伪随机(preundorandom):通过算法产生的随机数都是伪随机!!
只有通过真实的随机事件产生的随机数才是真随机!!比如,通过机器的硬件噪声产生随机数、通过大气噪声产生随机数
Random生成的随机数都是伪随机数!!!
是由可确定的函数(常用线性同余),通过一个种子(常用时钟),产生的伪随机数。这意味着:如果知道了种子,或者已经产生的随机数,都可能获得接下来随机数序列的信息(可预测性)
Random类拥有两个构造方法,用于实现随机数生成器:
| Random( ) | 构造一个随机数生成器 |
| Random(long seed) | 用种子seed构造一个随机数生成器 |
一、无参构造方法(不设置种子)
虽然表面上看我们未设置种子,但Random构造方法里有一套自己的种子生成机制,源码如下:
1 /** 2 * Creates a new random number generator. This constructor sets 3 * the seed of the random number generator to a value very likely 4 * to be distinct from any other invocation of this constructor. 5 */ 6 public Random() { 7 this(seedUniquifier() ^ System.nanoTime()); 8 } 9 10 private static long seedUniquifier() { 11 // L'Ecuyer, "Tables of Linear Congruential Generators of 12 // Different Sizes and Good Lattice Structure", 1999 13 for (;;) { 14 long current = seedUniquifier.get(); 15 long next = current * 181783497276652981L; 16 if (seedUniquifier.compareAndSet(current, next)) 17 return next; 18 } 19 } 20 21 private static final AtomicLong seedUniquifier 22 = new AtomicLong(8682522807148012L);
生成种子过程:(参考解密随机数生成器(二)——从java源码看线性同余算法)
1、获得一个长整形数作为“初始种子”(系统默认的是8682522807148012L)
2、不断与一个变态的数——181783497276652981L相乘(天知道这些数是不是工程师随便滚键盘滚出来的-.-)得到一个不能预测的值,直到 能把这个不能事先预期的值 赋给Random对象的静态常量seedUniquifier 。因为多线程环境下赋值操作可能失败,就for(;;)来保证一定要赋值成功
3、与系统随机出来的nanotime值作异或运算,得到最终的种子
nanotime算是一个随机性比较强的参数,用于描述代码的执行时间。源码中关于nanotime的描述(部分):
/** * Returns the current value of the running Java Virtual Machine's * high-resolution time source, in nanoseconds. * * <p>This method can only be used to measure elapsed time and is * not related to any other notion of system or wall-clock time.
二、有参构造方法(设置种子)
语法:Random ran = Random(long seed)
有参构造方法的源码如下:
1 /** 2 * Creates a new random number generator using a single {@code long} seed. 3 * The seed is the initial value of the internal state of the pseudorandom 4 * number generator which is maintained by method {@link #next}. 5 * 6 * <p>The invocation {@code new Random(seed)} is equivalent to: 7 * <pre> {@code 8 * Random rnd = new Random(); 9 * rnd.setSeed(seed);}</pre> 10 * 11 * @param seed the initial seed 12 * @see #setSeed(long) 13 */ 14 public Random(long seed) { 15 if (getClass() == Random.class) 16 this.seed = new AtomicLong(initialScramble(seed)); 17 else { 18 // subclass might have overriden setSeed 19 this.seed = new AtomicLong(); 20 setSeed(seed); 21 } 22 } 23 24 private static long initialScramble(long seed) { 25 return (seed ^ multiplier) & mask; 26 }
其中的multiplier和mask都是定值:
1 private static final long multiplier = 0x5DEECE66DL; 2 3 private static final long mask = (1L << 48) - 1;
三、代码测试
分别采用有参和无参两种方法,生成[0, 100)内的随机整数,各生成五组,每组十个随机数:
1 import java.util.Random; 2 3 public class RandomTest { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 RandomTest rt = new RandomTest(); 6 rt.testRandom(); 7 } 8 9 public void testRandom(){ 10 System.out.println("Random不设置种子:"); 11 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 12 Random random = new Random(); 13 for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) { 14 System.out.print(" " + random.nextInt(100) + ", "); 15 } 16 System.out.println(""); 17 } 18 19 System.out.println(""); 20 21 System.out.println("Random设置种子:"); 22 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 23 Random random = new Random(); 24 random.setSeed(100); 25 for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) { 26 System.out.print(" " + random.nextInt(100) + ", "); 27 } 28 System.out.println(""); 29 } 30 } 31 }
运行结果如下:
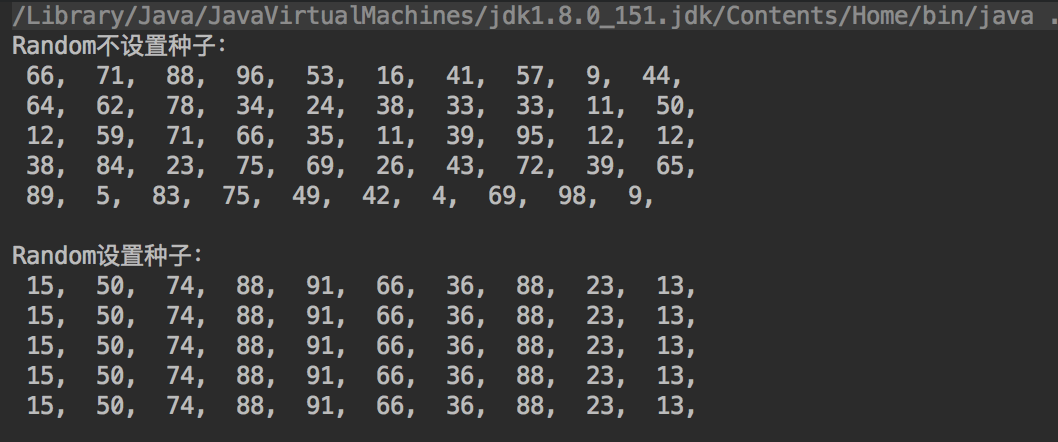
结论:
虽然二者都是伪随机,但是,无参数构造方法(不设置种子)具有更强的随机性,能够满足一般统计上的随机数要求。使用有参的构造方法(设置种子)无论你生成多少次,每次生成的随机序列都相同,名副其实的伪随机!!