新建项目
models:
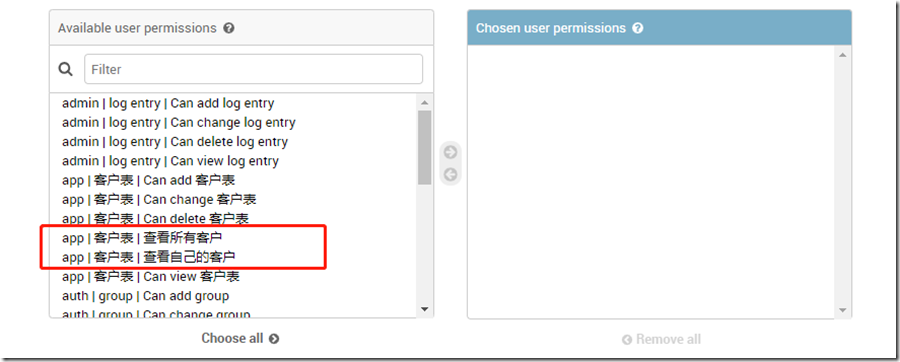
from django.db import models from django.contrib.auth.models import User # Create your models here. class Customers(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=20, verbose_name='姓名') phone = models.CharField(max_length=15, verbose_name='电话') owner = models.ForeignKey(User, on_delete=models.DO_NOTHING, verbose_name='所属用户') def __str__(self): return self.name class Meta: verbose_name = '客户表' verbose_name_plural = verbose_name permissions = ( ('show_all_customer', '查看所有客户'), ('show_own_customer', '查看自己的客户') )
‘show_all_customer’:这个是需要留意一下的,后面要用到. django的权限匹配 request.user.has_prem(“app.show_all_customer”) 就是将 app名 和 这个名称用.连接之后匹配的。
‘查看所有客户’ 这个就是显示在后台权限列表里的描述。
这里只列举两个权限简单说明一下用法,一个是查看所有客户,一个是查看自己的客户。
views:
from django.shortcuts import render from app.models import Customers from app.perm_check import check_permission # Create your views here. def show_all(request): customer_list = Customers.objects.all() return render(request, 'app/list.html', locals()) def show_own(request): uid = request.GET.get('uid', None) if uid: customer_list = Customers.objects.filter(owner_id=uid) return render(request, 'app/list.html', locals())
urls:
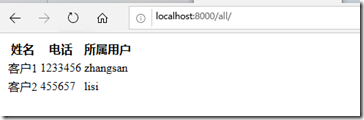
假设:访问所有客户列表 http://localhost:8000/all
访问自己的客户列表需要加参数uid , http://localhost:8000/own/?uid=2
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path from app.views import show_all, show_own urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('all/', show_all, name='show_all'), path('own/', show_own, name='show_own'), ]
settings.py中添加应用“app”, 我取的名字叫app. 并设置模版目录 “templates”.
同步数据库,并创建超级管理员
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migratepython manage.py createsuperuser启动项目,进入后台,添加数据
用户 zhangsan, lisi给予登录后台的权限,登录了后台,就等于用户已经登录了,访问其它非后台页面也是登录状态。
权限设计
app目录下新建 prem_list.py文件
perm_list = { 'app_show_all_customer': ['show_all', 'GET', []], 'app_show_own_customer': ['show_own', 'GET', ['uid',]] }
大体思路是这样: 请求过来之后,先到prem_list中去匹配 ‘show_all’这样的url_name, 然后再匹配 请求方法,再去列表中 匹配参数,如果都匹配上了,说明有给设置权限。那么再用request.user.has_perm()方法确定权限是否跟当前用户绑定了,如果绑定了说明有权限。
写一个权限检测的方法,和一个装饰器
app/perm_check.py
from django.urls import resolve from django.shortcuts import render from app.perm_list import perm_list def check(request, *args, **kwargs): url_obj = resolve(request.path_info) url_name = url_obj.url_name print('>>>>:', '权限匹配') if request.user.is_superuser: return True if url_name: url_method = request.method for k, v in perm_list.items(): per_url_name = v[0] per_method = v[1] per_args = v[2] args_match = False #匹配perm_list中的权限 if per_url_name == url_name and url_method == per_method: method_func = getattr(request, url_method) for arg in per_args: if method_func.get(arg): args_match = True else: args_match = False break else: args_match = True #prem_list权限匹配上了 if args_match: app_name, perm_name = k.split('_', 1) perm_str = '%s.%s' % (app_name, perm_name) print('>>>>: ', perm_name) if request.user.has_perm(perm_str): return True else: return False else: return False else: return False #没有匹配上权限,默认不允许 #装饰器 def check_permission(fun): def inner(request, *args, **kwargs): if check(request, *args, **kwargs): return fun(request, *args, **kwargs) return render(request, 'app/403.html', locals()) return inner
