一:二级缓存简介
为什么需要缓存:
查询大量数据时更快,拉高程序的性能
什么样的数据需要缓存:
很少被修改或根本不改的数据 数据字典
业务场景比如:耗时较高的统计分析sql、电话账单查询sql等
关系型数据库:
数据与数据之间存在关系(联系)的数据库 mysql/Oracle、sqlserver
非关系型数据库(数据与数据之间是不存在关系的,key-value):
- 基于文件存储的数据库:ehcache
- 基于内存存储的数据库:redis、memcache
- 基于文档存储的数据库:mongodb
ehcache是什么:
Ehcache 是现在最流行的纯Java开源缓存框架,配置简单、结构清晰、功能强大
我们来用map简单测试一下缓存原理:
package com.ht.six.test; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; /** * 利用map集合简易实现缓存原理 * @author Administrator * */ public class EhcacheDemo1 { static Map<String, Object> cache = new HashMap<String, Object>(); static Object getValue(String key) { Object value = cache.get(key); System.out.println("从缓存中获取数据。。。。"); if(value == null) { System.out.println("从软件相对应的配置文件中获取数据。。。"); cache.put(key, new String[] {"zs"}); return cache.get(key); } return value; } /** * 1.从缓存中获取数据。。。。 * 2.从软件相对应的配置文件中获取数据。。。 * 3."zs" * 4.从缓存中获取数据。。。。 * 5."zs" * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(getValue("sname")); System.out.println(getValue("sname")); } }
运行原理图解:

我们来看一下运行结果:

ehcache简介
ehcache特点:
-
够快
Ehcache的发行有一段时长了,经过几年的努力和不计其数的性能测试,Ehcache终被设计于large, high concurrency systems.
-
够简单
开发者提供的接口非常简单明了,从Ehcache的搭建到运用运行仅仅需要的是你宝贵的几分钟。其实很多开发者都不知道自己用在用Ehcache,Ehcache被广泛的运用于其他的开源项目
-
够小
关于这点的特性,官方给了一个很可爱的名字small foot print ,一般Ehcache的发布版本不会到2M,V 2.2.3 才 668KB。
-
够轻量
核心程序仅仅依赖slf4j这一个包,没有之一!
-
好扩展
Ehcache提供了对大数据的内存和硬盘的存储,最近版本允许多实例、保存对象高灵活性、提供LRU、LFU、FIFO淘汰算法,基础属性支持热配置、支持的插件多
-
监听器
缓存管理器监听器 (CacheManagerListener)和 缓存监听器(CacheEvenListener),做一些统计或数据一致性广播挺好用的
-
分布式缓存
从Ehcache 1.2开始,支持高性能的分布式缓存,兼具灵活性和扩展性
核心接口:
- CacheManager:缓存管理器
- Cache:缓存对象,缓存管理器内可以放置若干cache,存放数据的实质,所有cache都实现了Ehcache接口
- Element:单条缓存数据的组成单位
ehcache的使用
首先我们在POM.XML中导入相关依赖
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<junit.version>4.12</junit.version>
<servlet.version>4.0.0</servlet.version>
<hibernate.version>5.2.12.Final</hibernate.version>
<mysql.driver.version>5.1.46</mysql.driver.version>
<ehcache.version>2.10.0</ehcache.version>
<slf4j-api.version>1.7.7</slf4j-api.version>
<log4j-api.version>2.9.1</log4j-api.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>${servlet.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>${hibernate.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>${mysql.driver.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
<version>${ehcache.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-ehcache</artifactId>
<version>${hibernate.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- slf4j核心包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>${slf4j-api.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId>
<version>${slf4j-api.version}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!--用于与slf4j保持桥接 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j-impl</artifactId>
<version>${log4j-api.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--核心log4j2jar包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-api</artifactId>
