一 栈
相关概念
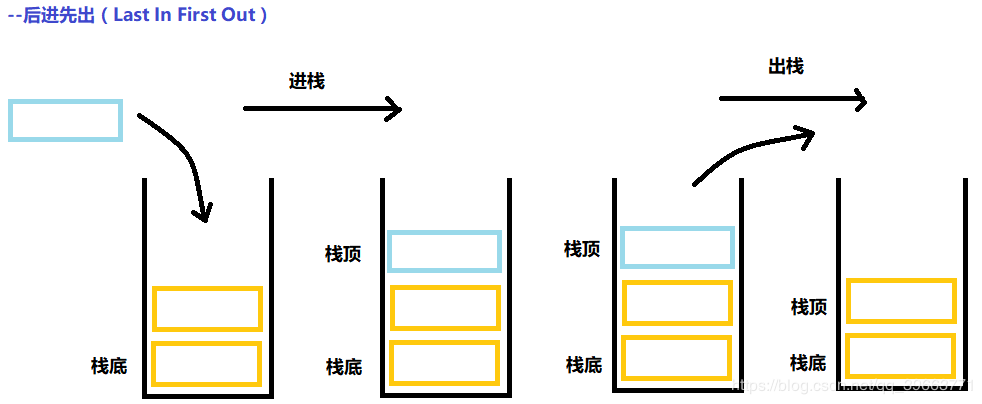
- 栈是一种特殊的线性表
- 只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。
- 进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。
- 原则:后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)
- 压栈:栈的插入操作,入数据在栈顶
- 出栈:栈的删除操作,出数据也在栈顶
我们来实现自己的栈
首先用数组来实现栈

package com.differ.jackyun.examples.javabasisc.datastructure; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.Arrays; /** * 实现自己的栈 * * @author hup * @data 2020-06-14 8:54 **/ public class MyStackWithArr<E> { /** * 数组 */ public Object[] arrStack; /** * 数组内元素数量 */ public int count; public MyStackWithArr() { arrStack = new Object[10]; } /** * 入栈 * * @param item */ public void push(E item) { //判断空间大小情况和扩容 this.relize(count + 1); //元素放入数组 arrStack[count] = item; count++; } /** * 判数组长度是否够用,自动扩容 * * @param maxCount 需要存储的总量 */ private void relize(int maxCount) { if (maxCount <= this.count) { return; } //扩容 10 arrStack = Arrays.copyOf(arrStack, 10); } /** * 出栈 * * @return */ public E pop() { E item = (E) arrStack[count - 1]; arrStack[count - 1] = null; count--; return item; } /** * 取栈顶数据 * * @return */ public E peek() { E item = (E) arrStack[count - 1]; return item; } }
然后我们测试下好不好用

@Test public void test() { MyStackWithArr mystack = new MyStackWithArr(); //入栈3个元素 mystack.push(new Node(1)); mystack.push(new Node(2)); mystack.push(new Node(3)); //出栈3个元素 System.out.println(mystack.pop()); System.out.println(mystack.pop()); System.out.println(mystack.pop()); }
测试输出结果:

Node{next=null, data=3}
Node{next=null, data=2}
Node{next=null, data=1}
可以看到,是后入先出的输出,栈生效了
用单向链表实现栈

package com.differ.jackyun.examples.javabasisc.datastructure; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.Arrays; /** * 实现自己的栈 * * @author hup * @data 2020-06-14 8:54 **/ public class MyStackWithList { /** * 头 */ public Node head; /** * 入栈 * 栈顶 * * @param data */ public void push(int data) { Node node = new Node(data); if (head == null) { head = node; return; } node.next = head; head = node; } /** * 出栈 * 栈顶 * * @return */ public int pop() { int result = 0; if (head == null) { return 0; } result = head.data; if (head.next == null) { head = null; } else { head.data = head.next.data; head.next = head.next.next; } return result; } /** * 取栈顶数据 * * @return */ public int peek() { return head == null ? 0 : head.data; } }
测试

@Test public void test() { MyStackWithList mystack = new MyStackWithList(); //入栈3个元素 mystack.push(1); mystack.push(2); mystack.push(3); //出栈3个元素 System.out.println(mystack.pop()); System.out.println(mystack.pop()); System.out.println(mystack.pop()); }
测试输出结果
3
2
1
可以看到,栈生效了
二 队列
1.队列的概念
队列正如其名,队列就像一支队伍,有队首(head)和队尾(tail)以及队列长度。队列和栈类似,也是一个遵循特殊规则约束的数据结构。我们知道栈是一个后进先出(LIFO)的数据结构,队列正好与之相反,是一个先进先出(FIFO,First In First Out),例如我们去肯德基排队,先排上队的肯定先拿到餐出队,这和我们对列认知是一致的。
上面说到队列是一个遵循特殊规则的数据结构,除了先进先出,队列的插入只能从队列的一端操作,我们称这端为队尾;对应的,移除只能从另一端出来,我们称之为队首。
将没有元素的队列称之为空队,往队列中插入元素的过程称之为入队,从队列中移除元素的过程称之为出队。
一般而言,队列的实现有两种方式:数组实现和链表实现
用数组实现的队列有两种:一种是顺序队列,另一种是循环队列,这两种队列的存储结构和特点下文会逐一介绍。
说明:用数组实现队列,若队列中出现队满的情况(因为在声明队列时,一般会指定一个初始容量),此时如果有新元素入队,但没有位置怎么办?要么丢弃,要么等待。
2.队列的存储结构
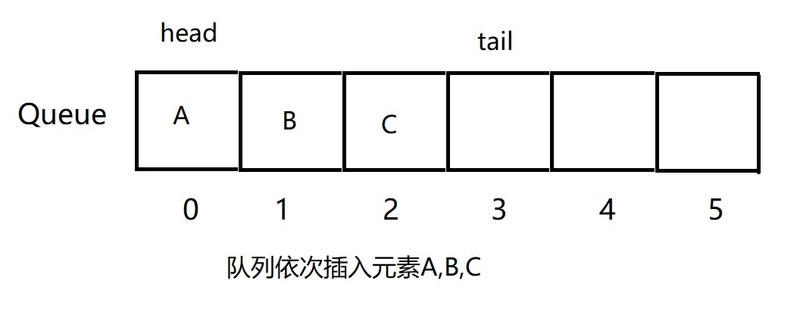
以下采用数组实现,初始化一个队列长度为6,队列有两个标记,一个队头的位置head,一个队尾的位置tail,初始都指向数组下标为0的位置,如图所示:

