发送广播之前先注册相应的广播。
而当你操作一下步骤时:
1.点击“sendStickybroadcast”
2.点击进入“StartAcitivity”
你会发现广播发送出去以后注册此广播的广播接收者是可以收到此消息的。