一、控制器定义
控制器提供访问应用程序的行为,通常通过服务接口定义或注解定义两种方法实现。 控制器解析用户的请求并将其转换为一个模型。在Spring MVC中一个控制器可以包含多个Action(动作、方法)。
使用注解@Controller定义控制器
org.springframework.stereotype.Controller注解类型用于声明Spring类的实例是一个控制器(在讲IOC时还提到了另外3个注解);Spring可以使用扫描机制来找到应用程序中所有基于注解的控制器类,为了保证Spring能找到你的控制器,需要在配置文件中声明组件扫描。
创建一个名了Bar的类,定义为一个控制器,类的具体实现如下:
package com.zhangsan.springmvc01; import org.springframework.ui.Model; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; @org.springframework.stereotype.Controller public class Controller { @RequestMapping("/bar") public String hi(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg","这是通过注解定义的一个控制器中的Action"); return "hi"; } }
还要需要修改Spring mvc配置文件,启用自动组件扫描功能,在beans中增加如下配置:
<!-- 自动扫描包,实现支持注解的IOC --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.zhangsan.springmvc01" />
运行结果如下:
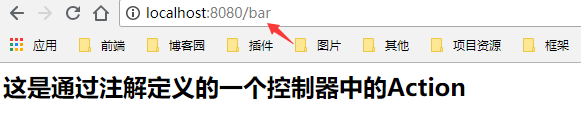
小结:从代码与运行结果可以看出BarController与FooController同时都指定了一个视图hi.jsp,但是页面结果的结果是不一样的,从这里可以看出视图是被复用的,而控制器与视图之间是弱偶合关系。
二、@RequestMapping详解
@RequestMapping注释用于映射url到控制器类或一个特定的处理程序方法。可用于类或方法上。用于类上,表示类中的所有响应请求的方法都是以该地址作为父路径。该注解共有8个属性,注解源码如下:
package org.springframework.web.bind.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor; /** * 用于映射url到控制器类或一个特定的处理程序方法. */ //该注解只能用于方法或类型上 @Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Mapping public @interface RequestMapping { /** * 指定映射的名称 */ String name() default ""; /** * 指定请求的路径映射,指定的地址可以是uri模板,别名为path */ @AliasFor("path") String[] value() default {}; /** 别名为value,使用path更加形象 * 只有用在一个Servlet环境:路径映射URI(例如“/myPath.do”)。 * Ant风格的路径模式,同时也支持(例如,“/myPath/*.do”)。在方法层面,在主要的映射在类型级别表示相对路径(例如,“edit.do”) * 的支持。路径映射的URI可能包含占位符(例如“/$ {}连接”) */ @AliasFor("value") String[] path() default {}; /** * 指定请求谓词的类型如GET, POST, HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, TRACE. 收窄请求范围 The * HTTP request methods to map to, narrowing the primary mapping: GET, POST, * HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, TRACE. */ RequestMethod[] method() default {}; /** * 映射请求的参数,收窄请求范围 The parameters of the mapped request, narrowing the * primary mapping. */ String[]params() default {}; /** * 映射请求头部,收窄请求范围 The headers of the mapped request, narrowing the primary * mapping. RequestMapping(value = "/something", headers = * "content-type=text/*") */ String[] headers() default {}; /** * 指定处理请求的提交内容类型(Content-Type),例如application/json, text/html,收窄请求范围 The * consumable media types of the mapped request, narrowing the primary * mapping. */ String[] consumes() default {}; /** * 指定返回的内容类型,仅当request请求头中的(Accept)类型中包含该指定类型才返回 The producible media types * of the mapped request, narrowing the primary mapping. produces = * "text/plain" produces = {"text/plain", "application/*"} produces = * "application/json; charset=UTF-8" */ String[] produces() default {}; }
