前言
SpringBoot启动时默认加载bootstrap.properties或bootstrap.yml(这两个优先级最高)、application.properties或application.yml,如果我们配置了spring.profiles,同时会加载对应的application-{profile}.properties或application-{profile}.yml,profile为对应的环境变量,比如dev,如果没有配置,则会加载profile=default的配置文件
虽然说配置项都写在同一个配置文件没有问题,但我们仍然希望能分开写,这样比较清晰,比如eureka的配置写在eureka.properties,数据库相关的配置写在datasource.properties等等,因此就需要设置加载外部配置文件
更多关于配置项信息请看官网:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.1.0.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#boot-features-external-config
本文记录SpringBoot加载自定义配置文件的两个方法
两种方法
方法一
直接在具体的类上面使用注解加载
比如当你在ServiceAImpl需要使用到xxx.properties时
//手动加载自定义配置文件 @PropertySource(value = { "classpath:xxx.properties", }, encoding = "utf-8") @Service public class ServiceAImpl{ @Value("${cn.huanzi.qch.xxx}") private String xxx; }
如果你需要在更早一点引入,则可以在启动类上进行引入
//手动加载自定义配置文件 @PropertySource(value = { "classpath:xxx.properties", "classpath:yyy.properties", "classpath:zzz.yml", }, encoding = "utf-8") @Component @SpringBootApplication public class SpringbootLoadmyprofilesApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringbootLoadmyprofilesApplication.class, args); } @Value("${cn.huanzi.qch.xxx}") private String xxx; @Value("${cn.huanzi.qch.yyy}") private String yyy; @Value("${cn.huanzi.qch.zzz}") private String zzz; @Bean void index(){ System.out.println(xxx); System.out.println(yyy); System.out.println(zzz); } }
如果我们只是在业务中需要用到自定义配置文件的值,这样引入并没有什么问题,但外部配置是一些启动项,SpringBoot官网并不推荐我们这样干

虽然在@SpringBootApplication上使用@PropertySource似乎是在环境中加载自定义资源的一种方便而简单的方法,但我们不推荐使用它,因为SpringBoot在刷新应用程序上下文之前就准备好了环境。使用@PropertySource定义的任何键都加载得太晚,无法对自动配置产生任何影响。
这种情况下需要采用第二种方法
方法二
自定义环境处理类,在启动之前定制环境或应用程序上下文,
Customize the Environment or ApplicationContext Before It Starts:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.1.0.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#howto-customize-the-environment-or-application-context

官网还提供了一个列子:
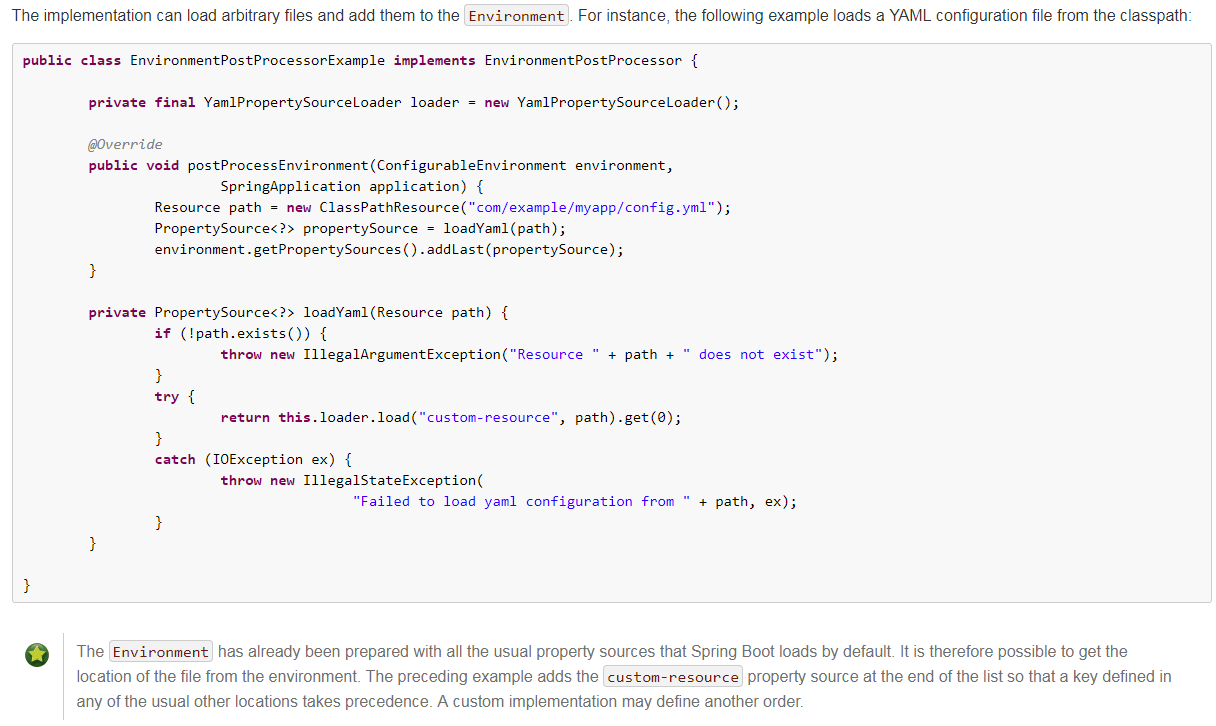
我们也来写一个自定义环境处理,在运行SpringApplication之前加载任意配置文件到Environment环境中
package cn.huanzi.qch.springbootloadmyprofiles; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor; import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment; import org.springframework.core.env.PropertiesPropertySource; import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource; import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource; import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Properties; /** 自定义环境处理,在运行SpringApplication之前加载任意配置文件到Environment环境中 */ public class MyEnvironmentPostProcessor implements EnvironmentPostProcessor { //Properties对象 private final Properties properties = new Properties(); @Override public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,SpringApplication application) { //自定义配置文件 String[] profiles = { "xxx.properties", "yyy.properties", "zzz.yml", }; //循环添加 for (String profile : profiles) { //从classpath路径下面查找文件 Resource resource = new ClassPathResource(profile); //加载成PropertySource对象,并添加到Environment环境中 environment.getPropertySources().addLast(loadProfiles(resource)); } } //加载单个配置文件 private PropertySource<?> loadProfiles(Resource resource) { if (!resource.exists()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("资源" + resource + "不存在"); } try { //从输入流中加载一个Properties对象 properties.load(resource.getInputStream()); return new PropertiesPropertySource(resource.getFilename(), properties); }catch (IOException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("加载配置文件失败" + resource, ex); } } }
并且在META-INF/spring.factories中
#启用我们的自定义环境处理类
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=cn.huanzi.qch.springbootloadmyprofiles.MyEnvironmentPostProcessor
简单测试
先看一下我们的工程结构

xxx、yyy、zzz里面就只有一个值(yyy、zzz就对应改成yyy、zzz)
cn.huanzi.qch.xxx=this is xxx
如果不手动加载自定义配置文件,启动将会报错

因为我们这里不是启动项,方法一、方法二启动效果都差不多

后记
部分代码参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/7ab1a62b04ed?from=timeline
代码开源
代码已经开源、托管到我的GitHub、码云: