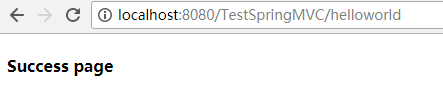
第一步:使用配置Tomcat服务器的Eclipse新建一个名为“TestSpringMVC”的web项目
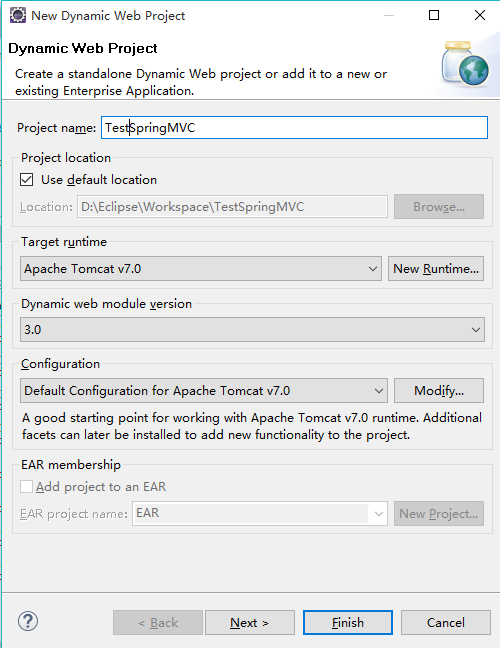
第二步:将所使用的jar包复制到WEB-INF/lib目录下
第三步:在web.xml中配置DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet就是SpringMVC的入口,SpringMVC的本质就是一个Servlet
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> 3 4 <!--配置DispatcherServlet --> 5 <servlet> 6 <servlet-name>springDispatcherServlet</servlet-name> 7 <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> 8 9 <init-param> 10 <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> 11 <param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value> 12 <!-- 配置DispatcherServlet的一个初始化参数 --> 13 </init-param> 14 <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> 15 </servlet> 16 <!-- Map all requests to the DispatcherServlet for handling --> 17 <servlet-mapping> 18 <servlet-name>springDispatcherServlet</servlet-name> 19 <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> 20 </servlet-mapping> 21 </web-app>
web.xml中load-on-startup的含义:标记容器是否在启动的时候就加载这个servlet。
当值为0或者大于0时,表示容器在应用启动时就加载这个servlet;
当是一个负数时或者没有指定时,则指示容器在该servlet被选择时才加载。
正数的值越小,启动该servlet的优先级越高。
Servlet中的url-pattern:
当浏览器发起一个url请求后,该请求发送到servlet容器的时候,容器先会将请求的url减去当前应用上下文的路径作为servlet的映射url,比如url是http://10.43.11.143/myapp/kata/detail.html,其应用上下文是myapp,容器会将http://10.43.11.143/myapp去掉,剩下的/kata/detail.html部分拿来做servlet的映射匹配。这个映射匹配过程是有优先顺序的(具体的优先顺序规则后面介绍),而且当有一个servlet匹配成功以后,就不会去理会剩下的servlet了。
如果<url-pattern>配置成如下两种的任意一种
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
则所有的url都可以被匹配上。其中/*是路径匹配,只是路径就是/。
第四步:创建SpringMVC的配置文件
在WEB-INF下新建一个名为“springmvc”的xml文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-cache-4.0.xsd"> <!-- 配置自定义扫描的包 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.java.springmvc"></context:component-scan> <!-- 配置视图解析器:如何把handler方法解析为实际的物理视图 --> <bean class ="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/"></property> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property> </bean> </beans>
第五步:创建处理请求的处理器
在Java Resource下新建一个类作为处理器
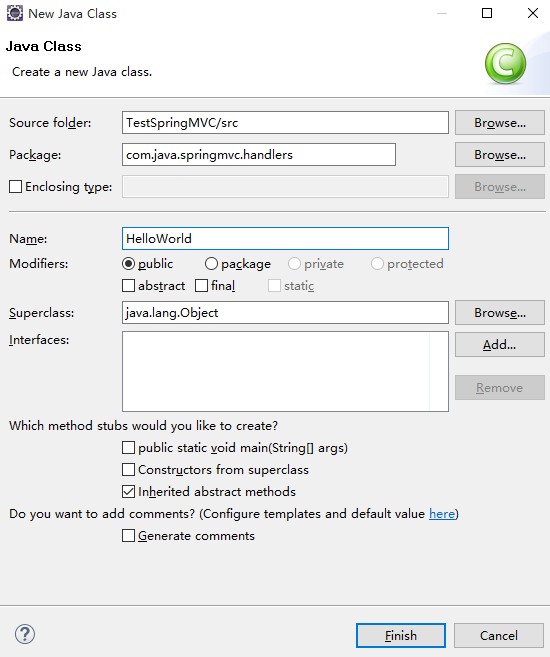
package com.java.springmvc.handlers; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; @Controller public class HelloWorld { /** * 使用@RequestMapping 注解映射请求的URL * 返回值会通过视图解析器返回为实际的物理视图 * @return */ @RequestMapping("/helloworld") public String hello(){ System.out.println("hello world"); return "success"; } }
第六步:创建视图
在WEBContent下创建一个名为“index”的jsp文件
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <a href="helloworld">Hello World</a> </body> </html>
在WEB-INF下创建一个名为views大的文件夹,然后在该文件下创建一个名为success的jsp文件
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <h4>Success page</h4> </body> </html>
创建完毕后WebContent下的结构图如图所示
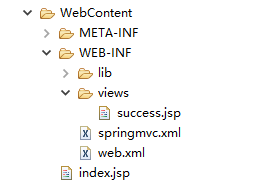
最后编译后部署到Tomcat运行该工程:
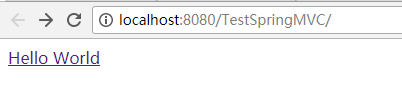
点击“Hello World”之后