在python中,反射包含以下几个函数

def hasattr(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return whether the object has an attribute with the given name. This is done by calling getattr(obj, name) and catching AttributeError. """ pass

def hasattr(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return whether the object has an attribute with the given name. This is done by calling getattr(obj, name) and catching AttributeError. """ pass

def setattr(x, y, v): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ Sets the named attribute on the given object to the specified value. setattr(x, 'y', v) is equivalent to ``x.y = v'' """ pass

def delattr(x, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ Deletes the named attribute from the given object. delattr(x, 'y') is equivalent to ``del x.y'' """ pass
hasattr 判断是否含有某属性
In [1]: class Person(object):
...: def __init__(self, name, age):
...: self.name = name
...: self.age = age
In [2]: p = Person('hkey', 20) # 实例化一个对象
In [3]: hasattr(p, 'name') # 通过 hasattr 判断 p 是否包含 name 属性,这里name参数必须是字符串类型
Out[3]: True
In [4]: hasattr(p, 'sex') # 如果 p 中没有 sex 属性,则返回 False
Out[4]: False
getattr 获取对象的属性
In [5]: getattr(p, 'name') # p.name = getattr(p, 'name') Out[5]: 'hkey' In [6]: getattr(p, 'age') # p.age = getattr(p, 'age') Out[6]: 20 In [7]: getattr(p, 'sex') # p.sex = getattr(p, 'sex') p 对象中不包含 sex 属性则报错. --------------------------------------------------------------------------- AttributeError Traceback (most recent call last) <ipython-input-7-36d4b75cf6b8> in <module> ----> 1 getattr(p, 'sex') AttributeError: 'Person' object has no attribute 'sex'
getattr 进阶用法:
当使用 getattr 获取不存在属性的时候,我们不希望直接抛出异常。
getattr(对象, 'str1', '对象属性不存在时的默认信息')
In [16]: getattr(p, 'sex', '不知道') # p 对象中是没有 sex 属性,直接返回默认值 Out[16]: '不知道' In [17]: getattr(p, 'sex', 'None') # 一般来说直接设置为 None Out[17]: 'None'
setattr 设置对象的属性
In [8]: setattr(p, 'sex', 'male') # 通过 setattr 为 p 对象设置为 sex 属性,属性值为 male In [9]: p.sex # 验证 setattr 是否设置成功 Out[9]: 'male'
setattr 进阶用法:
setattr 不仅可以为对象添加属性,还可以为对象绑定方法
In [23]: setattr(p, 'say_hello', lambda self: 'hello, ' + self.name) # setattr(对象名, '方法名', '匿名函数') self 代表对象本身 In [24]: p.say_hello(p) # 调用方式必须将对象传入 对象.方法名(对象) Out[24]: 'hello, hkey'
delattr 删除对象的属性
In [10]: delattr(p, 'sex') # 通过 delattr 删除 p 对象的 sex 属性 In [11]: p.sex # 验证 sex 属性是否删除成功 --------------------------------------------------------------------------- AttributeError Traceback (most recent call last) <ipython-input-13-0e282ee1b157> in <module> ----> 1 p.sex AttributeError: 'Person' object has no attribute 'sex'
反射在实际代码中使用的非常普遍,尤其是在和用户交互的时候。
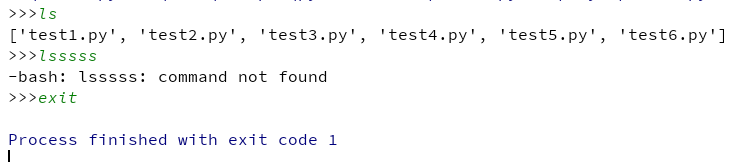
实例:自行编写一个shell,当要执行一个命令的时候使用反射来执行
import os
class Manage_cmd(object):
def run(self):
while True:
cmd = input('>>>').strip()
if not cmd: continue
if hasattr(self, cmd): # 通过 hasattr 来判断对象self是否含有cmd属性
getattr(self, cmd)()
else:
print('-bash: %s: command not found' % cmd)
def ls(self):
print(os.listdir('.'))
def exit(self):
exit(1)
cmd = Manage_cmd()
cmd.run()
执行结果: