题目描述
在数轴上有 $N$ 个闭区间 $[l_1,r_1],[l_2,r_2],...,[l_n,r_n]$ 。现在要从中选出 $M$ 个区间,使得这 $M$ 个区间共同包含至少一个位置。换句话说,就是使得存在一个 $x$ ,使得对于每一个被选中的区间 $[l_i,r_i]$ ,都有 $l_i≤x≤r_i$ 。
对于一个合法的选取方案,它的花费为被选中的最长区间长度减去被选中的最短区间长度。区间 $[l_i,r_i]$ 的长度定义为 $r_i-l_i$ ,即等于它的右端点的值减去左端点的值。
求所有合法方案中最小的花费。如果不存在合法的方案,输出 $-1$ 。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
第一行包含两个正整数 $N,M$ 用空格隔开,意义如上文所述。保证 $1≤M≤N$
接下来 $N$ 行,每行表示一个区间,包含用空格隔开的两个整数 $l_i$ 和 $r_i$ 为该区间的左右端点。
$N<=500000,M<=200000,0≤li≤ri≤10^9$
输出格式:
只有一行,包含一个正整数,即最小花费。
输入输出样例
说明
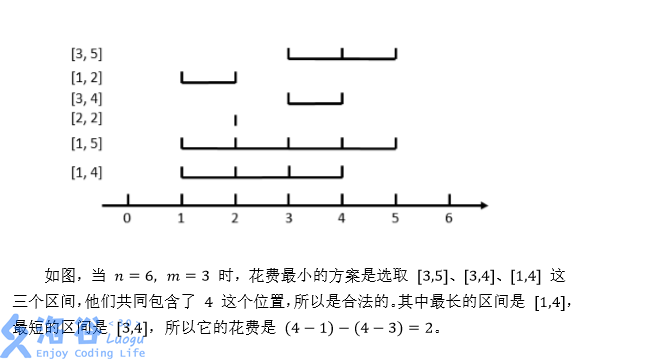
分析
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define lson now<<1,l,mid #define rson now<<1|1,mid+1,r using namespace std; const int N=1000010; const int INF=0x7f7f7f7f; int n,m,tot,top,c[N*2]; int x,y,k,ans,maxl[N*3],tag[N*3]; struct node{ int x,y,len; bool operator < (const node &j) const{ return len<j.len; } }a[N]; inline void pushup(int now){ maxl[now]=max(maxl[now<<1],maxl[now<<1|1]); } inline void pushdown(int now){ int lc=now<<1,rc=now<<1|1; maxl[lc]+=tag[now]; maxl[rc]+=tag[now]; tag[lc]+=tag[now]; tag[rc]+=tag[now]; tag[now]=0; } void modify(int now,int l,int r){ if(x<=l&&r<=y){ tag[now]+=k; maxl[now]+=k; return; } if(tag[now]) pushdown(now); int mid=(l+r)>>1; if(x<=mid) modify(lson); if(y>mid) modify(rson); pushup(now); } int main(){ scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){ scanf("%d%d",&a[i].x,&a[i].y); a[i].len=a[i].y-a[i].x; c[++tot]=a[i].x; c[++tot]=a[i].y; } top=0; ans=INF; sort(c+1,c+tot+1); tot=unique(c+1,c+tot+1)-c-1; for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){ a[i].x=lower_bound(c+1,c+tot+1,a[i].x)-c; a[i].y=lower_bound(c+1,c+tot+1,a[i].y)-c; } sort(a+1,a+n+1); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { while(maxl[1]<m&&top<n){ top++; x=a[top].x; y=a[top].y; k=1; modify(1,1,tot); } if(maxl[1]==m) ans=min(ans,a[top].len-a[i].len); x=a[i].x; y=a[i].y; k=-1; modify(1,1,tot); } if(ans==INF) printf("-1"); else printf("%d",ans); }