摘要:Hive UDF是什么?有什么用?怎么用?什么原理?本文从UDF使用入手,简要介绍相关源码,UDF从零开始。
本文分享自华为云社区《Hive UDF,就这》,作者:汤忒撒。
Hive中内置了很多函数,同时支持用户自行扩展,按规则添加后即可在sql执行过程中使用,目前支持UDF、UDTF、UDAF三种类型,一般UDF应用场景较多,本文主要介绍UDF使用,简要介绍相关源码。
UDF,(User Defined Function)用户自定义函数
UDTF,(User-defined Table Generating Function)自定义表生成函数,一行数据生成多行
UDAF,(User-defined Aggregation Function)用户自定义聚合函数,多行数据生成一行
1. UDF简介
UDF包含两种类型:1、临时函数仅当前会话中有效,退出后重新连接即无法使用;2、永久函数注册UDF信息到MetaStore元数据中,可永久使用。
实现UDF需要继承特定类UDF或GenericUDF二选一。
- apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.UDF,处理并返回基本数据类型,int、string、boolean、double等;
- apache.hadoop.hive.ql.udf.generic.GenericUDF,可处理并返回复杂数据类型,如Map、List、Array等,同时支持嵌套;
2. UDF相关语法
UDF使用需要将编写的UDF类编译为jar包添加到Hive中,根据需要创建临时函数或永久函数。
2.1. resources操作
Hive支持向会话中添加资源,支持文件、jar、存档,添加后即可在sql中直接引用,仅当前会话有效,默认读取本地路径,支持hdfs等,路径不加引号。例:add jar /opt/ht/AddUDF.jar;
添加资源 ADD { FILE[S] | JAR[S] | ARCHIVE[S] } <filepath1> [<filepath2>]* 查看资源 LIST { FILE[S] | JAR[S] | ARCHIVE[S] } [<filepath1> <filepath2> ..] 删除资源 DELETE { FILE[S] | JAR[S] | ARCHIVE[S] } [<filepath1> <filepath2> ..]
2.2. 临时函数
仅当前会话有效,不支持指定数据库,USING路径需加引号。
CREATE TEMPORARY FUNCTION function_name AS class_name [USING JAR|FILE|ARCHIVE 'file_uri' [, JAR|FILE|ARCHIVE 'file_uri'] ]; DROP TEMPORARY FUNCTION [IF EXISTS] function_name;
2.3. 永久函数
函数信息入库,永久有效,USING路径需加引号。临时函数与永久函数均可使用USING语句,Hive会自动添加指定文件到当前环境中,效果与add语句相同,执行后即可list查看已添加的文件或jar包。
CREATE FUNCTION [db_name.]function_name AS class_name [USING JAR|FILE|ARCHIVE 'file_uri' [, JAR|FILE|ARCHIVE 'file_uri'] ]; DROP FUNCTION [IF EXISTS] function_name; RELOAD (FUNCTIONS|FUNCTION);
2.4. 查看函数
查看所有函数,不区分临时函数与永久函数 show functions; 函数模糊查询,此处为查询x开头的函数 show functions like 'x*'; 查看函数描述 desc function function_name; 查看函数详细描述 desc function extended function_name;
3. Description注解
Hive已定义注解类型org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.Description,用于执行desc function [extended] function_name时介绍函数功能,内置函数与自定义函数用法相同。
【备注】若Description注解名称与创建UDF时指定名称不同,以创建UDF时指定名称为准。
public @interface Description { //函数简单介绍 String value() default "_FUNC_ is undocumented"; //函数详细使用说明 String extended() default ""; //函数名称 String name() default ""; }
例:Hive内置ceil函数GenericUDFCeil代码定义如下,
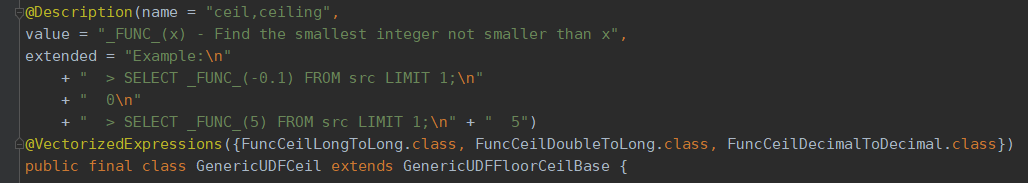
desc function ceil;
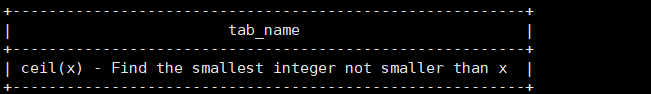
desc function extended ceil;
4. UDF
继承UDF类必须实现evaluate方法,支持定义多个evaluate方法不同参数列表用于处理不同类型数据,如下
public Text evaluate(Text s) public int evaluate(Integer s) …
4.1. UDF示例
实现UDF函数,若字符串执行拼接,int类型执行加法运算。
@Description( name="my_plus", value="my_plus() - if string, do concat; if integer, do plus", extended = "Example : \n >select my_plus('a', 'b');\n >ab\n >select my_plus(3, 5);\n >8" ) public class AddUDF extends UDF { public String evaluate(String... parameters) { if (parameters == null || parameters.length == 0) { return null; } StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for (String param : parameters) { sb.append(param); } return sb.toString(); } public int evaluate(IntWritable... parameters) { if (parameters == null || parameters.length == 0) { return 0; } long sum = 0; for (IntWritable currentNum : parameters) { sum = Math.addExact(sum, currentNum.get()); } return (int) sum; } }
