Snacks
Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1779 Accepted Submission(s): 427
Problem Description
百度科技园内有n
个零食机,零食机之间通过n−1
条路相互连通。每个零食机都有一个值v
,表示为小度熊提供零食的价值。
由于零食被频繁的消耗和补充,零食机的价值v 会时常发生变化。小度熊只能从编号为0的零食机出发,并且每个零食机至多经过一次。另外,小度熊会对某个零食机的零食有所偏爱,要求路线上必须有那个零食机。
为小度熊规划一个路线,使得路线上的价值总和最大。
由于零食被频繁的消耗和补充,零食机的价值v 会时常发生变化。小度熊只能从编号为0的零食机出发,并且每个零食机至多经过一次。另外,小度熊会对某个零食机的零食有所偏爱,要求路线上必须有那个零食机。
为小度熊规划一个路线,使得路线上的价值总和最大。
Input
输入数据第一行是一个整数T(T≤10)
,表示有T
组测试数据。
对于每组数据,包含两个整数n,m(1≤n,m≤100000) ,表示有n 个零食机,m 次操作。
接下来n−1 行,每行两个整数x 和y(0≤x,y<n) ,表示编号为x 的零食机与编号为y 的零食机相连。
接下来一行由n 个数组成,表示从编号为0到编号为n−1 的零食机的初始价值v(|v|<100000) 。
接下来m 行,有两种操作:0 x y ,表示编号为x 的零食机的价值变为y ;1 x ,表示询问从编号为0的零食机出发,必须经过编号为x 零食机的路线中,价值总和的最大值。
本题可能栈溢出,辛苦同学们提交语言选择c++,并在代码的第一行加上:
`#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000") `
对于每组数据,包含两个整数n,m(1≤n,m≤100000) ,表示有n 个零食机,m 次操作。
接下来n−1 行,每行两个整数x 和y(0≤x,y<n) ,表示编号为x 的零食机与编号为y 的零食机相连。
接下来一行由n 个数组成,表示从编号为0到编号为n−1 的零食机的初始价值v(|v|<100000) 。
接下来m 行,有两种操作:0 x y ,表示编号为x 的零食机的价值变为y ;1 x ,表示询问从编号为0的零食机出发,必须经过编号为x 零食机的路线中,价值总和的最大值。
本题可能栈溢出,辛苦同学们提交语言选择c++,并在代码的第一行加上:
`#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000") `
Output
对于每组数据,首先输出一行”Case #?:”,在问号处应填入当前数据的组数,组数从1开始计算。
对于每次询问,输出从编号为0的零食机出发,必须经过编号为x 零食机的路线中,价值总和的最大值。
对于每次询问,输出从编号为0的零食机出发,必须经过编号为x 零食机的路线中,价值总和的最大值。
Sample Input
1
6 5
0 1
1 2
0 3
3 4
5 3
7 -5 100 20 -5 -7
1 1
1 3
0 2 -1
1 1
1 5
Sample Output
Case #1:
102
27
2
20
Source
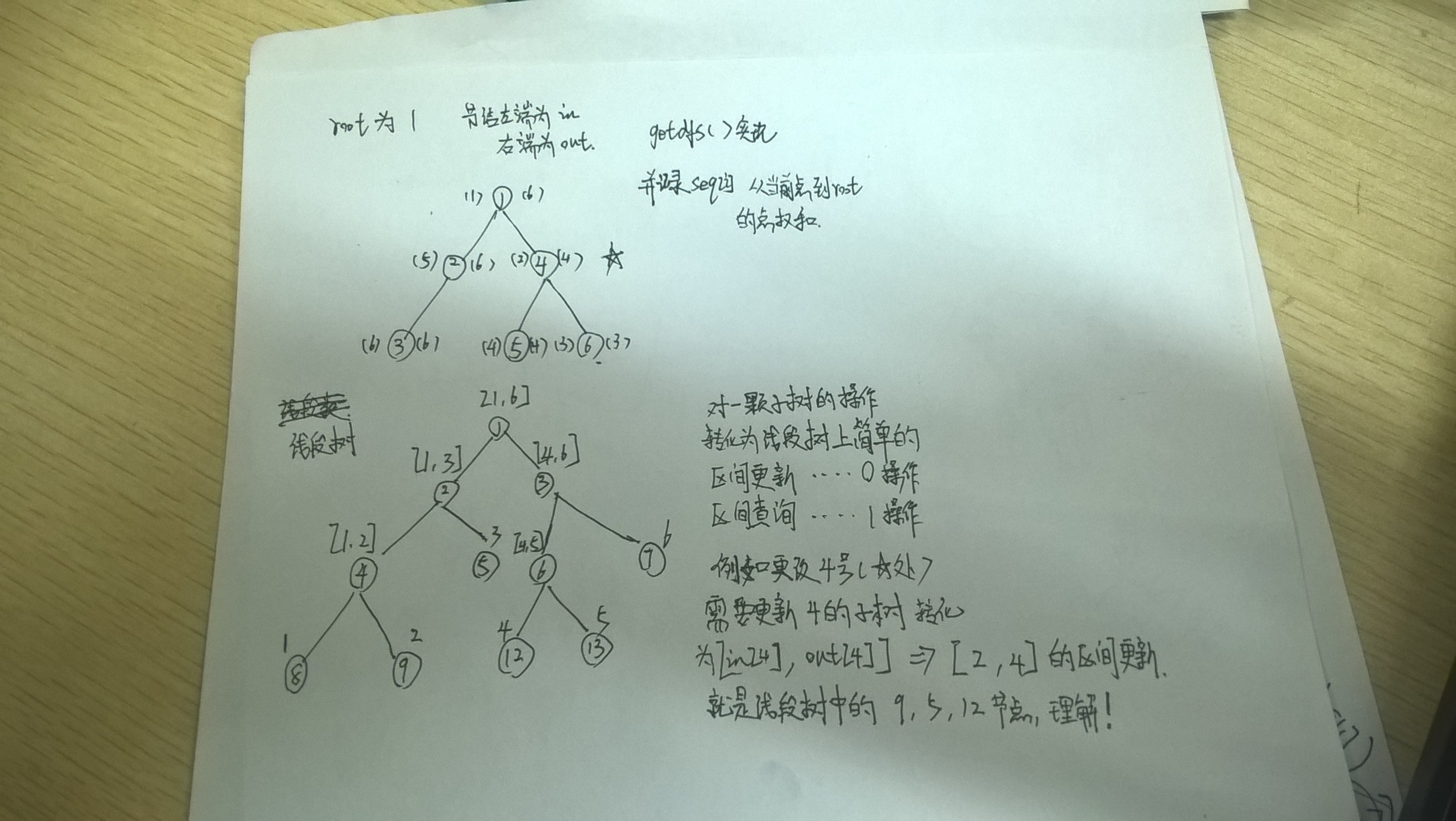
题意:中文题面
题解:第一次写线段树+dfs序列
1 /****************************** 2 code by drizzle 3 blog: www.cnblogs.com/hsd-/ 4 ^ ^ ^ ^ 5 O O 6 ******************************/ 7 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 8 #include<map> 9 #include<set> 10 #include<cmath> 11 #include<queue> 12 #include<bitset> 13 #include<math.h> 14 #include<vector> 15 #include<string> 16 #include<stdio.h> 17 #include<cstring> 18 #include<iostream> 19 #include<algorithm> 20 #pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000") 21 using namespace std; 22 #define A first 23 #define B second 24 const int mod=1000000007; 25 const int MOD1=1000000007; 26 const int MOD2=1000000009; 27 const double EPS=0.00000001; 28 //typedef long long ll; 29 typedef __int64 ll; 30 const ll MOD=1000000007; 31 const int INF=1000000010; 32 const ll MAX=1ll<<55; 33 const double eps=1e-5; 34 const double inf=~0u>>1; 35 const double pi=acos(-1.0); 36 typedef double db; 37 typedef unsigned int uint; 38 typedef unsigned long long ull; 39 int T,n,m,x,judge,nedge=0,dfn, y; 40 struct node 41 { 42 int ed; 43 int pre; 44 } N[200005]; 45 int pre[200005],in[200005],out[200005]; 46 ll v[200005]; 47 ll seq[200005]; 48 ll fuck; 49 struct tree 50 { 51 int l,r; 52 ll lazy; 53 ll maxn; 54 } tree[400005]; 55 inline void add(int st,int ed) 56 { 57 nedge++; 58 N[nedge].ed=ed; 59 N[nedge].pre=pre[st]; 60 pre[st]=nedge; 61 } 62 inline void getdfs(int x,int y,ll s) 63 { 64 s+=v[x]; 65 in[x]=++dfn; 66 seq[dfn]=s; 67 for(int i=pre[x]; i; i=N[i].pre) 68 { 69 if(N[i].ed!=y) 70 { 71 getdfs(N[i].ed,x,s); 72 } 73 } 74 out[x]=dfn; 75 } 76 inline void pushdown(int root) 77 { 78 if(tree[root].lazy==0) return; 79 tree[root<<1].lazy+=tree[root].lazy; 80 tree[root<<1|1].lazy+=tree[root].lazy; 81 tree[root<<1].maxn+=tree[root].lazy; 82 tree[root<<1|1].maxn+=tree[root].lazy; 83 tree[root].lazy=0; 84 } 85 inline void buildtree(int root,int left,int right) 86 { 87 tree[root].l=left; 88 tree[root].r=right; 89 tree[root].lazy=0; 90 if(left==right) 91 { 92 tree[root].maxn=seq[left]; 93 return ; 94 } 95 int mid=(left+right)>>1; 96 buildtree(root<<1,left,mid); 97 buildtree(root<<1|1,mid+1,right); 98 tree[root].maxn=max(tree[root<<1].maxn,tree[root<<1|1].maxn); 99 } 100 inline void updata(int