转载于:博主链接
相信我,只要记住本文的 7️⃣ 步口诀,就能彻底掌握 JS 中的 this 指向。
先念口诀:箭头函数、new、bind、apply 和 call、欧比届点(obj.)、直接调用、不在函数里。
按照口诀的顺序,只要满足前面某个场景,就可以确定 this 指向了。
接下来按照口诀顺序对它们进行详解,文中示例代码都运行在 Chrome 的 Console 控制台中。
文末有精心准备的练习题,用于检验学习成果,别忘了试试~
- 箭头函数
箭头函数排在第一个是因为它的 this 不会被改变,所以只要当前函数是箭头函数,那么就不用再看其他规则了。
箭头函数的 this 是在创建它时外层 this 的指向。这里的重点有两个:
创建箭头函数时,就已经确定了它的 this 指向。
箭头函数内的 this 指向外层的 this。
所以要知道箭头函数的 this 就得先知道外层 this 的指向,需要继续在外层应用七步口诀。
2. new
当使用 new 关键字调用函数时,函数中的 this 一定是 JS 创建的新对象。
读者可能会有疑问,“如果使用 new 关键调用箭头函数,是不是箭头函数的 this 就会被修改呢?”。
我们在控制台试一下。
func = () => {}
new func() // throw error
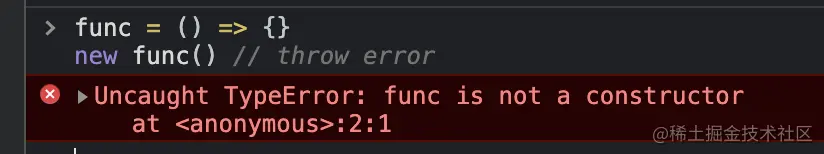
从控制台中可以看出,箭头函数不能当做构造函数,所以不能与 new 一起执行。
3. bind
bind 是指 Function.prototype.bind()。
多次 bind 时只认第一次 bind 的值
易错点
点击查看代码
function func() {
console.log(this)
}
func.bind(1).bind(2)() // 1
箭头函数中 this 不会被修改
点击查看代码
func = () => {
// 这里 this 指向取决于外层 this,参考口诀 7 「不在函数里」
console.log(this)
}
func.bind(1)() // Window,口诀 1 优先
bind 与 new
易错点
点击查看代码
function func() {
console.log(this, this.__proto__ === func.prototype)
}
boundFunc = func.bind(1)
new boundFunc() // Object true,口诀 2 优先
点击查看代码
func = () => {
// 这里 this 指向取决于外层 this,参考口诀 7 「不在函数里」
console.log(this)
}
func.apply(1) // Window,口诀 1 优先
点击查看代码
function func() {
console.log(this)
}
boundFunc = func.bind(1)
boundFunc.apply(2) // 1,口诀 3 优先
点击查看代码
function func() {
console.log(this.x)
}
obj = { x: 1 }
obj.func = func
obj.func() // 1
点击查看代码
function func() {
console.log(this)
}
func() // Window
点击查看代码
function outerFunc() {
console.log(this) // { x: 1 }
function func() {
console.log(this) // Window
}
func()
}