hdfs dfs -put AddUDF.jar /tmp/ht/
create function my_plus as 'com.huawei.ht.test.AddUDF' using jar 'hdfs:///tmp/ht/AddUDF.jar';
desc function my_plus;
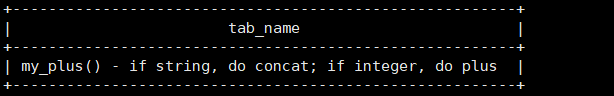
desc function extended my_plus;
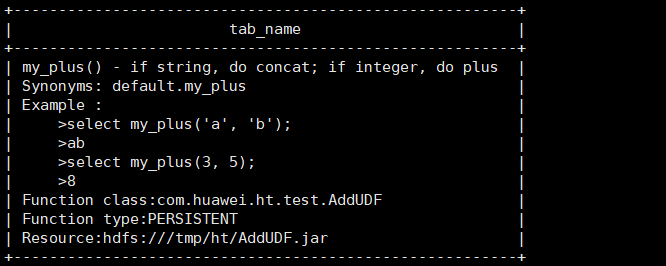
UDF添加后记录在元数据表FUNCS、FUNC_RU表中
4.2. 源码浅析
UDF类调用入口为方法解析器,默认方法解析器DefaultUDFMethodResolver,执行时由解析器反射获取UDF类的evaluate方法执行,类代码如下:
UDF
public class UDF { //udf方法解析器 private UDFMethodResolver rslv; //默认构造器DefaultUDFMethodResolver public UDF() { rslv = new DefaultUDFMethodResolver(this.getClass()); } protected UDF(UDFMethodResolver rslv) { this.rslv = rslv; } public void setResolver(UDFMethodResolver rslv) { this.rslv = rslv; } public UDFMethodResolver getResolver() { return rslv; } public String[] getRequiredJars() { return null; } public String[] getRequiredFiles() { return null; } }
DefaultUDFMethodResolver
public class DefaultUDFMethodResolver implements UDFMethodResolver { //The class of the UDF. private final Class<? extends UDF> udfClass; public DefaultUDFMethodResolver(Class<? extends UDF> udfClass) { this.udfClass = udfClass; } @Override public Method getEvalMethod(List<TypeInfo> argClasses) throws UDFArgumentException { return FunctionRegistry.getMethodInternal(udfClass, "evaluate", false, argClasses); } }
5. GenericUDF
GenericUDF相比与UDF功能更丰富,支持所有参数类型,参数类型由ObjectInspector封装;参数Writable类由DeferredObject封装,使用时简单类型可直接从Writable获取,复杂类型可由ObjectInspector解析。
继承GenericUDF必须实现如下3个接口:
//初始化,ObjectInspector为数据类型封装类,无实际参数值,返回结果类型 public ObjectInspector initialize(ObjectInspector[] objectInspectors) throws UDFArgumentException { return null; } //DeferredObject封装实际参数的对应Writable类 public Object evaluate(DeferredObject[] deferredObjects) throws HiveException { return null; } //函数信息 public String getDisplayString(String[] strings) { return null; }
5.1. GenericUDF示例
自定义函数实现count函数,支持int与long类型,Hive中无long类型,对应类型为bigint,create function与数据库保存与UDF一致,此处不再赘述。
initialize,遍历ObjectInspector[]检查每个参数类型,根据参数类型构造ObjectInspectorConverters.Converter,用于将Hive传递的参数类型转换为对应的Writable封装对象ObjectInspector,供后续统一处理。
evaluate,初始化时已记录每个参数具体类型,从DeferredObject中获取对象,根据类型使用对应Converter对象转换为Writable执行计算。
例:处理int类型,
UDF查询常量时,DeferredObject中封装类型为IntWritable;
UDF查询表字段时,DeferredObject中封装类型为LazyInteger。
@Description( name="my_count", value="my_count(...) - count int or long type numbers", extended = "Example :\n >select my_count(3, 5);\n >8\n >select my_count(3, 5, 25);\n >33" ) public class MyCountUDF extends GenericUDF { private PrimitiveObjectInspector.PrimitiveCategory[] inputType; private transient ObjectInspectorConverters.Converter intConverter; private transient ObjectInspectorConverters.Converter longConverter; @Override public ObjectInspector initialize(ObjectInspector[] objectInspectors) throws UDFArgumentException { int length = objectInspectors.length; inputType = new PrimitiveObjectInspector.PrimitiveCategory[length]; for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { ObjectInspector currentOI = objectInspectors[i]; ObjectInspector.Category type = currentOI.getCategory(); if (type != ObjectInspector.Category.PRIMITIVE) { throw new UDFArgumentException("The function my_count need PRIMITIVE Category, but get " + type); } PrimitiveObjectInspector.PrimitiveCategory primitiveType = ((PrimitiveObjectInspector) currentOI).getPrimitiveCategory(); inputType[i] = primitiveType; switch (primitiveType) { case INT: if (intConverter == null) { ObjectInspector intOI = PrimitiveObjectInspectorFactory.getPrimitiveWritableObjectInspector(primitiveType); intConverter = ObjectInspectorConverters.getConverter(currentOI, intOI); } break; case LONG: if (longConverter == null) { ObjectInspector longOI = PrimitiveObjectInspectorFactory.getPrimitiveWritableObjectInspector(primitiveType); longConverter = ObjectInspectorConverters.getConverter(currentOI, longOI); } break; default: throw new UDFArgumentException("The function my_count need INT OR BIGINT, but get " + primitiveType); } } return PrimitiveObjectInspectorFactory.writableLongObjectInspector; } @Override public Object evaluate(DeferredObject[] deferredObjects) throws HiveException { LongWritable out = new LongWritable(); for (int i = 0; i < deferredObjects.length; i++) { PrimitiveObjectInspector.PrimitiveCategory type = this.inputType[i]; Object param = deferredObjects[i].get(); switch (type) { case INT: Object intObject = intConverter.convert(param); out.set(Math.addExact(out.get(), ((IntWritable) intObject).get())); break; case LONG: Object longObject = longConverter.convert(param); out.set(Math.addExact(out.get(), ((LongWritable) longObject).get())); break; default: throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected type in MyCountUDF evaluate : " + type); } } return out; } @Override public String getDisplayString(String[] strings) { return "my_count(" + Joiner.on(", ").join(strings) + ")"; } }
create function my_count as 'com.huawei.ht.test.MyCountUDF' using jar 'hdfs:///tmp/countUDF.jar';
create table test_numeric(i1 int, b1 bigint, b2 bigint, i2 int, i3 int);
insert into table test_numeric values(0, -10, 25, 300, 15), (11, 22, 33, 44, 55);
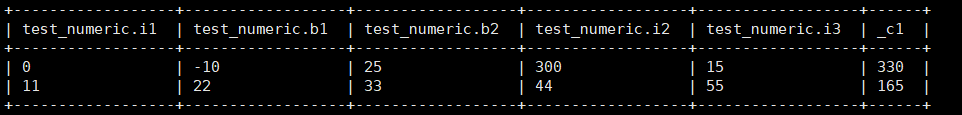
select *, my_count(*) from test_numeric;
5.2. 源码浅析
GenericUDF内部定义了方法调用顺序,子类实现相应功能即可,调用时根据函数名称从FunctionRegistry中获取UDF对象,返回执行结果。
Hive中数据类型均使用ObjectInspector封装,为区分普通类型与负责结构类型,定义枚举Category,共包含PRIMITIVE,LIST,MAP,STRUCT,UNION这5种类型,其中PRIMITIVE表示普通类型(int、long、double等)。
ObjectInspector
public interface ObjectInspector extends Cloneable { //用于类型名称 String getTypeName(); //用于获取ObjectInspector封装的字段类型 ObjectInspector.Category getCategory(); public static enum Category { PRIMITIVE, LIST, MAP, STRUCT, UNION; private Category() { } } }
PrimitiveObjectInspector.PrimitiveCategory,基本类型
public static enum PrimitiveCategory { VOID, BOOLEAN, BYTE, SHORT, INT, LONG, … }
GenericUDF. initializeAndFoldConstants
调用initialize获取输出ObjectInspector,若为常量类型,直接evaluate计算结果值。
此方法编译阶段通过AST构造Operator遍历sql节点时,常量直接计算结果值,其他类型仅执行initialize。
计算表字段时,在MR等任务中,Operator执行时调用initialize、evaluate计算结果值(例:SelectOperator)。
