前述
前端三大框架Angular、React和Vue都推行单页面应用SPA开发模式,这是因为在路由切换时,替换DOM Tree中发生修改的DOM部分,来减少原来因为多页面应用跳转带来巨大的性能损耗。
他们都有自己典型的路由解决方案:@Angular/router、react-router、vue-router。
一般来说,这些路由插件总是提供俩种不同的路由方式:Hash和History,有时候也会提供非浏览器环境下的路由方式Abstract,在vue-router中使用外观模式将不同的几种路由方式提供了一个一致的高层接口,让我们可以在不同路由方式中切换。
Hash 和 History 除了外观上的不同之外。还有一个重要的区别:
1.1 相关api
MDN:Location
MDN上的例子:
var url = document.createElement('a'); url.href = 'https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/search?q=URL#search-results-close-container'; console.log(url.href); // https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/search?q=URL#search-results-close-container console.log(url.protocol); // https: console.log(url.host); // developer.mozilla.org console.log(url.hostname); // developer.mozilla.org console.log(url.port); // (blank - https assumes port 443) console.log(url.pathname); // /en-US/search console.log(url.search); // ?q=URL console.log(url.hash); // #search-results-close-container console.log(url.origin); // https://developer.mozilla.org
1.2 实例
原理是吧目标路由和对应的回调记录下来,点击跳转触发hashchange的时候获取当前路径并执行对应的回调,效果:
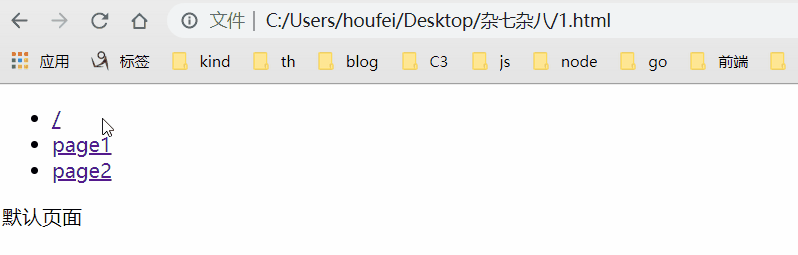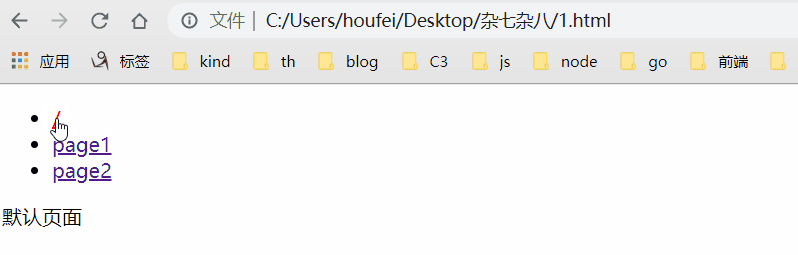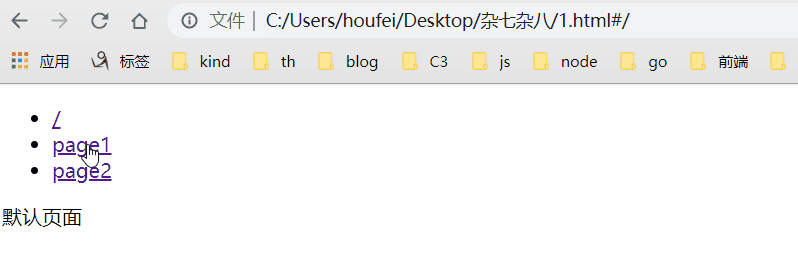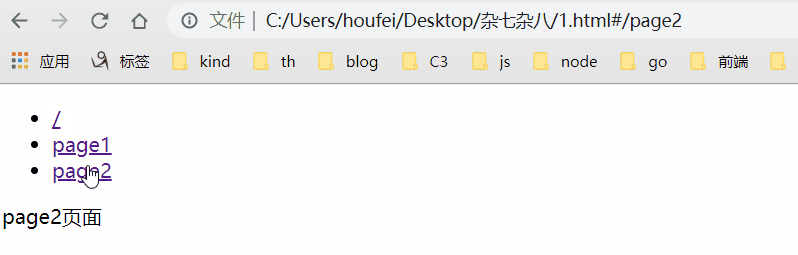
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <ul> <li><a href="#/">/</a></li> <li><a href="#/page1">/page1</a></li> <li><a href="#/page2">/page2</a></li> </ul> <div class="content-div"></div> <script> // 创建路由类 class RouterClass { constructor() { this.routes = {} // 记录路径标识符对应的 cb this.currentUrl = '' // 记录hash只为方便执行 cb window.addEventListener('load', () => this.render()) window.addEventListener('hashchange', () => this.render()) } // 初始化 static init() { window.Router = new RouterClass() } // 注册路由 和 回调 @param - path - 路径 // @param - cb - 回调 route(path, cb) { // 将路径及其对应的方法添加到 this.routes 对象中 this.routes[path] = cb || function() {} } // 记录当前 hash,执行cb render() { this.currentUrl = location.hash.slice(1) || '/' this.routes[this.currentUrl]() // 默认页面 } } // 调用方法,监听 load 和 hashchange 事件 RouterClass.init() // 过去div 并 给div中添加数据 const ContentDom = document.querySelector('.content-div') const changeContent = content => ContentDom.innerHTML = content // 调用方法 Router.route('/', () => changeContent('默认页面')) Router.route('/page1', () => changeContent('page1页面')) Router.route('/page2', () => changeContent('page2页面')) </script> </body> </html>
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <ul> <li><a href="#/">/</a></li> <li><a href="#/page1">page1</a></li> <li><a href="#/page2">page2</a></li> </ul> <div class='content-div'></div> <button>back</button> <script> class RouterClass { constructor() { this,isBack = false this.routes = {} // 记录路径标识符对应的cb this.currentStack = [] // hash 栈 window.addEventListener('load', () => this.render()) window.addEventListener('hashchange', () => this.render()) } // 初始化 static init() { window.Router = new RouterClass() } // 记录 path 对应的 cb 和 cb 的 回调 route(path, cb) { this.routes[path] = cb || function() {} } // 入栈当前hash,执行 cb 跳转页面 render() { if(this.isBack) { // 如果是由backoff进入,则置false之后return this.isBack = false return } this.currentUrl = location.hash.slice(1) || '/' this.historyStack.push(this.currentUrl) this.routes[this.currentUrl]() } // 路由后退 back() { this.isback = true this.historyStack.pop() // 移除当前 hash, 回退到上一个 const { length } = this.historyStack if(!length) return let prev = this.historyStack[length -1] // 拿到要回退到的目标hash location.hash = `#${ prev }` this.currentStack = prev this.routes[prev]() // 执行对应cb } } RouterClass.init() const BtnDom = document.querySelector('button') const ContentDom = document.querySelector('.content-div') const changeContent = content => ContentDom.innerHTML = content Router.route('/', () => changeContent('默认页面')) Router.route('/page1', () => changeContent('page1页面')) Router.route('/page2', () => changeContent('page2页面')) // bind() 可以改变函数内部的this的指向,并返回一个新的函数,你必须调用它才会被执行 BtnDom.addEventListener('click', Router.back.bind(Router), false) </script> </body> </html>
2.1
window.history.back(); // 这和用户点击浏览器回退按钮的效果相同 window.history.forward(); // 向前跳转 window.history.go(n); // 跳转到 history 中指定的一个点 window.history.go(-1); // 向后移动一个页面 (等同于调用 back()) window.history.go(1); // 向前移动一个页面, 等同于调用了 forward() window.history.length; // 长度属性的值来确定的历史堆栈中页面的数量
history.pushState() // 追加一条新的历史记录 // history.pushState('状态对象:历史记录的标题', '标题:历史记录的描述', url) history.replaceState() // 替换当前的历史记录为一条新的记录 // history.replaceState('历史记录的标题', '历史记录的描述', url) // window.onpopstate 事件 历史切换事件
pushState() 方法的例子
假设在http://mozilla.org/foo.html中执行了以下js代码:
let stateObj = { foo: "bar", }; history.pushState(stateObj, "page 2", "bar.html");
假设用户又访问了http://google.com,然后点击了返回按钮,此时地址栏现实的是`http://mozilla.org/bar.html,history.state中包含了stateObj的一份拷贝。页面此时展现为bar.html。切页面被重新加载了,所以popstate事件将不会被触发。
如果我们再次点击返回按钮,页面URL会变为http://mozilla.org/foo.html,文档对象document会触发另外一个 popstate 事件,这一次的事件对象state object为null。 这里也一样,返回并不改变文档的内容,尽管文档在接收 popstate 事件时可能会改变自己的内容,其内容仍与之前的展现一致。