权限到这就写完了。
模版
list.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <table> <tr> <th>姓名</th> <th>电话</th> <th>所属用户</th> </tr> {% for c in customer_list %} <tr> <td>{{ c.name }}</td> <td>{{ c.phone }}</td> <td>{{ c.owner }}</td> </tr> {% endfor %} </table> </body> </html>
403.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div> 403 </div> </body> </html>
现在给两个视图加上装饰器,检测 权限
from django.shortcuts import render from app.models import Customers from app.perm_check import check_permission # Create your views here. @check_permission def show_all(request): customer_list = Customers.objects.all() return render(request, 'app/list.html', locals()) @check_permission def show_own(request): uid = request.GET.get('uid', None) if uid: customer_list = Customers.objects.filter(owner_id=uid) return render(request, 'app/list.html', locals())
给zhangsan分配查看所有客户的权限 ,lisi分配 查看自己客户 的权限 ,测试 一下
使用zhangsan登录后台后 :
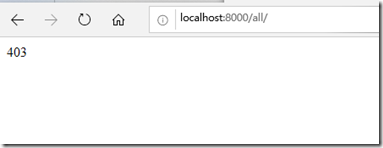
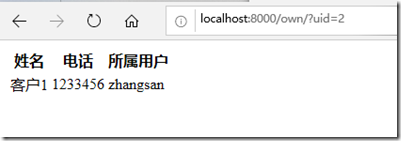
查看所有客户
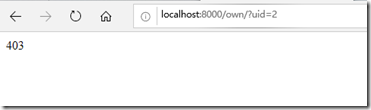
查看自己的客户:
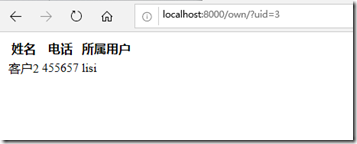
再使用lisi登录后台:
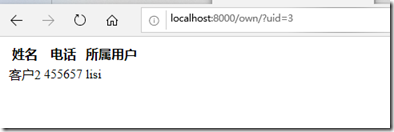
这里发现一个问题,手动改变uid的值 后,lisi也能看到zhangsan的客户,这就不符合要求了。
要解决这个问题,可以使用勾子函数的方法 。
定义勾子函数
app/perm_hook.py
def own_hook(request): uid = request.GET.get('uid', None) if uid == str(request.user.id): return True return False
修改 app/perm_list.py
from app import perm_hook perm_list = { 'app_show_all_customer': ['show_all', 'GET', []], 'app_show_own_customer': ['show_own', 'GET', ['uid',], perm_hook.own_hook] }
修改 app/perm_check.py
from django.urls import resolve from django.shortcuts import render from app.perm_list import perm_list def check(request, *args, **kwargs): url_obj = resolve(request.path_info) url_name = url_obj.url_name print('>>>>:', '权限匹配') if request.user.is_superuser: return True if url_name: url_method = request.method for k, v in perm_list.items(): per_url_name = v[0] per_method = v[1] per_args = v[2] args_match = False #匹配perm_list中的权限 if per_url_name == url_name and url_method == per_method: method_func = getattr(request, url_method) for arg in per_args: if method_func.get(arg): args_match = True else: args_match = False break else: args_match = True hook_match = True if len(v) >= 4: hook_func = v[3] hook_match = hook_func(request) #prem_list权限匹配上了 if args_match and hook_match: app_name, perm_name = k.split('_', 1) perm_str = '%s.%s' % (app_name, perm_name) print('>>>>: ', perm_name) if request.user.has_perm(perm_str): return True else: return False else: return False else: return False else: return False #没有匹配上权限,默认不允许 #装饰器 def check_permission(fun): def inner(request, *args, **kwargs): if check(request, *args, **kwargs): return fun(request, *args, **kwargs) return render(request, 'app/403.html', locals()) return inner
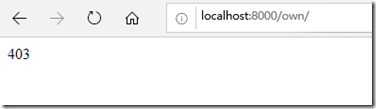
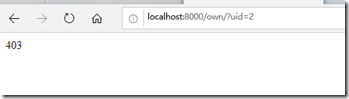
修改完之后,启动应用 ,再用lisi访问zhangsan的客户:
发现已经 不能访问了,再访问一下自己的客户: