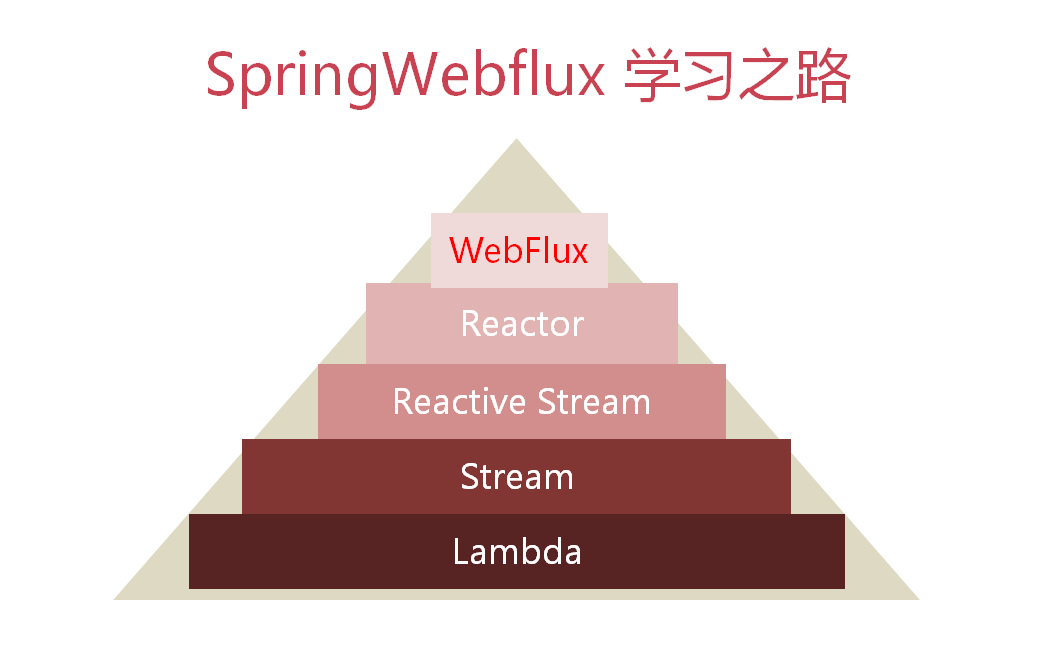
学习路径
函数式编程/lambda 表达式
Runnable runnable = () -> log.info("ok2");
System.out.println(runnable); // lambda.ThreadDemo$$Lambda$1/174573182@5ce81285
new Thread(runnable).start();
lambda 表达式是实现了函数式接口的对象实例。
java.util.function 包下已经定义了很多函数式接口,参考 On Java8 第十三章 函数式编程
方法引用
方法参数中使用 this 的特殊用法
JVM 编译时非静态方法的第一个参数是 this
public int eat(Dog this, int num) {
return num * 2;
}
// 等价于下面的用法,两种方式不能同时存在
public int eat(int num) {
return num * 2;
}
方法引用的方式
public class MethodRefDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 方法引用 简单示例
Consumer<String> consumer = System.out::println;
consumer.accept("abc");
// 静态方法,使用类名,方法引用
Consumer<Dog> consumer1 = Dog::bark;
consumer1.accept(new Dog("dog1"));
// 非静态方法,使用对象实例,方法引用
Dog dog2 = new Dog("dog2");
Function<Integer, String> dogEat = dog2::eat;
System.out.println(dogEat.apply(2));
// 非静态方法,使用类名,方法引用
BiFunction<Dog, Integer, String> eatFunction = Dog::eat;
System.out.println(eatFunction.apply(new Dog("dog3"), 3));
// 构造函数,不带参数,方法引用
Supplier<Dog> supplierDog = Dog::new;
Dog dog4 = supplierDog.get();
// 构造函数,带参数,方法引用
Function<String, Dog> dogFunction = Dog::new;
Dog dog5 = dogFunction.apply("dog5");
}
}
级联表达式和柯里化
柯里化:把多个参数的函数转换为只有一个参数的函数。目的是函数标准化
高阶函数:返回函数的函数
public class CurryDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Function<Integer, Function<Integer, Integer>> fun = x -> y -> x + y;
System.out.println(fun.apply(2).apply(3));
Function<Integer, Function<Integer, Function<Integer, Integer>>> fun2 = x -> y -> z -> x + y + z;
System.out.println(fun2.apply(4).apply(5).apply(6));
int[] nums = {2, 3, 4};
Function f = fun2;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
Object obj = f.apply(nums[i]);
if (obj instanceof Function) {
f = (Function) obj;
} else {
System.out.println("结果为:" + obj);
}
}
}
}
Stream 流编程
区分外部迭代和内部迭代
public class StreamDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1, 2, 3};
int sum1 = 0;
// 外部迭代
for (int num : nums) {
sum1 += num;
}
System.out.println(sum1);
// 内部迭代
int sum2 = IntStream.of(nums).sum();
System.out.println(sum2);
}
}
区分中间操作和终止操作
- 中间操作就是返回流的操作
- 终止操作就是返回结果的操作
中间操作
中间操作分为无状态操作和有状态操作,区别是操作与其他元素有没有关系
无状态操作
- map/flatMap
- filter
- peek
- unordered
有状态操作:
- distinct
- sorted
- limit/skip
终止操作
终止操作分为非短路操作和短路操作,区别是是否需要等待所有结果计算完毕才可以结束
非短路操作:
- forEach/forEachOrdered
- collect/toArray
- reduce
- min/max/count
短路操作:
- findFirst/findAny
- allMatch/anyMatch/noneMatch
惰性求值
惰性求值就是没有调用终止操作的情况下,中间操作不会执行
并行流
- sequential
- parallel
多次调用已最后一次为准
并行流使用默认线程池,线程个数为CPU个数
也可以使用自定义线程池执行并行流
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool(20);
pool.submit(()->IntStream.range(1,100).parallel().peek(StreamDemo2::debug).count());