public ObjectInspector initializeAndFoldConstants(ObjectInspector[] arguments) throws UDFArgumentException { ObjectInspector oi = this.initialize(arguments); if (this.getRequiredFiles() == null && this.getRequiredJars() == null) { boolean allConstant = true; for(int ii = 0; ii < arguments.length; ++ii) { if (!ObjectInspectorUtils.isConstantObjectInspector(arguments[ii])) { allConstant = false; break; } } if (allConstant && !ObjectInspectorUtils.isConstantObjectInspector((ObjectInspector)oi) && FunctionRegistry.isConsistentWithinQuery(this) && ObjectInspectorUtils.supportsConstantObjectInspector((ObjectInspector)oi)) { GenericUDF.DeferredObject[] argumentValues = new GenericUDF.DeferredJavaObject[arguments.length]; for(int ii = 0; ii < arguments.length; ++ii) { argumentValues[ii] = new GenericUDF.DeferredJavaObject(((ConstantObjectInspector)arguments[ii]).getWritableConstantValue()); } try { Object constantValue = this.evaluate(argumentValues); oi = ObjectInspectorUtils.getConstantObjectInspector((ObjectInspector)oi, constantValue); } catch (HiveException var6) { throw new UDFArgumentException(var6); } } return (ObjectInspector)oi; } else { return (ObjectInspector)oi; } }
6. UDF相关源码
6.1. 运算符
Hive SQL中,“+、-、*、/、=”等运算符都是是UDF函数,在FunctionRegistry中声明,所有UDF均在编译阶段由AST生成Operator树时解析,常量直接计算结果值,其他类型仅初始化,获取输出类型用于生成Operator树,后续在Operator真正执行时计算结果值。
static { HIVE_OPERATORS.addAll(Arrays.asList( "+", "-", "*", "/", "%", "div", "&", "|", "^", "~", "and", "or", "not", "!", "=", "==", "<=>", "!=", "<>", "<", "<=", ">", ">=", "index")); }
6.2. 函数类型
Hive中包含BUILTIN, PERSISTENT, TEMPORARY三种函数;
public static enum FunctionType { BUILTIN, PERSISTENT, TEMPORARY; }
6.3. FunctionRegistry
Hive的所有UDF均由FunctionRegistry管理,FunctionRegistry仅管理内存中的UDF,不操作数据库。
内置函数都在FunctionRegistry静态块中初始化,不在数据库中记录;用户自定义UDF添加、删除都在HiveServer本地执行,临时函数在SessionState中处理,永久函数由FunctionTask调用FunctionRegistry对应方法处理,加载后FunctionTask负责写库。
public final class FunctionRegistry { … private static final Registry system = new Registry(true); static { system.registerGenericUDF("concat", GenericUDFConcat.class); system.registerUDF("substr", UDFSubstr.class, false); … } … public static void registerTemporaryMacro( String macroName, ExprNodeDesc body, List<String> colNames, List<TypeInfo> colTypes) { SessionState.getRegistryForWrite().registerMacro(macroName, body, colNames, colTypes); } public static FunctionInfo registerPermanentFunction(String functionName, String className, boolean registerToSession, FunctionResource[] resources) { return system.registerPermanentFunction(functionName, className, registerToSession, resources); } … }
6.4. GenericUDFBridge
Hive中UDF与GenericUDF实际均以GenericUDF方式处理,通过GenericUDFBridge适配,GenericUDFBridge继承GenericUDF。
添加UDF时,FunctionRegistry调用Registry对象添加UDF,Registry将UDF封装为GenericUDFBridge保存到内置中。
Registry
private FunctionInfo registerUDF(String functionName, FunctionType functionType, Class<? extends UDF> UDFClass, boolean isOperator, String displayName, FunctionResource... resources) { validateClass(UDFClass, UDF.class); FunctionInfo fI = new FunctionInfo(functionType, displayName, new GenericUDFBridge(displayName, isOperator, UDFClass.getName()), resources); addFunction(functionName, fI); return fI; }