outerFunc.bind({ x: 1 })()
- 不在函数里
不在函数中的场景,可分为浏览器的<script />标签里,或Node.js的模块文件里。
在<script />标签里,this 指向 Window。
在 Node.js 的模块文件里,this 指向 Module 的默认导出对象,也就是 module.exports。
非严格模式
严格模式是在 ES5 提出的。在 ES5 规范之前,也就是非严格模式下,this 不能是 undefined 或 null。所以在非严格模式下,通过上面七步口诀,如果得出 this 指向是 undefined 或 null,那么 this 会指向全局对象。在浏览器环境中全局对象是 Window,在 Node.js 环境中是 Global。
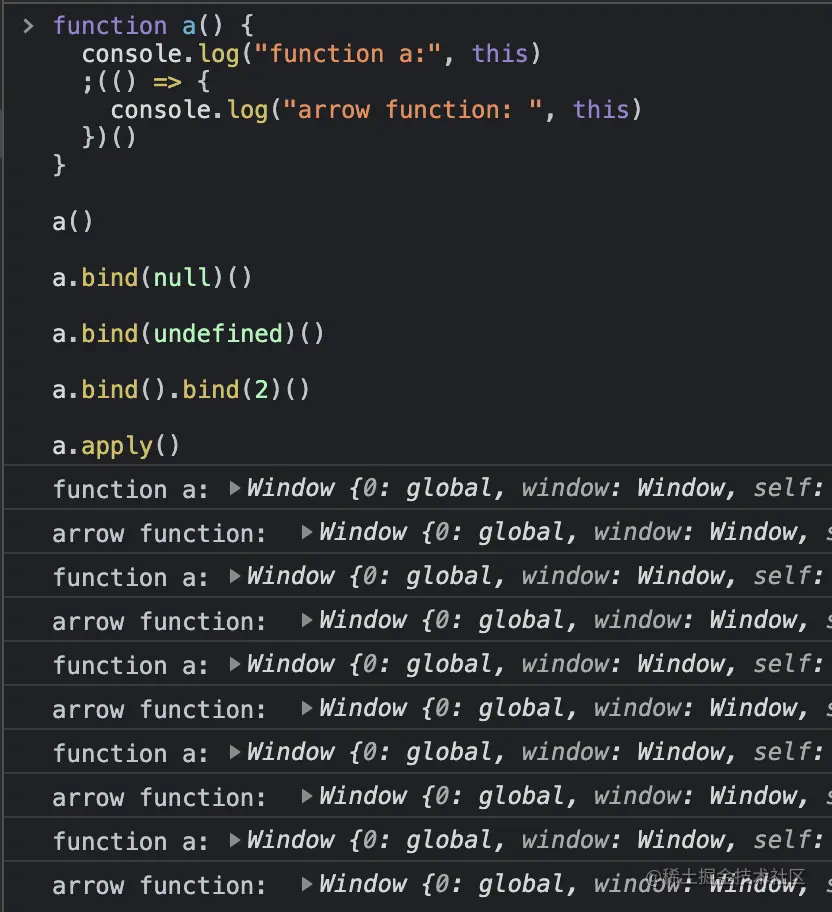
例如下面的代码,在非严格模式下,this 都指向全局对象。
点击查看代码
function a() {
console.log("function a:", this)
;(() => {
console.log("arrow function: ", this)
})()
}
a()
a.bind(null)()
a.bind(undefined)()
a.bind().bind(2)()
a.apply()
非严格模式下执行结果为:
在严格模式下,执行同样的代码进行对比。记住要一次性将所有代码复制粘贴到控制台中,才能运行在严格模式下(因为第一行 "use strict" 才会对后面的代码生效)。
点击查看代码
"use strict"
function a() {
console.log("function a:", this)
;(() => {
console.log("arrow function: ", this)
})()
}
a()
a.bind(null)()
a.bind(undefined)()
a.bind().bind(2)()
a.apply()
严格模式下执行结果为:
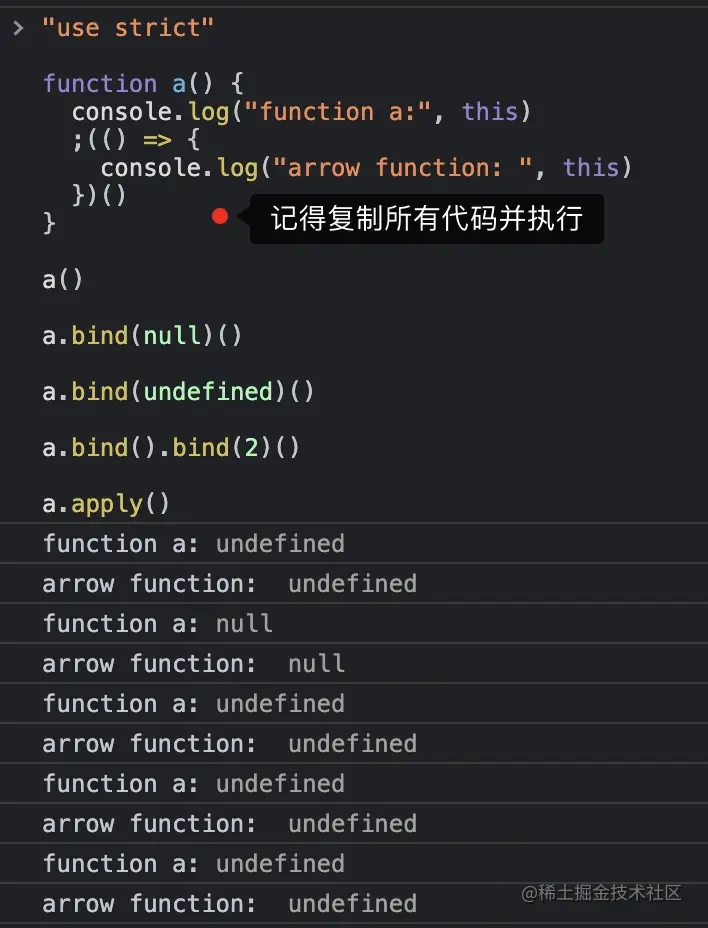
七步口诀在严格模式下和非严格模式下都是完备的,只是在非严格模式下 null 或 undefined 会被转换为全局对象。所以我没有将这点列入口诀中。
做题复习
先背诵口诀再做题,“箭头函数、new、bind、apply 和 call、欧比届点(obj.)、直接调用、不在函数里”。
- 下面代码执行后,func.count 值为多少?
点击查看代码
function func(num) {
this.count++
}
func.count = 0
func(1)
答案
func.count 值为 0。
按照口诀,func() 调用时属于第 6 类「直接调用」。在非严格模式下,this 指向全局对象。this 跟 func 一点关系都没有,所以 func.count 保持不变。so easy。
2. 以下箭头函数中 this 指向谁呢?
点击查看代码
obj = {
func() {
const arrowFunc = () => {
console.log(this._name)
}
return arrowFunc
},
_name: "obj",
}
obj.func()()
func = obj.func
func()()
obj.func.bind({ _name: "newObj" })()()
obj.func.bind()()()
obj.func.bind({ _name: "bindObj" }).apply({ _name: "applyObj" })()