在上文中讲了Spring的事件监听机制,流程是:定义事件、监听器,发布事件,控制台输出监听到的事件内容。
在上文的扩展中 使用 @EventListener 注解来自定义监听器,监听指定的事件,比如下面的案例:
@Component public class UserManagerListener { //ApplicationEvent能监听到所有的事件,如果为EmailEvent.class则只能监听到关于邮件的事件 //EventListener有两个参数(可以不写,直接在方法参数里面写上要监听的事件即可): // classes:表示哪一个事件类 // condition:当满足什么条件是会调用该方法 @EventListener(classes = ApplicationEvent.class) public void listen(ApplicationEvent event){ System.out.println("用户管理功能监听到的事件。。。。"+event); } }
通过上面的案例发现代码比实现 ApplicationListener 接口更简洁,那这个注解为什么功能这么强大呢,接下来我们来分析它的源码:
/** * @author Stephane Nicoll * @author Sam Brannen * @since 4.2 * @see EventListenerMethodProcessor */ @Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface EventListener { ....... }
通过源码发现是通过使用 EventListenerMethodProcessor 处理器来解析该注解,将标注了 @EventListener 的方法进行解析, 获取拦截方法,对拦截方法进行转换,变成 ApplicationListener 然
后放入到 IOC 容器中,在publishEvent 时,通过 getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(a
pplicationEvent, eventType)方法,获取到 ApplicationListener 对象,通过反射调用方法。下面是 EventListenerMethodProcessor 处理器的类图关系:
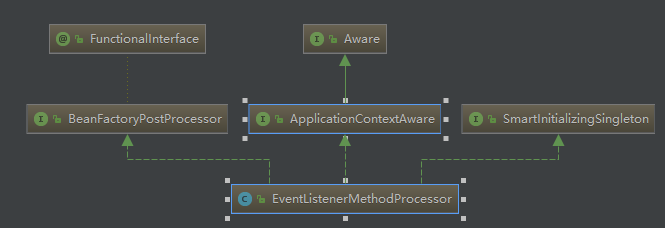
可以看到 EventListenerMethodProcessor 是实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 和 SmartInitializingSingleton 这两个接口。在前文 Spring的BeanFactoryPostProcessor探究 中讲述了
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的执行时机,在 refresh 容器的时候, 调用 invokeBeanFactoryPostProce
ssors() 方法时, 会执行 BeanFactoryPostProcessor#postProcessBeanFactory() 方法设置一个默认的监听器工厂 :DefaultEventListenerFactory。
/** * Registers {@link EventListener} methods as individual {@link ApplicationListener} instances. * Implements {@link BeanFactoryPostProcessor} (as of 5.1) primarily for early retrieval, * avoiding AOP checks for this processor bean and its {@link EventListenerFactory} delegates. * * @author Stephane Nicoll * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 4.2 * @see EventListenerFactory * @see DefaultEventListenerFactory */ public class EventListenerMethodProcessor implements SmartInitializingSingleton, ApplicationContextAware, BeanFactoryPostProcessor { ...... @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; Map<String, EventListenerFactory> beans = beanFactory.getBeansOfType(EventListenerFactory.class, false, false); List<EventListenerFactory> factories = new ArrayList<>(beans.values()); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(factories); //DefaultEventListenerFactory this.eventListenerFactories = factories; } ....... }
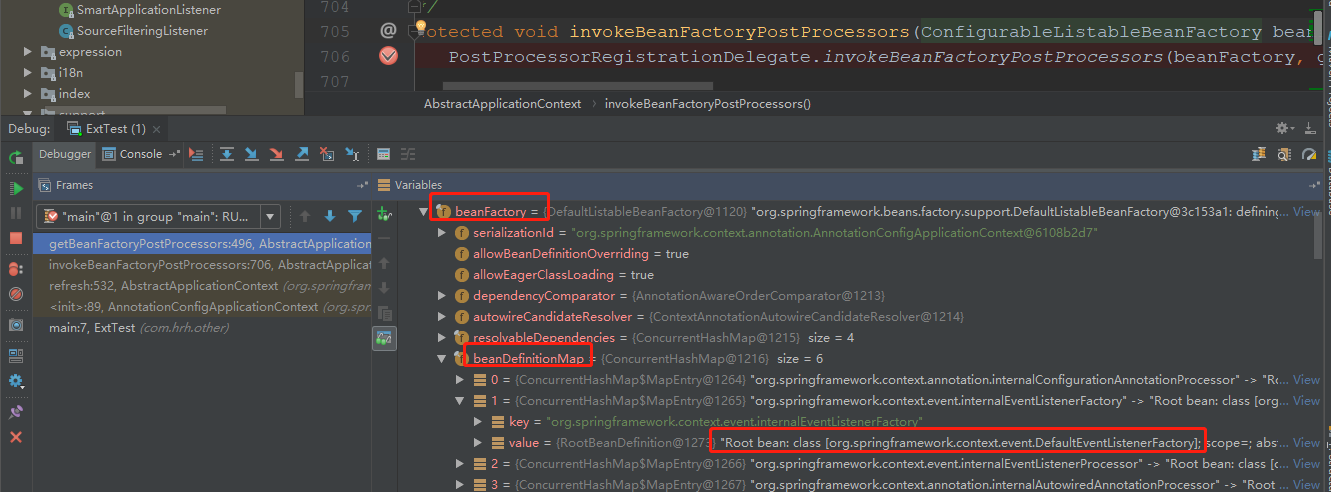
而SmartInitializingSingleton 这个接口只有一个方法 afterSingletonsInstantiated(),这个方法在全部单实例创建完成之后执行,接下来对这个方法进行深入探讨,我们对 EventListenerMethodProcessor里面的实现方法 afterSingletonsInstantiated 打一个断点 debug 运行下:
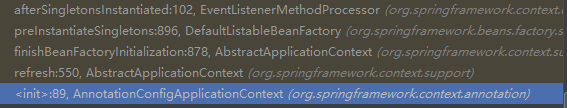
从中我们可以看到,流程是: IOC容器创建对象 --> refresh() --> finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)(初始化剩下的所有单实例bean) --> beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons()(初始化剩下的所有单实例bean)--> smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated()
@Override public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this); } // Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions. // While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine. //获取所有的注册bean名称 List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames); // Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans... //先创建所有的单实例bean for (String beanName : beanNames) { RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) { if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) { Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName); if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) { final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean; boolean isEagerInit; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) { isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Boolean>) ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit, getAccessControlContext()); } else { isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean && ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit()); } if (isEagerInit) { getBean(beanName);//创建bean实例 } } } else { getBean(beanName);//创建bean实例 } } } // Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans... //创建完成后进行遍历,如果bean是SmartInitializingSingleton类型,执行afterSingletonsInstantiated方法 for (String beanName : beanNames) { Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName); if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) { final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> { smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated(); return null; }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated(); } } } }
从上面可以看出其调用时机是,遍历容器中注册的 BeanDefinition, 调用所有 getBean() 方法创建实例之后, 才会开始遍历执行 afterSingletonsInstantiated() 方法。
接下来详细解析下 EventListenerMethodProcessor 的 afterSingletonsInstantiated 方法,重点看 processBean 方法:
@Override public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() { ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.beanFactory; Assert.state(this.beanFactory != null, "No ConfigurableListableBeanFactory set"); String[] beanNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(Object.class); for (String beanName : beanNames) { if (!ScopedProxyUtils.isScopedTarget(beanName)) { Class<?> type = null; try { type = AutoProxyUtils.determineTargetClass(beanFactory, beanName); } catch (Throwable ex) { // An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it. if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Could not resolve target class for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex); } } if (type != null) { if (ScopedObject.class.isAssignableFrom(type)) { try { Class<?> targetClass = AutoProxyUtils.determineTargetClass( beanFactory, ScopedProxyUtils.getTargetBeanName(beanName)); if (targetClass != null) { type = targetClass; } } catch (Throwable ex) { // An invalid scoped proxy arrangement - let's ignore it. if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Could not resolve target bean for scoped proxy '" + beanName + "'", ex); } } } try { processBean(beanName, type); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanInitializationException("Failed to process @EventListener " + "annotation on bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex); } } } } } private void processBean(final String beanName, final Class<?> targetType) { //不包含没有注解的class,注解是EventListener的类型,是Spring容器的类型 if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(targetType) && AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(targetType, EventListener.class) && !isSpringContainerClass(targetType)) { Map<Method, EventListener> annotatedMethods = null; try { //获取标注了 @EventListener 注解的监听方法 annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(targetType, (MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<EventListener>) method -> AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, EventListener.class)); } catch (Throwable ex) { // An unresolvable type in a method signature, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it. if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Could not resolve methods for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex); } } //监听方法添加到没有注解的集合 if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(annotatedMethods)) { this.nonAnnotatedClasses.add(targetType); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No @EventListener annotations found on bean class: " + targetType.getName()); } } else { // Non-empty set of methods ConfigurableApplicationContext context = this.applicationContext; Assert.state(context != null, "No ApplicationContext set"); List<EventListenerFactory> factories = this.eventListenerFactories; Assert.state(factories != null, "EventListenerFactory List not initialized"); for (Method method : annotatedMethods.keySet()) { for (EventListenerFactory factory : factories) { // 判断是否支持该方法 在DefaultEventListenerFactory中写死的返回true if (factory.supportsMethod(method)) { //选择方法 beanName 这里是AddDataEventListener的beanName 默认是addDataEventListener Method methodToUse = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, context.getType(beanName)); //将监听方法转换为ApplicationListener(ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter)对象 ApplicationListener<?> applicationListener = factory.createApplicationListener(beanName, targetType, methodToUse); // 如果是ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter对象 就把context和evaluator传进去 if (applicationListener instanceof ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) { ((ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) applicationListener).init(context, this.evaluator); } //将创建的 ApplicationListener 加入到容器中 context.addApplicationListener(applicationListener); break; } } } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug(annotatedMethods.size() + " @EventListener methods processed on bean '" + beanName + "': " + annotatedMethods); } } } } //class是在org.springframework包下,注解类型不是组件 private static boolean isSpringContainerClass(Class<?> clazz) { return (clazz.getName().startsWith("org.springframework.") && !AnnotatedElementUtils.isAnnotated(ClassUtils.getUserClass(clazz), Component.class)); }
后面就是添加listener到Context中:
1)如果有applicationEventMulticaster,添加到ApplicationContext.applicationEventMulticas
ter中;
2)如果没有applicationEventMulticaster,添加到ApplicationContext.applicationListeners中;
最后是触发事件监听了 AbstractApplicationContext.publishEvent --> SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.multicastEvent --> invokeListener --> doInvokeListener --> ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter.onApplicationEvent
@Override public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { processEvent(event); } ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter#processEvent public void processEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { Object[] args = resolveArguments(event); if (shouldHandle(event, args)) { // 反射执行真正的方法 Object result = doInvoke(args); if (result != null) { handleResult(result); } else { logger.trace("No result object given - no result to handle"); } } }
在ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter.doInvoke中会反射执行真正的方法:
protected Object doInvoke(Object... args) { //获取目标对象 Object bean = getTargetBean(); ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(this.method); try { //反射执行监听方法 return this.method.invoke(bean, args); } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { assertTargetBean(this.method, bean, args); throw new IllegalStateException(getInvocationErrorMessage(bean, ex.getMessage(), args), ex); } catch (IllegalAccessException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException(getInvocationErrorMessage(bean, ex.getMessage(), args), ex); } catch (InvocationTargetException ex) { // Throw underlying exception Throwable targetException = ex.getTargetException(); if (targetException instanceof RuntimeException) { throw (RuntimeException) targetException; } else { String msg = getInvocationErrorMessage(bean, "Failed to invoke event listener method", args); throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(targetException, msg); } } }