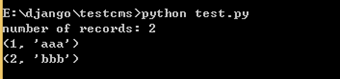
以SQLit3为例:
import sqlite3 conn = sqlite3.connect('db.sqlite3') #获取游标对象 cur = conn.cursor() #执行一系列SQL语句 #建立一张表 #cur.execute("create table demo(num int, str vachar(20));") #插入一些记录 cur.execute("insert into demo values(%d, '%s')" % (1, 'aaa')) cur.execute("insert into demo values(%d, '%s')" % (2, 'bbb')) #更新一条记录 cur.execute("update demo set str='%s' where num =%d" % ('ddd',3)) #查询 cur.execute("select * from demo;") rows = cur.fetchall() print("number of records:", len(rows)) for i in rows: print(i) #提交事务 conn.commit() #关闭游标对象 cur.close() #关闭数据库连接 conn.close()
运行结果:
SQLAlchemy
SQLAlchemy是一款开源软件,提供了SQL工具包及对象关系映射(ORM)工具,它采用python语言,为高效和高性能的数据库访问设计,实现了完整的企业级持久模型,sqlalchemy非常关注数据库的量级和性能。
使用SQLAlchemy至少需要三部分代码,这们分别是定义表,定义数据库连接,进行增、删、改、查等操作。
创建表的例子:
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base from sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, String Base = declarative_base() #定义一个实例,所有表必须继承该实例 class Account(Base): __tablename__ = 'account' #表名 #字段名 id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) user_name = Column(String(50), nullable=False) password = Column(String(200), nullable=False) title = Column(String(50)) salary = Column(Integer) def is_active(self): #假设所有用户都是活跃用户 return True def get_id(self): #返回帐户id,该方法返回属性值提高了表的封装性 return self.id def is_authenticated(self): #假设已通过验证 return True def is_anonymous(self): #具有登录名和密码的帐户不是匿名用户 return False
定义数据库连接的代码示例:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine from sqlalchemy.orm import scoped_session, sessionmaker #定义连接数据库用到的数据库字符串 db_connect_string = 'mysql://root:123456@localhost:3306/sqlalchemy_db?charset=utf8' #如果数据库开启了ssl连接,定义ssl字符串 ssl_args = { 'ssl':{ 'cert': '/home/ssl/client-cert.pem', 'key': '/home/shouse/ssl/client-key.pem', 'ca': '/home/shouse/ssl/ca-cert.pem' } } #如果数据库开启了ssl连接,需要传入ssl engine = create_engine(db_connect_string, connect_args=ssl_args) #定义会话类型 SessionType = scoped_session(sessionmaker(bind=engine, expire_on_commit=False)) def GetSession(): #创建SessionType的实例,用于数据库操作 return SessionType() from contextlib import contextmanager #定义上下文函数,使能够自动进行事务处理, #定义上下文件函数的方法就是加上contextmanager装饰器 #执行逻辑:在函数开始时建立数据库会话,此时会自动建立一个数据库事务;当发生异常时回滚(rollback)事务,当 #退出时关闭(close)连接 @contextmanager def session_scope(): session = GetSession() try: yield session session.commit() except: session.rollback() raise finally: session.close()
进行数据库操作的示例代码
import orm from sqlalchemy import or_ def InsertAccount(user, password, title, salary): with session_scope() as session: #新增操作 account = orm.Account(user_name=user, password=password, title=title, salary=salary) session.add(account) def CetAccount(id=None, user_name=None): #查询操作,查询结果是一个对象集合,同样可以用all()获取所有数据 with session_scope() as session: return session.query(orm.Account).filter( or_(orm.Account.id==id, orm.Account.user_name==user_name) ).first() def DeleteAccount(user_name): #删除操作 with session_scope() as session: account = GetAccount(user_name=user_name) if account: session.delete(account) def UpdateAccount(id, user_name, password, title, salary): #更新操作 with session_scope() as session: account = session.query(orm.Account).filter(orm.Account.id=id).first() if not account: return account.user_name = user_name account.password = password account.title = title account.salary = salary #调用新增操作 InsertAccount('David Li', "123", "System Manager", 3000) InsertAccount('Rebeca Li', '', 'Accountant', 3000) #查询操作 GetAccount(2) #删除操作 DeleteAccount('David Li') #更新操作 UpdateAccount(1, "David Li", "none", "System Manager", 2000)
代码解释:
- 用import 引入数据库表Account所在的包orm(orm.py), 引入多条件查询时的 或连接 or_
- 每个函数通过with语句启用上下文函数session_scope(), 通过它获取到session对象,并自动开启事务
- 在InsertAccount中,通过新建一个表account实例,并通过session.add将其添加到数据库中,由于上下文函数退出时会自动提交事务,把以无须显示地调用session.commit()使新增生
主流数据库的连接方式
| 数据库 | 连接字符串 |
| Microsoft SQLServer | ‘mssql+pymssql://username:password@ip:port/dbname’ |
| MySQL | ‘mysql://username:password@ip:port/dbname’ |
| oracle | ‘orcle://username:password@ip:port/dbname’ |
| PostgreSQL | ‘postgresql://username:password@ip:port/dbname’ |
| SQLite | ‘sqlite://file_pathname’ |
查询条件设置:
在实际编程过程中需要根据各种不同的条件查询数据库记录, SQLAlchemy查询条件被称为过滤器。
1. 等值过滤器
session.query(Account).filter(Account.user_name=='Jack') session.query(Account).filter(Account.salary==2000)
2. 不等于过滤器(!=, <, >, <=, >=)
session.query(Account).filter(Account.user_name != 'Jack') session.query(Account).filter(Account.salary != 2000) session.query(Account).filter(Account.salary > 3000)
3. 模糊查询(like)
模糊查询只适用于查询字符串类型,不适用于数值类型
#查询所有名字中包含字母i的用户 session.query(Account).filter(Account.user_name.like('%i%')) #查询所有title中以Manager结尾的用户 session.query(Account).filter(Account.title.like('%Manager')) #查询的有名字中以Da开头的用户 session.query(Account).filter(Account.user_name.like('Da%'))
4. 包括过滤器(in_)
#查询id不为1,3,5的记录 session.query(Account).filter(~Account.id.in_([1,3,5])) #查询工资不为2000,3000,4000的记录 session.query(Account).filter(~Account.salary.in_([2000,3000,4000])) #查询所有title不为Engineer和Accountant的记录 session.query(Account).filter(~Account.title.in_(['Account','Engineer']))
5. 判断是否为空(is NULL, is not NULL)
#查询salary为空值的记录 session.query(Account).filter(Account.salary.is_(None)) session.query(Account).filter(Account.salary == None) #查询salary不为空值的记录 session.query(Account).filter(Account.salary.isnot(None)) session.query(Account).filter(Account.salary != None)
6. 非逻辑 ~
#查询id不为1,3,5的记录 session.query(Account).filter(~Account.id.in_([1,3,5]))
7. 与逻辑 (and_)
#直接多个条件查询 session.query(Account).filter(Account.title='Engineer', Account.salary==3000) #用关键字and_进行与逻辑查询 from sqlalchemy import and_ session.query(Account).filter(and_(Account.title=='Engineer', Account.salary==3000)) #通过多个filter链接查询 session.query(Account).filter(Account.title=='Engineer').filter(Account.salary==3000)
from sqlalchemy import or_ #查询title是Engineer或者salary为3000的记录 session.query(Account).filter(or_(Account.title=='Engineer', Account.salary==3000))