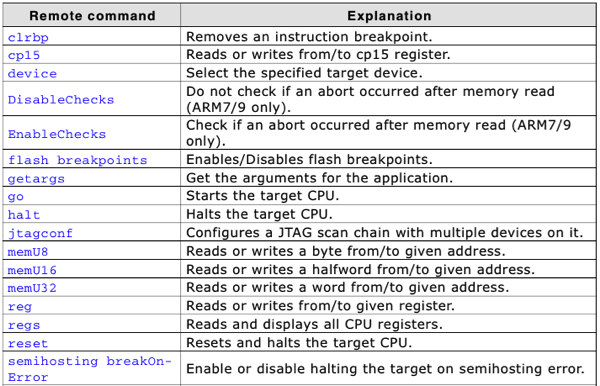
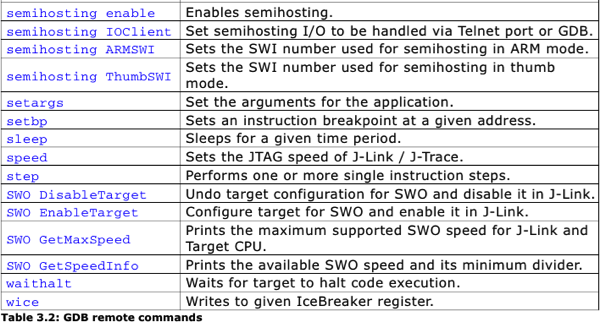
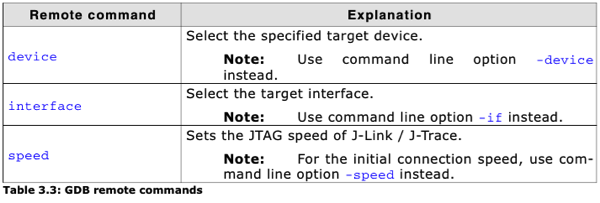
Note1: The remote commands are case-insensitive.
Note2: Optional parameters are set into square brackets.
Note3: The examples are described as follows:
Note4: Lines starting with ’#’ are comments and not used in GDB / GDB Server.
Note5: Lines starting with ’>’ are input commands from the GDB.
Note6: Lines starting with ’<’ is the output from GDB Server as printed in GDB.
3.3.3.1 clrbp
Syntax
ClrBP [<BPHandle>]
or
ci [<BPHandle>]
Description
Removes an instruction breakpoint, where <BPHandle> is the handle of breakpoint to be removed. If no handle is specified this command removes all pending breakpoints.
Example
> monitor clrbp 1
or
> monitor ci 1
3.3.3.2 cp15
Syntax
cp15 <CRn>, <CRm>, <op1>, <op2> [= <data>]
Description
Reads or writes from/to cp15 register. If <data> is specified, this command writes the data to the cp15 register. Otherwise this command reads from the cp15 register. For further information please refer to the ARM reference manual.
Example
#Read:
> monitor cp15 1, 2, 6, 7
< Reading CP15 register (1,2,6,7 = 0x0460B77D)
#Write:
> monitor cp15 1, 2, 6, 7 = 0xFFFFFFFF
3.3.3.3 device
Note: Deprecated. Use command line option -device instead.
Syntax
device <DeviceName>
Description
Selects the specified target device. This is necessary for the connection and some special handling of the device.
Note: The device should be selected via commandline option -device when starting GDB Server.
Example
> monitor device STM32F417IG
< Selecting device: STM32F417IG
3.3.3.4 DisableChecks
Syntax
DisableChecks
Description
Disables checking if a memory read caused an abort (ARM7/9 devices only). On some CPUs during the init sequence for enabling access to the internal memory (for exam- ple on the TMS470) some dummy reads of memory are required which will cause an abort as long as the access-init is not completed.
3.3.3.5 EnableChecks
Syntax
EnableChecks
Description
Enables checking if a memory read caused an abort (ARM7/9 devices only). On some CPUs during the init sequence for enabling access to the internal memory (for exam- ple on the TMS470) some dummy reads of memory are required which will cause an abort as long as the access-init is not completed. The default state is: Checks enabled.
3.3.3.6 flash breakpoints
Syntax
monitor flash breakpoints = <Value>
Description
This command enables/disables the Flash Breakpoints feature.
By default Flash Breapkoints are enabled and can be used for evaluation.
Example
#Disable Flash Breakpoints:
> monitor flash breakpoints = 0
< Flash breakpoints disabled
#Enable Flash Breakpoins:
> monitor flash breakpoints = 1
< Flash breakpoints enabled
3.3.3.7 getargs
Syntax
getargs
Description
Get the currently set argument list which will be given to the application when calling semihosting command SYS_GET_CMDLINE (0x15). The argument list is given as one string.
Example
#No arguments set via setargs:
> monitor getargs
< No arguments.
#Arguments set via setargs:
> monitor getargs
< Arguments: test 0 1 2 arg0=4
3.3.3.8 go
Syntax
go
Description
Starts the target CPU.
Example
> monitor go
3.3.3.9 halt
Syntax
halt
Description
Halts the target CPU.
Example
> monitor halt
3.3.3.10 interface
Note: Deprecated. Use command line option -if instead. Syntax
interface <InterfaceIdentifier>
Description
Selects the target interface used by J-Link / J-Trace.
3.3.3.11 jtagconf
Syntax
jtagconf <IRPre> <DRPre>
Description
Configures a JTAG scan chain with multiple devices on it. <IRPre> is the sum of IRLens of all devices closer to TDI, where IRLen is the number of bits in the IR (Instruction Register) of one device. <DRPre> is the number of devices closer to TDI. For more detailed information of how to configure a scan chain with multiple devices please refer to See ìDetermining values for scan chain configurationî on page 145..
Note: To make sure the connection to the device can be established correctly, it is recommended to configure the JTAG scan chain via command line options at start of GDB Server.
Example
#Select the second device, where there is 1 device in front with IRLen 4
> monitor jtagconf 4 1
3.3.3.12 memU8
Syntax
MemU8 <address> [= <value>]
Description
Reads or writes a byte from/to a given address. If <value> is specified, this com- mand writes the value to the given address. Otherwise this command reads from the given address.
Example
#Read:
> monitor memU8 0x50000000
< Reading from address 0x50000000 (Data = 0x04)
#Write:
> monitor memU8 0x50000000 = 0xFF
< Writing 0xFF @ address 0x50000000
3.3.3.13 memU16
Syntax
memU16 <address> [= <value>]
Description
Reads or writes a halfword from/to a given address. If <value> is specified, this com- mand writes the value to the given address. Otherwise this command reads from the given address.
Example
#Read:
> monitor memU16 0x50000000
< Reading from address 0x50000000 (Data = 0x3004)
#Write:
> monitor memU16 0x50000000 = 0xFF00
< Writing 0xFF00 @ address 0x50000000
3.3.3.14 memU32
Syntax
MemU32 <address> [= <value>]
Description
Reads or writes a word from/to a given address. If <value> is specified, this com- mand writes the value to the given address. Otherwise this command reads from the given address. This command is similar to the long command.
Example
#Read:
> monitor memU32 0x50000000
< Reading from address 0x50000000 (Data = 0x10023004)
#Write:
> monitor memU32 0x50000000 = 0x10023004
< Writing 0x10023004 @ address 0x50000000
3.3.3.15 reg
Syntax
reg <RegName> [= <value>]
or
reg <RegName> [= (<address>)]
Description
Reads or writes from/to given register. If <value> is specified, this command writes the value into the given register. If <address> is specified, this command writes the memory content at address <address> to register <RegName>. Otherwise this com- mand reads the given register.
Example
#Write value to register:
> monitor reg pc = 0x00100230
< Writing register (PC = 0x00100230)
#Write value from address to register:
> monitor reg r0 = (0x00000040)
< Writing register (R0 = 0x14813004)
#Read register value:
> monitor reg PC
< Reading register (PC = 0x00100230)
3.3.3.16 regs
Syntax
regs
Description
Reads all CPU registers.
Example
> monitor regs
< PC = 00100230, CPSR = 20000013 (SVC mode, ARM)
R0 = 14813004, R1 = 00000001, R2 = 00000001, R3 = 000003B5
R4 = 00000000, R5 = 00000000, R6 = 00000000, R7 = 00000000
USR: R8 =00000000, R9 =00000000, R10=00000000, R11 =00000000, R12 =00000000
R13=00000000, R14=00000000
FIQ: R8 =00000000, R9 =00000000, R10=00000000, R11 =00000000, R12 =00000000
R13=00200000, R14=00000000, SPSR=00000010
SVC: R13=002004E8, R14=0010025C, SPSR=00000010
ABT: R13=00200100, R14=00000000, SPSR=00000010
IRQ: R13=00200100, R14=00000000, SPSR=00000010
UND: R13=00200100, R14=00000000, SPSR=00000010
3.3.3.17 reset
Syntax
reset
Description
Resets and halts the target CPU. Make sure the device is selected prior to using this command to make use of the correct reset strategy.
Add. information
There are different reset strategies for different CPUs. Moreover, the reset strategies which are available differ from CPU core to CPU core. J-Link can perform various reset strategies and always selects the best fitting strategy for the selected device.
Example
> monitor reset
< Resetting target
3.3.3.18 semihosting breakOnError
Syntax
semihosting breakOnerror <Value>
Description
Enables or disables halting the target at the semihosting breakpoint / in SVC handler if an error occurred during a semihosting command, for example a bad file handle for SYS_WRITE. The GDB Server log window always shows a warning in these cases. breakOnError is disabled by default.