从上面的源码可以发现除了name基本都是数组类型,在设置时我们可以指定单个值,如@RequestMapping(value="/foo");也可以同时指定多个值如:@RequestMapping(value={"/foo","/bar"})。
2.1、指定具体路径字符
2.1.1 只注解方法
@Controller public class Controller { @RequestMapping("/h1") public String h1(){ return "h1"; } }
访问路径:http://localhost:8080/h1
2.1.2 同时注解类与方法
@Controller @RequestMapping("/foo") public class Controller { @RequestMapping("/h1") public String h1(){ return h1"; } }
访问路径:http://localhost:8080/foo/h1
需要先指定类的路径再指定方法的路径
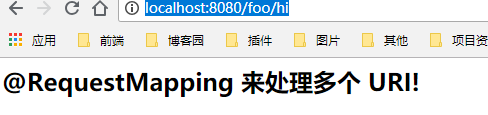
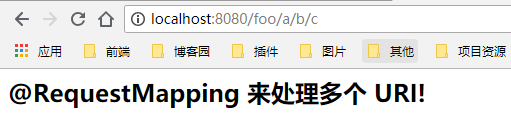
2.1.3 @RequestMapping 来处理多个 URI
@Controller @RequestMapping("/foo") public class Controller { @RequestMapping(value = {"/hi","/a/b/c"}) public String h2(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg","@RequestMapping 来处理多个 URI!"); return "hi"; } }
访问路径:1、http://localhost:8080/foo/hi
2、http://localhost:8080/foo/a/b/c
2.1.4、路径变量占位,URI模板模式
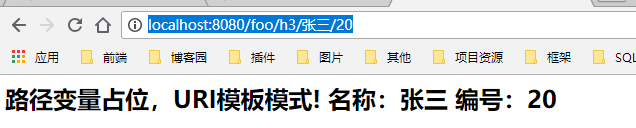
在Spring MVC可以使用@PathVariable 注释方法参数的值绑定到一个URI模板变量。
@Controller @RequestMapping("/foo") public class Controller { @RequestMapping(value = {"/h3/{name}/{id}"}) public String h3(Model model, @PathVariable String name,@PathVariable int id){ model.addAttribute("msg","路径变量占位,URI模板模式! 名称:"+name+" 编号:"+id); return "hi"; } }
访问路径:http://localhost:8080/foo/h3/张三/20
2.1.5、正则表达式模式的URI模板
@Controller @RequestMapping("/foo") public class Controller { @RequestMapping(value = "/h4/{id:\d{6}}-{name:[a-z]{3}}") public String h4(Model model, @PathVariable String name,@PathVariable int id){ model.addAttribute("msg","正则表达式模式的URI模板! 名称:"+name+" 编号:"+id); return "hi"; } }
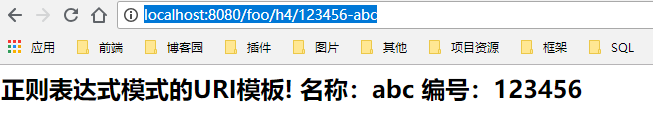
访问路径:http://localhost:8080/foo/h4/123456-abc
正则要求id必须为6位的数字,而name必须为3位小写字母,访问结果如下:
2.1.6、Ant风格路径模式
@RequestMapping注解也支持ant风格的路径模式,如/foo/h5/*.do,示例代码如下:
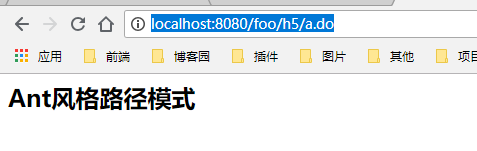
@Controller @RequestMapping("/foo") public class Controller { @RequestMapping(value = "/h5/*.do") public String h5(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg","Ant风格路径模式"); return "hi"; } }
访问路径:http://localhost:8080/foo/h5/任意符号.do
ANT通配符有三种:


2.2、method属性指定谓词类型
用于约束请求的谓词类型,可以收窄请求范围。指定请求谓词的类型如GET, POST, HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, TRACE,如下代码所示:
@Controller @RequestMapping("/foo") public class Controller { @RequestMapping(value = "/h6",method = {RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.DELETE}) public String h6(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg","请求谓词只能是POST与DELETE"); return "hi"; } }
