内置函数
接下来,我们就一起来看看python里的内置函数。截止到python版本3.6.2,现在python一共为我们提供了68个内置函数。它们就是python提供给你直接可以拿来使用的所有函数。这些函数有些我们已经用过了,有些我们还没用到过,还有一些是被封印了,必须等我们学了新知识才能解开封印的。那今天我们就一起来认识一下python的内置函数。这么多函数,我们该从何学起呢?
作用域相关
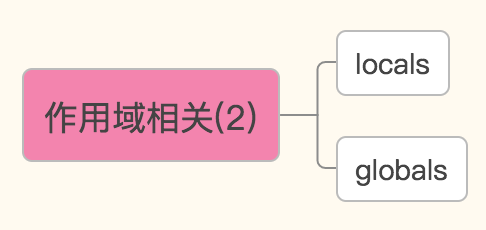
基于字典的形式获取局部变量和全局变量
globals()——获取全局变量的字典
locals()——获取执行本方法所在命名空间内的局部变量的字典
其他
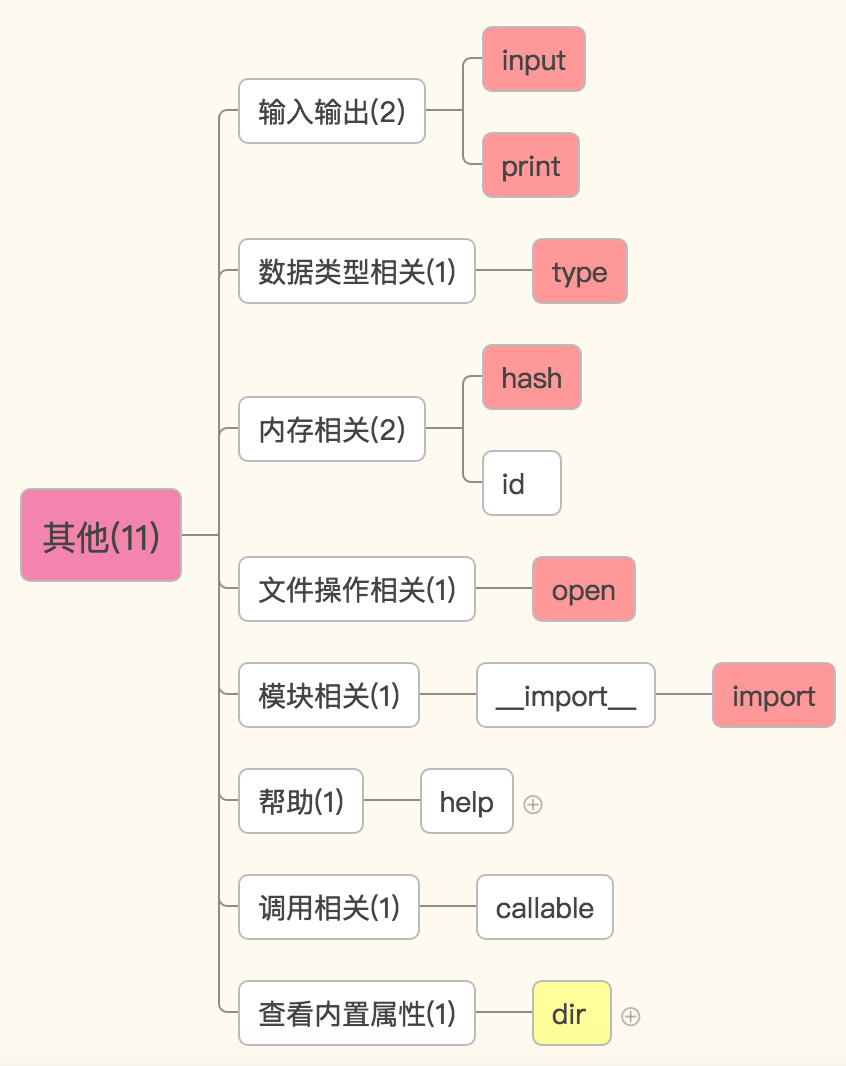
输入输出相关:
input() 输入

s = input("请输入内容 : ") #输入的内容赋值给s变量
print(s) #输入什么打印什么。数据类型是str
s = input("请输入内容 : ") #输入的内容赋值给s变量
print(s) #输入什么打印什么。数据类型是str
print() 输出

def print(self, *args, sep=' ', end='
', file=None): # known special case of print
"""
print(value, ..., sep=' ', end='
', file=sys.stdout, flush=False)
file: 默认是输出到屏幕,如果设置为文件句柄,输出到文件
sep: 打印多个值之间的分隔符,默认为空格
end: 每一次打印的结尾,默认为换行符
flush: 立即把内容输出到流文件,不作缓存
"""
def print(self, *args, sep=' ', end='
', file=None): # known special case of print
"""
print(value, ..., sep=' ', end='
', file=sys.stdout, flush=False)
file: 默认是输出到屏幕,如果设置为文件句柄,输出到文件
sep: 打印多个值之间的分隔符,默认为空格
end: 每一次打印的结尾,默认为换行符
flush: 立即把内容输出到流文件,不作缓存
"""

f = open('tmp_file','w')
print(123,456,sep=',',file = f,flush=True)
f = open('tmp_file','w')
print(123,456,sep=',',file = f,flush=True)

import time
import sys
for i in range(0,101,2):
time.sleep(0.1)
char_num = i//2 #打印多少个#
per_str = '%s%% : %s
' % (i, '*' * char_num) if i == 100 else '
%s%% : %s'%(i,'*'*char_num)
print(per_str,end='', file=sys.stdout, flush=True)
import time
import sys
for i in range(0,101,2):
time.sleep(0.1)
char_num = i//2 #打印多少个#
per_str = '%s%% : %s
' % (i, '*' * char_num) if i == 100 else '
%s%% : %s'%(i,'*'*char_num)
print(per_str,end='', file=sys.stdout, flush=True)
数据类型相关:
type(o) 返回变量o的数据类型
内存相关:
id(o) o是参数,返回一个变量的内存地址
hash(o) o是参数,返回一个可hash变量的哈希值,不可hash的变量被hash之后会报错。

t = (1,2,3) l = [1,2,3] print(hash(t)) #可hash print(hash(l)) #会报错 ''' 结果: TypeError: unhashable type: 'list' '''
t = (1,2,3) l = [1,2,3] print(hash(t)) #可hash print(hash(l)) #会报错 ''' 结果: TypeError: unhashable type: 'list' '''
hash函数会根据一个内部的算法对当前可hash变量进行处理,返回一个int数字。
*每一次执行程序,内容相同的变量hash值在这一次执行过程中不会发生改变。
文件操作相关
open() 打开一个文件,返回一个文件操作符(文件句柄)
操作文件的模式有r,w,a,r+,w+,a+ 共6种,每一种方式都可以用二进制的形式操作(rb,wb,ab,rb+,wb+,ab+)
可以用encoding指定编码.
模块操作相关
__import__导入一个模块
 import time
import time
import time
帮助方法
在控制台执行help()进入帮助模式。可以随意输入变量或者变量的类型。输入q退出
或者直接执行help(o),o是参数,查看和变量o有关的操作。。。
和调用相关
callable(o),o是参数,看这个变量是不是可调用。
如果o是一个函数名,就会返回True

def func():pass print(callable(func)) #参数是函数名,可调用,返回True print(callable(123)) #参数是数字,不可调用,返回False
查看参数所属类型的所有内置方法
dir() 默认查看全局空间内的属性,也接受一个参数,查看这个参数内的方法或变量