Example
#Enable breakOnError:
> monitor semihosting breakOnError 1
3.3.3.19 semihosting enable
Syntax
semihosting enable [<VectorAddr>]
Description
Enables semihosting with the specified vector address. If no vector address is speci- fied, the SWI vector (at address 0x8) will be used. GDBServer will output semihost- ing terminal data from the target via a separate connection on port 2333. Some IDEs already establish a connection automatically on this port and show terminal data in a specific window in the IDE.
For IDEs which do not support semihosting terminal output directly, the easiest way to view semihosting output is to open a telnet connection to the GDBServer on port 2333. The connection on this port can be opened all the time as soon as GDBServer is started, even before this remote command is executed.
Example
> monitor semihosting enable
< Semihosting enabled (VectorAddr = 0x08)
3.3.3.20 semihosting IOClient
Syntax
semihosting IOClient <ClientMask>
Description
GDB itself can handle (file) I/O operations, too. With this command it is selected wheter to print output via TELNET port (2333), GDB, or both.
<ClientMask> is
ï 1 for TELNET Client (Standard port 2333) (Default)
ï 2 for GDB Client
ï or 3 for both (Input via GDB Client)
Example
#Select TELNET port as output source
> monitor semihosting ioclient 1
< Semihosting I/O set to TELNET Client
#Select GDB as output source
> monitor semihosting ioclient 2
< Semihosting I/O set to GDB Client
#Select TELNET port and GDB as output source
> monitor semihosting ioclient 3
< Semihosting I/O set to TELNET and GDB Client
3.3.3.21 semihosting ARMSWI
Syntax
semihosting ARMSWI <Value>
Description
Sets the SWI number used for semihosting in ARM mode. The default value for the ARMSWI is 0x123456.
Example
> monitor semihosting ARMSWI 0x123456
< Semihosting ARM SWI number set to 0x123456
3.3.3.22 semihosting ThumbSWI
Syntax
semihosting ThumbSWI <Value>
Description
Sets the SWI number used for semihosting in thumb mode. The default value for the ThumbSWI is 0xAB
Example
> monitor semihosting ThumbSWI 0xAB
< Semihosting Thumb SWI number set to 0xAB
3.3.3.23 setargs
Syntax
setargs <ArgumentString>
Description
Set arguments for the application, where all arguments are in one <Argument- String> separated by whitespaces.
The argument string can be gotten by the application via semihosting command SYS_GET_CMDLINE (0x15).
Semihosting has to be enabled for getting the argumentstring (semihosting enable). "monitor setargs" can be used before enabeling semihosting.
The maximum length for <ArgumentString> is 512 characters.
Example
> monitor setargs test 0 1 2 arg0=4
< Arguments: test 0 1 2 arg0=4
3.3.3.24 setbp
Syntax
setbp <Addr> [<Mask>]
Description
Sets an instruction breakpoint at the given address, where <Mask> can be 0x03 for ARM instruction breakpoints (Instruction width 4 Byte, mask out lower 2 bits) or 0x01 for THUMB instruction breakpoints (Instruction width 2 Byte, mask out lower bit). If no mask is given, an ARM instruction breakpoint will be set.
Example
#Set a breakpoint (implicit for ARM instructions)
> monitor setbp 0x00000000
#Set a breakpoint on a THUMB instruction
> monitor setbp 0x00000100 0x01
3.3.3.25 sleep
Syntax
sleep <Delay>
Description
Sleeps for a given time, where <Delay> is the time period in milliseconds to delay. While sleeping any communication is blocked until the command returns after the given period.
Example
> monitor sleep 1000
< Sleep 1000ms
3.3.3.26 speed
Note: Deprecated. For setting the initial connection speed, use command line option -speed instead.
Syntax
speed <kHz>|auto|adaptive
Description
Sets the JTAG speed of J-Link / J-Trace. Speed can be either fixed (in kHz), automatic recognition or adaptive. In general, Adaptive is recommended if the target has an RTCK signal which is connected to the corresponding RTCK pin of the device (S-cores only). For detailed information about the different modes, refer to JTAG Speed on page 146.
The speed has to be set after selecting the interface, to change it from its default value.
Example
> monitor speed auto
< Select auto target interface speed (8000 kHz)
> monitor speed 4000
< Target interface speed set to 4000 kHz
> monitor speed adaptive
< Select adaptive clocking instead of fixed JTAG speed
3.3.3.27 step
Syntax
step [<NumSteps>]
or
si [<NumSteps>]
Description
Performs one or more single instruction steps, where <NumSteps> is the number of instruction steps to perform. If <NumSteps> is not specified only one instruction step will be performed.
Example
> monitor step 3
注:SWO命令暂不使用,因为我的板子时JTAG接口。