GenericUDFBridge
内部根据参数反射获取UDF类evaluate方法并适配参数,自动转化为相应类型,故UDF不需要感知函数本地执行与yarn运行时的具体类型是否一致。
部分代码如下:
public GenericUDFBridge(String udfName, boolean isOperator, String udfClassName) { this.udfName = udfName; this.isOperator = isOperator; this.udfClassName = udfClassName; } @Override public ObjectInspector initialize(ObjectInspector[] arguments) throws UDFArgumentException { //初始化UDF对象 try { udf = (UDF)getUdfClassInternal().newInstance(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new UDFArgumentException( "Unable to instantiate UDF implementation class " + udfClassName + ": " + e); } // Resolve for the method based on argument types ArrayList<TypeInfo> argumentTypeInfos = new ArrayList<TypeInfo>( arguments.length); for (ObjectInspector argument : arguments) { argumentTypeInfos.add(TypeInfoUtils .getTypeInfoFromObjectInspector(argument)); } udfMethod = udf.getResolver().getEvalMethod(argumentTypeInfos); udfMethod.setAccessible(true); // Create parameter converters conversionHelper = new ConversionHelper(udfMethod, arguments); // Create the non-deferred realArgument realArguments = new Object[arguments.length]; // Get the return ObjectInspector. ObjectInspector returnOI = ObjectInspectorFactory .getReflectionObjectInspector(udfMethod.getGenericReturnType(), ObjectInspectorOptions.JAVA); return returnOI; } @Override public Object evaluate(DeferredObject[] arguments) throws HiveException { assert (arguments.length == realArguments.length); // Calculate all the arguments for (int i = 0; i < realArguments.length; i++) { realArguments[i] = arguments[i].get(); } // Call the function,反射执行UDF类evaluate方法 Object result = FunctionRegistry.invoke(udfMethod, udf, conversionHelper .convertIfNecessary(realArguments)); // For non-generic UDF, type info isn't available. This poses a problem for Hive Decimal. // If the returned value is HiveDecimal, we assume maximum precision/scale. if (result != null && result instanceof HiveDecimalWritable) { result = HiveDecimalWritable.enforcePrecisionScale ((HiveDecimalWritable) result, HiveDecimal.SYSTEM_DEFAULT_PRECISION, HiveDecimal.SYSTEM_DEFAULT_SCALE); } return result; }
6.5. 函数调用入口
sql中使用函数时,可能有3处调用,不同版本代码行数可能不一致,流程类似。
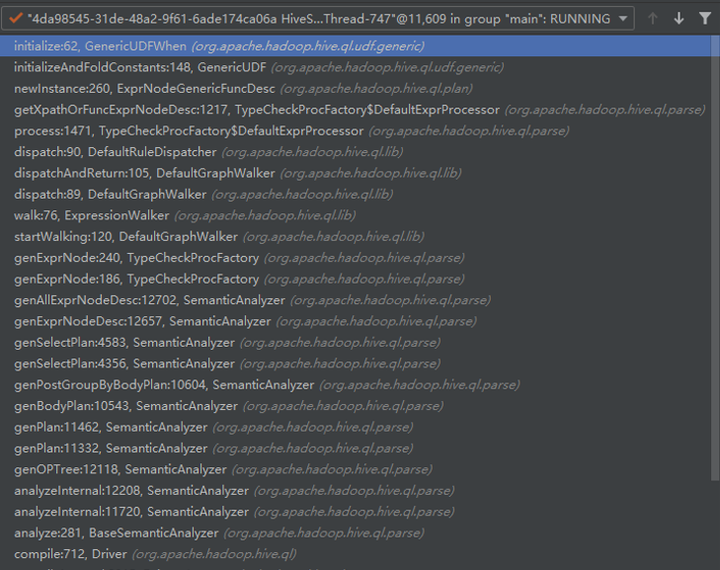
1. 编译时遍历语法树转换Operator。
TypeCheckProcFactory.getXpathOrFuncExprNodeDesc中根据sql中运算符或UDF名称生成表达式对象ExprNodeGenericFuncDesc,内部调用GenericUDF方法。
2. 启用常量传播优化器优化时,ConstantPropagate中遍历树过程调用;
此优化器默认开启,可参数控制"hive.optimize.constant.propagation"。
ConstantPropagate优化时遍历节点,尝试提前计算常量表达式,由ConstantPropagateProcFactory.evaluateFunction计算UDF。

3. UDF参数不是常量,SQL按计划执行过程中Operator真正执行时;
Operator真正执行时,由ExprNodeGenericFuncEvaluator. _evaluate处理每行数据,计算UDF结果值。
@Override protected Object _evaluate(Object row, int version) throws HiveException { if (isConstant) { // The output of this UDF is constant, so don't even bother evaluating. return ((ConstantObjectInspector) outputOI).getWritableConstantValue(); } rowObject = row; for (GenericUDF.DeferredObject deferredObject : childrenNeedingPrepare) { deferredObject.prepare(version); } return genericUDF.evaluate(deferredChildren); }