print(dir(list)) #查看列表的内置方法 print(dir(int)) #查看整数的内置方法
print(dir(list)) #查看列表的内置方法 print(dir(int)) #查看整数的内置方法
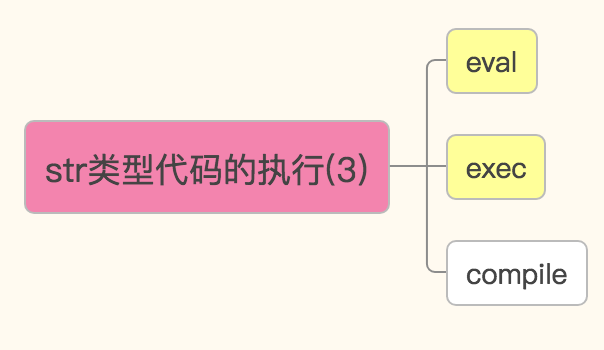
str类型代码的执行
http://www.cnblogs.com/huchong/p/8296429.html
和数字相关
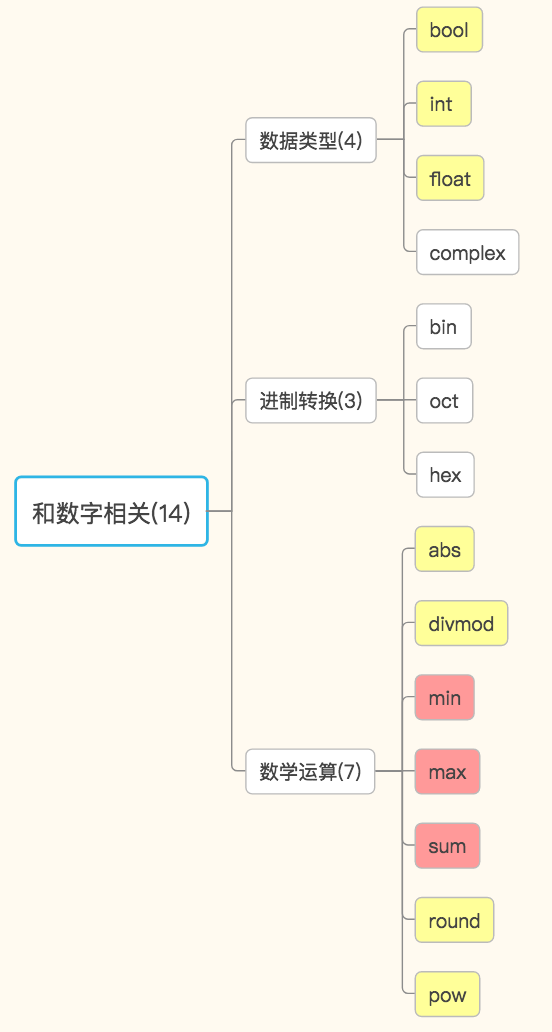
数字——数据类型相关:bool,int,float,complex
数字——进制转换相关:bin,oct,hex
数字——数学运算:abs,divmod,min,max,sum,round,pow
和数据结构相关
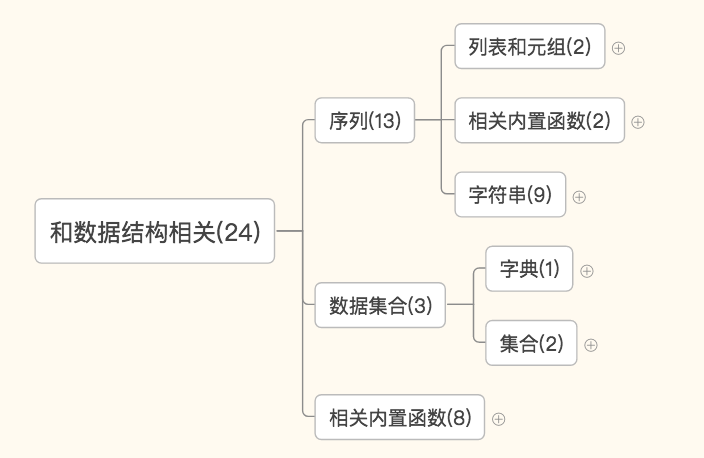
序列——列表和元组相关的:list和tuple
序列——字符串相关的:str,format,bytes,bytesarry,memoryview,ord,chr,ascii,repr
序列:reversed,slice
数据集合——字典和集合:dict,set,frozenset
数据集合:len,sorted,enumerate,all,any,zip,filter,map
filter和map:http://www.cnblogs.com/huchong/p/8296453.html
sorted方法:http://www.cnblogs.com/huchong/p/8296025.html
reduce方法:http://www.cnblogs.com/huchong/p/8214250.html
匿名函数(lambda)
匿名函数:为了解决那些功能很简单的需求而设计的一句话函数
#这段代码
def calc(n):
return n**n
print(calc(10))
#换成匿名函数
calc = lambda n:n**n
print(calc(10))
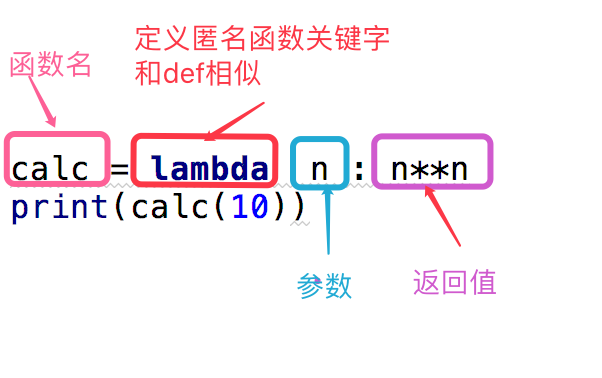
上面是我们对calc这个匿名函数的分析,下面给出了一个关于匿名函数格式的说明
函数名 = lambda 参数 :返回值 #参数可以有多个,用逗号隔开 #匿名函数不管逻辑多复杂,只能写一行,且逻辑执行结束后的内容就是返回值 #返回值和正常的函数一样可以是任意数据类型
我们可以看出,匿名函数并不是真的不能有名字。
匿名函数的调用和正常的调用也没有什么分别。 就是 函数名(参数) 就可以了~~~
练一练:
请把以下函数变成匿名函数
def add(x,y):
return x+y
上面是匿名函数的函数用法。除此之外,匿名函数也不是浪得虚名,它真的可以匿名。在和其他功能函数合作的时候
l=[3,2,100,999,213,1111,31121,333]
print(max(l))
dic={'k1':10,'k2':100,'k3':30}
print(max(dic))
print(dic[max(dic,key=lambda k:dic[k])])
res = map(lambda x:x**2,[1,5,7,4,8])
for i in res:
print(i)
输出
1
25
49
16
64
res = filter(lambda x:x>10,[5,8,11,9,15])
for i in res:
print(i)
输出
11
15
面试题练一练
现有两个元组(('a'),('b')),(('c'),('d')),请使用python中匿名函数生成列表[{'a':'c'},{'b':'d'}]

#答案一
test = lambda t1,t2 :[{i:j} for i,j in zip(t1,t2)]
print(test(t1,t2))
#答案二
print(list(map(lambda t:{t[0]:t[1]},zip(t1,t2))))
#还可以这样写
print([{i:j} for i,j in zip(t1,t2)])
#答案一
test = lambda t1,t2 :[{i:j} for i,j in zip(t1,t2)]
print(test(t1,t2))
#答案二
print(list(map(lambda t:{t[0]:t[1]},zip(t1,t2))))
#还可以这样写
print([{i:j} for i,j in zip(t1,t2)])
本章小结
说学习内置函数,不如说整理自己的知识体系。其实整理这些内置函数的过程也是在整理自己的知识体系。
一个优秀的程序员就应该是在该用这个方法的时候信手拈来,把每一个内置的函数都用的恰到好处。
要想做到这一点,至少要先了解,才能在需要的时候想起,进而将它用在该用的地方。
但是在这里,我还是以自己的一点经验之谈,把几个平时工作中相对更常用的方法推荐一下,请务必重点掌握:
其他:input,print,type,hash,open,import,dir
str类型代码执行:eval,exec
数字:bool,int,float,abs,divmod,min,max,sum,round,pow
序列——列表和元组相关的:list和tuple
序列——字符串相关的:str,bytes,repr
序列:reversed,slice
数据集合——字典和集合:dict,set,frozenset
数据集合:len,sorted,enumerate,zip,filter,map
参考文档:
