1、Vuex是干什么的
Vuex是一个专门为Vuejs应用程序开发的状态管理模式
状态管理模式到底是什么?
1)你可以简单的将其看成:把需要多个组件共享的变量全部存储在一个对象里面
2)然后将这个对象放在顶层的Vue实例中,让其他组件可以使用
3)那么,多个组件是不是可以共享这个对象中的所有变量属性了呢?
2、使用vuex入门
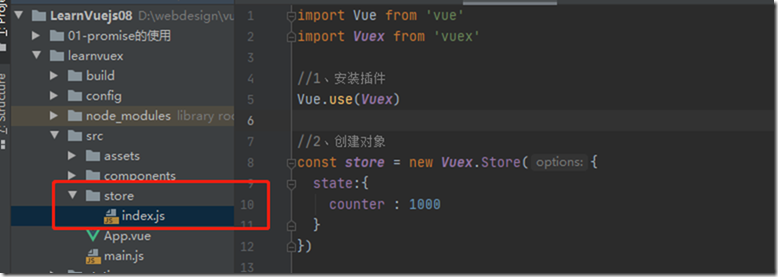
1)创建一个store文件夹和一个index.js,vuex相关的内容放在此处
2)index.js中添加如下内容
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' //1、安装插件 Vue.use(Vuex) //2、创建对象 const store = new Vuex.Store({ state:{ counter : 1000 } }) //3、导出store对象 export default store
3)最后在main.js中导入并且引用
import store from "./store"; Vue.prototype.$store = store /* eslint-disable no-new */ new Vue({ el: '#app', store, render: h => h(App) })
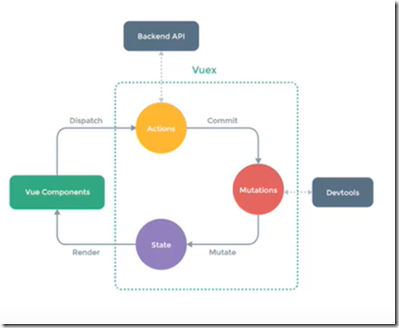
3、Vuex的状态管理过程
state: 存储共享的变量
Action:做一些异步操作
Mutitions :函数,直接操作vuex存放的变量
为什么不提倡直接在Vue Component中直接修改State中的内容?
原因:State被多个组件共享,如果不经过Mutations修改State,就无法通过Devtools
监控State被哪些组件修改过。
4、Vuex的核心概念
state : 存放共享的变量
state:{ counter : 100, student : [ {id:1,name:'tom',age:18}, {id:1,name:'tony',age:23}, {id:1,name:'harry',age:30}, {id:1,name:'jack',age:40} ] },
getters: 对共享的变量做一些处理,类似于组件中的 compute
getters:{ powerCounter(state){ return state.counter*state.counter }, more20Stu(state){ return state.student.filter(s => s.age > 20) }, moreAgeStu(state){ return function (age) { return state.student.filter(s => s.age > age) } } }
Mutation 状态更新:
Vuex的store状态更新的唯一方式就是提交Mutation
Mutation 主要包含两部分:
字符串的事件类型(type)
一个回调函数(handler),该回调函数的第一个参数就是state
1、基本使用:
定义: mutations: { // 方法 increment(state){ state.counter++ }, decrement(state){ state.counter-- } } 使用: methods:{ addition(){ this.$store.commit('increment') } }
2、传递参数
在通过mutation更新数据的时候,有可能我们希望携带一些额外的参数,这些参数被称之为
mutation的载荷(Payload)
// 在store的index.js中定义 incrementCount(state,count){ state.counter += count } //在 component 中使用 addCount(count){ this.$store.commit('incrementCount',count) }
3、mutation另一种提交风格
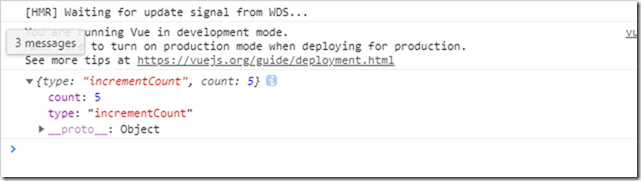
incrementCount(state,payload){ //payload是一个对象
console.log(payload);
}
addCount(count){
//this.$store.commit('incrementCount',count)
this.$store.commit({
type: 'incrementCount',
count: count
})
}
打印出来的其实是一个对象
4、mutation的响应规则
Vuex store中的state是响应式的,当state中的数据发生变化时,Vue组件会自动更新
但是这要求我们必须遵循一些Vuex对应的规则
提前在store中初始化所需的属性
当给state中的对象添加新属性时,使用下面的方式
Vue.set(state.info,'address','洛杉矶‘)
Vue.delete(state.info,'age')
这些属性都会加入到响应式系统中,而响应式系统会监听属性的变化,当属性发生变化时,
会通知所有界面中用到该属性的地方,让界面发生刷新
Actions的使用详解
通常情况下,Vuex要求我们Mutation中的方法必须是同步方法
主要原因是,当我们使用devtools时,可以使用devtools帮找我们捕捉mutation的快照
但是如果使用异步操作,那么devtools将不能很好的追踪这个操作什么时候会被完成
//定义 actions:{ aUpdateInfo(context){ //context:上下文 setTimeout(function () { context.commit('updateInfo') },1000) } } //使用 updateInfo(){ this.$store.dispatch('aUpdateInfo') }
当actions中的异步操作需要回调函数时:
//当异步操作需要有回调函数时 aUpdateInfo(context){ return new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{ setTimeout(function () { context.commit('updateInfo') resolve('1111') },1000) }) } updateInfo(){ //this.$store.dispatch('aUpdateInfo') this.$store.dispatch('aUpdateInfo').then(res =>{ console.log(res); } ) }
Vuex-modules的使用详解
Module是模块的意思,为什么在Vuex中我们要使用模块呢?
Vuex使用单一状态树,那么也意味着很多状态会交给Vuex来管理
当应用变得非常复杂时,store对象有可能变得相当臃肿
为了解决这个问题,Vuex允许我们将store分隔成模块(Module).而每个模块拥有自己的state,mutations,actions,getters
//2、创建对象 const moduleA = { state:{ name: 'hermine' }, getters:{ fullname(state){ return state.name + "tom"; } }, mutations: { updateName(state,payload){ state.name = payload } }, actions:{ aUpdateName(context){ setTimeout(() => { context.commit('updateName','wangwu') },2000) } } } const store = new Vuex.Store({ modules: { a: moduleA } }) <!--modules使用的演示--> <h2>modules使用的演示</h2> <h2>{{$store.state.a.name}}</h2> <button @click="updateName">修改名称</button> <h2>{{$store.getters.fullname}}</h2> <button @click="syncUpdateName">异步修改名称</button> updateName() { this.$store.commit('updateName','jack') }, syncUpdateName(){ this.$store.dispatch('aUpdateName') }
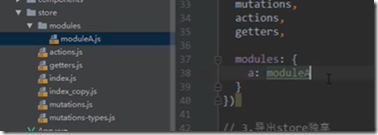
5、Vuex-store文件夹的目录结构
将 mutations,getters...抽成单独的js,但是state不抽离出来