<version>${log4j-api.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>${log4j-api.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
用二级缓存来演示存储数据
导入相关配置文件
ehcache.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd" updateCheck="false"> <!--磁盘存储:将缓存中暂时不使用的对象,转移到硬盘,类似于Windows系统的虚拟内存--> <!--path:指定在硬盘上存储对象的路径--> <!--java.io.tmpdir 是默认的临时文件路径。 可以通过如下方式打印出具体的文件路径 System.out.println(System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir"));--> <diskStore path="D://xxx"/> <!--defaultCache:默认的管理策略--> <!--eternal:设定缓存的elements是否永远不过期。如果为true,则缓存的数据始终有效,如果为false那么还要根据timeToIdleSeconds,timeToLiveSeconds判断--> <!--maxElementsInMemory:在内存中缓存的element的最大数目--> <!--overflowToDisk:如果内存中数据超过内存限制,是否要缓存到磁盘上--> <!--diskPersistent:是否在磁盘上持久化。指重启jvm后,数据是否有效。默认为false--> <!--timeToIdleSeconds:对象空闲时间(单位:秒),指对象在多长时间没有被访问就会失效。只对eternal为false的有效。默认值0,表示一直可以访问--> <!--timeToLiveSeconds:对象存活时间(单位:秒),指对象从创建到失效所需要的时间。只对eternal为false的有效。默认值0,表示一直可以访问--> <!--memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:缓存的3 种清空策略--> <!--FIFO:first in first out (先进先出)--> <!--LFU:Less Frequently Used (最少使用).意思是一直以来最少被使用的。缓存的元素有一个hit 属性,hit 值最小的将会被清出缓存--> <!--LRU:Least Recently Used(最近最少使用). (ehcache 默认值).缓存的元素有一个时间戳,当缓存容量满了,而又需要腾出地方来缓存新的元素的时候,那么现有缓存元素中时间戳离当前时间最远的元素将被清出缓存--> <defaultCache eternal="false" maxElementsInMemory="1000" overflowToDisk="false" diskPersistent="false" timeToIdleSeconds="0" timeToLiveSeconds="600" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/> </ehcache>
EhcacheUtil类
package com.ht.six.util; import net.sf.ehcache.Cache; import net.sf.ehcache.CacheManager; import net.sf.ehcache.Element; import java.io.InputStream; public class EhcacheUtil { private static CacheManager cacheManager; static { try { InputStream is = EhcacheUtil.class.getResourceAsStream("/ehcache.xml"); cacheManager = CacheManager.create(is); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } private EhcacheUtil() { } public static void put(String cacheName, Object key, Object value) { Cache cache = cacheManager.getCache(cacheName); if (null == cache) { //以默认配置添加一个名叫cacheName的Cache cacheManager.addCache(cacheName); cache = cacheManager.getCache(cacheName); } cache.put(new Element(key, value)); } public static Object get(String cacheName, Object key) { Cache cache = cacheManager.getCache(cacheName); Element element = cache.get(key); return null == element ? null : element.getValue(); } public static void remove(String cacheName, Object key) { Cache cache = cacheManager.getCache(cacheName); cache.remove(key); } }
测试类:
package com.ht.six.test; import com.ht.six.util.EhcacheUtil; /** * 演示利用缓存存储数据 * @author Administrator * */ public class EhcacheDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir")); EhcacheUtil.put("com.ht.four.entity.Book", 11, "zhangsan"); System.out.println(EhcacheUtil.get("com.ht.four.entity.Book", 11)); } }
若是自己没有去配置槽中的内容,管理器一般就是自动规划为默认配置,不会存储到硬盘里面去
什么是槽?由下面的图告诉你cache的内部结构