root,int in,int out,ll after) 101 { 102 if(in==tree[root].l&&tree[root].r==out) 103 { 104 tree[root].lazy+=after; 105 tree[root].maxn+=after; 106 return ; 107 } 108 pushdown(root); 109 int mid=(tree[root].l+tree[root].r)>>1; 110 if(out<=mid) 111 updata(root<<1,in,out,after); 112 else 113 { 114 if(in>mid) 115 updata(root<<1|1,in,out,after); 116 else 117 { 118 updata(root<<1,in,mid,after); 119 updata(root<<1|1,mid+1,out,after); 120 } 121 } 122 tree[root].maxn=max(tree[root<<1].maxn,tree[root<<1|1].maxn); 123 } 124 inline ll query(int root,int in,int out) 125 { 126 if(in==tree[root].l&&tree[root].r==out) 127 { 128 return tree[root].maxn; 129 } 130 pushdown(root); 131 int mid=(tree[root].l+tree[root].r)>>1; 132 if(out<=mid) 133 return query(root<<1,in,out); 134 else 135 { 136 if(in>mid) 137 return query(root<<1|1,in,out); 138 else 139 return max(query(root<<1,in,mid),query(root<<1|1,mid+1,out)); 140 } 141 } 142 void init() 143 { 144 memset(tree,0,sizeof(tree)); 145 memset(N,0,sizeof(N)); 146 memset(pre,0,sizeof(pre)); 147 memset(in,0,sizeof(in)); 148 memset(out,0,sizeof(out)); 149 memset(v,0,sizeof(v)); 150 memset(seq,0,sizeof(seq)); 151 nedge=0; 152 dfn=0; 153 } 154 int main() 155 { 156 scanf("%d",&T); 157 for(int i=1; i<=T; i++) 158 { 159 init(); 160 scanf("%d %d",&n,&m); 161 for(int j=1; j<n; j++) 162 { 163 scanf("%d %d",&x,&y); 164 x++; 165 y++; 166 add(x,y); 167 add(y,x); 168 } 169 for(int j=1; j<=n; j++) 170 scanf("%I64d",&v[j]); 171 getdfs(1,1,0); 172 buildtree(1,1,n); 173 printf("Case #%d: ",i); 174 for(int j=1; j<=m; j++) 175 { 176 scanf("%d %d",&judge,&x); 177 if(judge==0) 178 { 179 scanf("%I64d",&fuck); 180 x++; 181 ll exm=fuck; 182 fuck=fuck-v[x]; 183 updata(1,in[x],out[x],fuck); 184 v[x]=exm; 185 } 186 else 187 { 188 x++; 189 printf("%I64d ",query(1,in[x],out[x])); 190 } 191 } 192 } 193 return 0; 194 }