replaceState() 方法的例子
history.replaceState() 的使用与 history.pushState() 非常相似,区别在于 replaceState() 是修改了当前的历史记录项而不是新建一个。 注意这并不会阻止其在全局浏览器历史记录中创建一个新的历史记录项。
假设http://mozilla.org/foo.html执行了如下JavaScript代码:
let stateObj = { foo: "bar", }; history.pushState(stateObj, "page 2", "bar.html");
history.replaceState(stateObj, "page 3", "bar2.html");
假设现在用户重新导向到了http://www.microsoft.com,然后点击了回退按钮。这里,地址栏会显示http://mozilla.org/bar2.html。假如用户再次点击回退按钮,地址栏会显示http://mozilla.org/foo.html,完全跳过了bar.html。
每当活动的历史记录项发生变化时, popstate 事件都会被传递给window对象。如果当前活动的历史记录项是被 pushState 创建的,或者是由 replaceState 改变的,那么 popstate事件的状态属性 state 会包含一个当前历史记录状态对象的拷贝。
使用示例请参见 window.onpopstate 。
获取当前状态
页面加载时,或许会有个非null的状态对象。这是有可能发生的,举个例子,假如页面(通过pushState() 或 replaceState() 方法)设置了状态对象而后用户重启了浏览器。那么当页面重新加载时,页面会接收一个onload事件,但没有 popstate 事件。然而,假如你读取了history.state属性,你将会得到如同popstate 被触发时能得到的状态对象。
你可以读取当前历史记录项的状态对象state,而不必等待popstate 事件, 只需要这样使用history.state 属性:
let currentState = history.state;
2.2 实例
将之前的例子改造一下,在需要路由跳转的地方使用 history.pushState 来入栈并记录 cb,
前进后退的时候监听 popstate 事件拿到之前传给 pushState 的参数并执行对应 cb,因为借用了浏览器自己的 Api。

<html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>h5 router</title> </head> <body> <ul> <li><a href="/">/</a></li> <li><a href="/page1">page1</a></li> <li><a href="/page2">page2</a></li> </ul> <div class='content-div'></div> <script> class RouterClass { constructor(path) { this.routes = {} // 记录路径标识符对应的cb history.replaceState({ path }, null, path) this.routes[path] && this.routes[path]() window.addEventListener('popstate', e => { console.log(e, ' --- e') const path = e.state && e.state.path this.routes[path] && this.routes[path]() }) } /** * 初始化 */ static init() { window.Router = new RouterClass(location.pathname) } /** * 记录 path 对应 cb * @param path 路径 * @param cb 回调 */ route(path, cb) { this.routes[path] = cb || function() {} } /** * 触发路由对应回调 * @param path */ go(path) { history.pushState({ path }, null, path) this.routes[path] && this.routes[path]() } } RouterClass.init() const ul = document.querySelector('ul') const ContentDom = document.querySelector('.content-div') const changeContent = content => ContentDom.innerHTML = content Router.route('/', () => changeContent('默认页面')) Router.route('/page1', () => changeContent('page1页面')) Router.route('/page2', () => changeContent('page2页面')) ul.addEventListener('click', e => { if (e.target.tagName === 'A') { e.preventDefault() Router.go(e.target.getAttribute('href')) } }) </script> </body> </html>