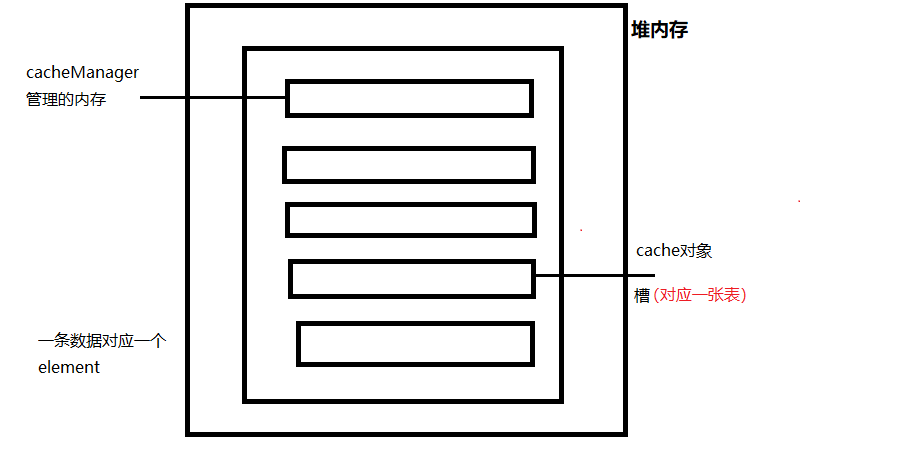
把槽中数据修改一下测试一下
<!--name: Cache的名称,必须是唯一的(ehcache会把这个cache放到HashMap里)-->
<cache name="com.ht.one.entity.User" eternal="false" maxElementsInMemory="100"
overflowToDisk="true" diskPersistent="true" timeToIdleSeconds="0"
timeToLiveSeconds="300" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
测试结果中,我们在D盘中发现存储进去的文件:
hibernate中使用二级缓存(ehcache)
-
依赖包已经在上面全部导入 所以这里就不重复了
hibernate一级缓存使用
/** * 默认情况下,sql语句形成了三次,这里为了提高性能,必须使用二级缓存SessionFactory缓存 * <!-- 开启二级缓存 --> * <property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property> <!-- 开启查询缓存 --> <property name="hibernate.cache.use_query_cache">true</property> <!-- EhCache驱动 --> <property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory</property> 映射文件中添加标签 <cache usage="read-write" region="com.javaxl.one.entity.User"/> 这里的region指的是Ehcache.xml中cacheName * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { UserDao userDao = new UserDao(); User u = new User(); u.setId(7); User user = userDao.get(u); System.out.println(user); User user2 = userDao.get(u); System.out.println(user2); User user3 = userDao.get(u); System.out.println(user3); }
因为一个session中只生产一个sql语句,所以这里用了多个session,要是小数据还可行,大量数据就大大降低性能,那么就要用到二级缓存了。
-
hibernate.cfg.xml中添加二级缓存相关配置
<!-- 开启二级缓存 -->
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property>
<!-- 开启查询缓存 -->
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_query_cache">true</property>
<!-- EhCache驱动 -->
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.internal.EhCacheRegionFactory</property>
-
对应的映射文件中添加缓存配置 User.hbm.xml
<!-- 添加缓存标号 指定槽 --> <cache usage="read-write" region="com.ht.one.entity.User"/>
-
调用 测试方法
/** * 同一个session,sql语句只生成一次,这里用到了一级缓存 * * session级别的缓存就是一级缓存 * sessionfactory级别的缓存就是二级缓存 * 默认的一级缓存开启的 */ public static void test1() { Session session = SessionFactoryUtils.openSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); User user = session.get(User.class, 7); System.out.println(user); User user2 = session.get(User.class, 7); System.out.println(user2); User user3 = session.get(User.class, 7); System.out.println(user3); transaction.commit(); session.close(); }
EhcacheDemo4
package com.ht.six.test; import java.util.List; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.Transaction; import org.hibernate.query.Query; import com.ht.two.util.SessionFactoryUtils; /** * hibernate二级缓存不会同时缓存多条数据 * @author Administrator * */ public class EhcacheDemo4 { public static void main(String[] args) { Session session = SessionFactoryUtils.openSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); Query query = session.createQuery("from User"); query.setCacheable(true); List list = query.list(); System.out.println(list); List list2 = query.list(); System.out.println(list2); List list3 = query.list(); System.out.println(list3); transaction.commit(); session.close(); } }
发现他也执行多次
原因:对于查询单条数据的时候,缓存机制是默认用一级缓存的,若是想要用二级缓存来提高性能,还得靠自己手动开启二级缓存
query.setCacheable(true);