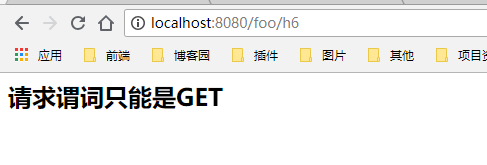
要访问h6请求谓词类型必须是POST或者为DELETE,当我们从浏览器的URL栏中直接请求时为一个GET请求,则结果是405,如下所示:

如果将POST修改为GET则正常了,如下所示:
@Controller @RequestMapping("/foo") public class Controller { @RequestMapping(value = "/h6",method = {RequestMethod.GET}) public String h6(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg","请求谓词只能是GET"); return "hi"; } }
Spring MVC 的 @RequestMapping 注解能够处理 HTTP 请求的方法, 比如 GET, PUT, POST, DELETE 以及 PATCH。
所有的请求默认都会是 HTTP GET 类型的。
为了能降一个请求映射到一个特定的 HTTP 方法,你需要在 @RequestMapping 中使用 method 来声明 HTTP 请求所使用的方法类型,如下所示:
@RestController @RequestMapping("/home") public class IndexController { @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET) String get() { return "Hello from get"; } @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.DELETE) String delete() { return "Hello from delete"; } @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST) String post() { return "Hello from post"; } @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT) String put() { return "Hello from put"; } @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PATCH) String patch() { return "Hello from patch"; } }
在上述这段代码中, @RequestMapping 注解中的 method 元素声明了 HTTP 请求的 HTTP 方法的类型。
所有的处理处理方法会处理从这同一个 URL( /home)进来的请求, 但要看指定的 HTTP 方法是什么来决定用哪个方法来处理。
例如,一个 POST 类型的请求 /home 会交给 post() 方法来处理,而一个 DELETE 类型的请求 /home 则会由 delete() 方法来处理。
你会看到 Spring MVC 将使用这样相同的逻辑来映射其它的方法。
2.3、consumes属性指定请求的Content-Type
@RequestMapping 注解的 produces 和 consumes 这两个元素来缩小请求映射类型的范围,达到处理生产和消费对象的目的。
指定处理请求的提交内容类型(Content-Type),例如application/json, text/html,收窄请求范围,如果用户发送的请求内容类型不匹配则方法不会响应请求,具体使用如下代码所示:
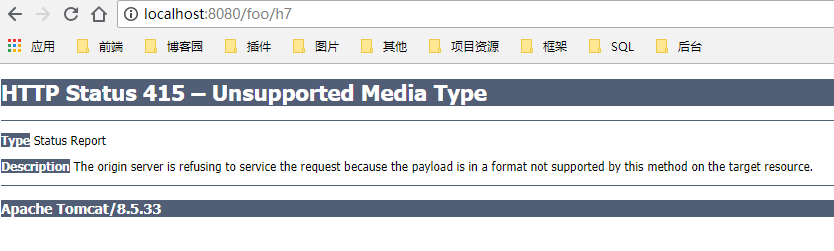
@Controller @RequestMapping("/foo") public class Controller { @RequestMapping(value = "/h7",consumes = "text/html") public String h7(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg", "请求的提交内容类型(Content-Type)是text/html"); return "hi"; } }
在h7的注解中约束发送到服务器的Content-Type必须是text/html类型,如果类型不一致则会报错(415),测试结果如下:
请求的提交内容类型(Content-Type)是text/html
注意:可以使用!号,如consumes="!text/html"
2.4、produces属性指定响应的Content-Type,约束Accept类型
指定返回的内容类型,仅当request请求头中的(Accept)类型中包含该指定类型才返回,方法才处理客户端的请求否则会报406错误,常用设置如下:
produces = "text/plain" //客户端只接收纯文本
produces = {"text/plain", "application/*"} //客户端接收纯文本与application/*类型的内容
produces = "application/json; charset=UTF-8" //客户端接收json且编码为utf-8/;
@Controller @RequestMapping("/foo") public class Controller { @RequestMapping(value = "/h8",produces = "application/json;charset=UTF-8") public String h8(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg", "客户端可以接收的类型是application/json; charset=UTF-8"); return "hi"; } }
运行结果:
注意:可以使用!号,如produces="!text/html"