pool.shutdown();
收集器
- collect
- Collectors
Stream 运行机制
-
所有操作都是链式调用,一个元素只迭代一次
-
每一个中间操作返回一个新的流,流里面又一个属性 sourceStage,指向同一个地方,就是 Head
Head -> nextStage -> nextStage -> .. -> null
-
有状态操作会把无状态操作截断,单独处理
-
并行环境下,有状态的中间操作不一定能并行操作
-
parallel/sequetial 这两个操作也是中间操作,但是它们不创建流,它们只修改 Head 的并行标志
Reactive Stream
背压 backpress
使用 Java9 的 java.util.concurrent.Flow
public class FlowDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 不带处理器
// test1();
// 带处理器
test2();
}
private static void test2() throws InterruptedException {
SubmissionPublisher<Integer> publisher = new SubmissionPublisher<>();
MyProcessor myProcessor = new MyProcessor();
Flow.Subscriber<String> subscriber = new Flow.Subscriber<>() {
private Flow.Subscription subscription;
@Override
public void onSubscribe(Flow.Subscription subscription) {
this.subscription = subscription;
// 请求一个数据
this.subscription.request(1);
}
@Override
public void onNext(String item) {
System.out.println("收到一个数据:" + item);
// 再请求一个数据
this.subscription.request(1);
// 不再接收数据
// this.subscription.cancel();
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
this.subscription.cancel();
}
@Override
public void onComplete() {
}
};
publisher.subscribe(myProcessor);
myProcessor.subscribe(subscriber);
publisher.submit(-111);
publisher.submit(111);
publisher.close();
// 主线程延迟停止,否则数据没有消费就退出了
Thread.currentThread().join(1000);
}
private static void test1() throws InterruptedException {
SubmissionPublisher<Integer> publisher = new SubmissionPublisher<>();
Flow.Subscriber<Integer> subscriber = new Flow.Subscriber<>() {
private Flow.Subscription subscription;
@Override
public void onSubscribe(Flow.Subscription subscription) {
this.subscription = subscription;
// 请求一个数据
this.subscription.request(1);
}
@Override
public void onNext(Integer item) {
System.out.println("收到一个数据:" + item);
// 再请求一个数据
this.subscription.request(1);
// 不再接收数据
// this.subscription.cancel();
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
this.subscription.cancel();
}
@Override
public void onComplete() {
}
};
publisher.subscribe(subscriber);
int data = 111;
publisher.submit(data);
publisher.close();
// 主线程延迟停止,否则数据没有消费就退出了
Thread.currentThread().join(1000);
}
}
public class MyProcessor extends SubmissionPublisher<String> implements Flow.Processor<Integer, String> {
private Flow.Subscription subscription;
@Override
public void onSubscribe(Flow.Subscription subscription) {
this.subscription = subscription;
// 请求一个数据
this.subscription.request(1);
}
@Override
public void onNext(Integer item) {
System.out.println("处理器收到一个数据:" + item);
if (item > 0) {
this.submit("转换后的数据:" + item);
}
// 再请求一个数据
this.subscription.request(1);
// 不再接收数据
// this.subscription.cancel();
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
this.subscription.cancel();
}
@Override
public void onComplete() {
}
}
Spring WebFlux
比较重要的几个类:
- Mono
- Flux
- RouterFunction
- HandlerFunction
- WebClient
@Configuration
public class GlobalRouterConfig {
@Bean
TestHandler testHandler() {
return new TestHandler();
}
@Bean
RouterFunction<ServerResponse> router(TestHandler testHandler) {
return RouterFunctions.nest(RequestPredicates.path("/testH"), RouterFunctions.route(RequestPredicates.GET("/mono"), testHandler::mono).andRoute(RequestPredicates.GET("/flux"), testHandler::flux).andRoute(RequestPredicates.GET("/sse"), testHandler::sse));
}
}
@Slf4j
public class TestHandler {
public Mono<ServerResponse> mono(ServerRequest serverRequest) {
return ServerResponse.ok().contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).body(Mono.just("mono-1"), String.class);
}
public Mono<ServerResponse> flux(ServerRequest serverRequest) {
return ServerResponse.ok().contentType(MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM).body(Flux.fromArray(new String[]{"flux-1", "flux-2", "flux-3"}), String.class);
}
public Mono<ServerResponse> sse(ServerRequest serverRequest) {
return ServerResponse.ok().contentType(MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM).body(Flux.interval(Duration.ofSeconds(1)).map(l -> new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())), String.class);
}
}
@Slf4j
public class WebClientTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
WebClient webClient = WebClient.create("http://localhost:8080");
Mono<String> stringMono = webClient.get().uri("/testH/mono").retrieve().bodyToMono(String.class);
System.out.println(stringMono.block());
Flux<String> stringFlux = webClient.get().uri("/testH/flux").retrieve().bodyToFlux(String.class);
stringFlux.subscribe(getSubscribe());
Flux<String> stringFlux2 = webClient.get().uri("/testH/sse").retrieve().bodyToFlux(String.class);
stringFlux2.subscribe(getSubscribe());
System.in.read();
}
public static Subscriber<String> getSubscribe() {
Subscriber<String> subscriber = new Subscriber<String>() {
private Subscription subscription;
@Override
public void onSubscribe(Subscription subscription) {
this.subscription = subscription;
// 请求一个数据
this.subscription.request(1);
}
@Override
public void onNext(String item) {
log.info("收到一个数据:" + item);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 再请求一个数据
this.subscription.request(1);
// 不再接收数据
// this.subscription.cancel();
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
this.subscription.cancel();
}
@Override
public void onComplete() {
log.info("处理完成。。");
}
};
return subscriber;
}
}