在插入元素时,tail标记+1,比如入队三个元素,依次为A,B,C(注意是有顺序的),则当前队列存储情况如图:
当前head为0,tail为3,接下来进行出队操作,此处将A元素出队,则head+1,此时队列的存储情况如图:
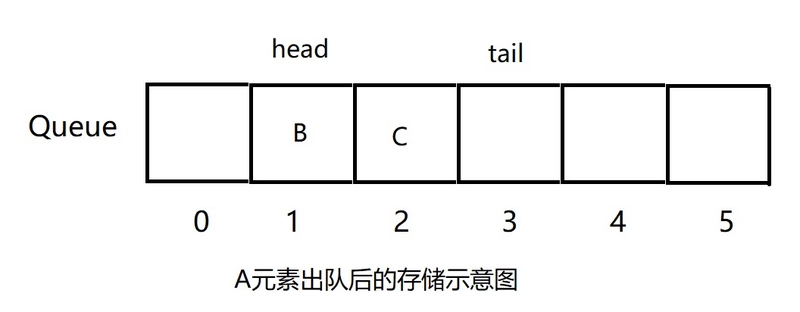
根据上面的图例,我们可以通过tail-head获得队列中元素的个数。当tail==head时,此时队列为空,而当tail等于数组长度时,此时将无法出入元素,那么队列是否已经满呢?
未必!因为head和tail在入队和出队操作中只增不减,因此head和tail都会最终指向队列之外的存储位置,此时虽然数组为空,但也无法将元素入队。
上溢: 当队列中无法插入元素时,称之为上溢;
假上溢: 在顺序队列中,数组还有空间(不一定全空)但无法入队称之为假上溢;
真上溢: 如果head为0,tail指向数组之外,即数组真满了,称之为真上溢;
下溢: 如果空队中执行出队操作,此时队列中无元素,称之为下溢
如何解决“假上溢”的问题呢?此时引入循环队列。出现假上溢时,此时数组还有空闲的位置,将tail从新指向数组的0索引处即可,如图所示:
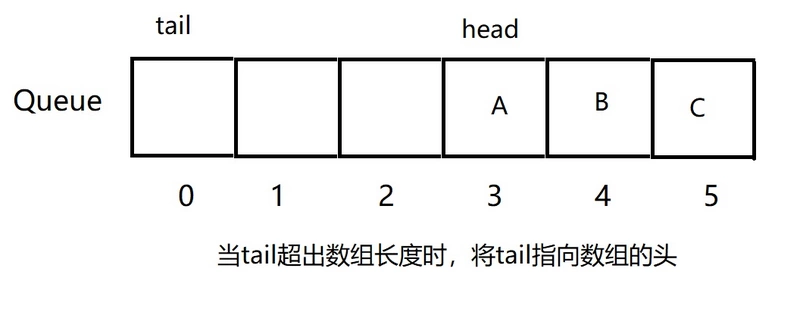
如果继续入队E和F,则队列的存储结构如图:
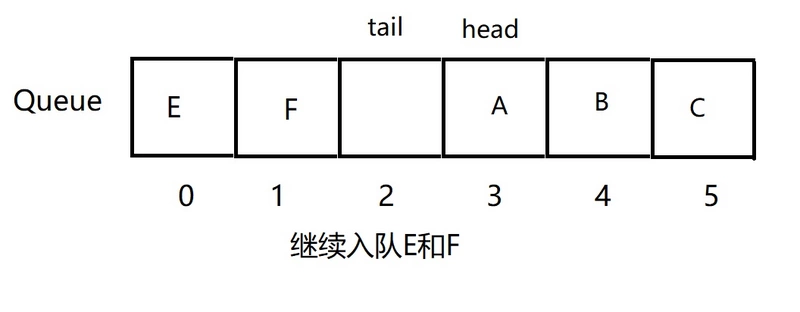
通常而言,在对head和tail加1时,为了方便采用对数组长度取余操作。另外由于顺序队列存在“假上溢”的现象,所以一般用循环队列实现。
在采用循环队列实现的过程中,当队列满队时,tail等于head,而当队列空时,tail也等于head,为了区分两种状态,一般规定循环队列的长度为数组长度-1,即有一个位置不放元素,此时head==tail时为空队,而当head==(tail+1)%数组长度,说明对满。
3 代码实现 (数组实现队列)

package com.differ.jackyun.examples.javabasisc.datastructure; import org.junit.Test; /** * 循环队列 * * @author hup * @data 2020-06-16 20:30 **/ public class ArrayQueue { /** * 数组 */ private String[] arr; /** * 队列头 */ int head; /** * 队列尾 */ int tail; public ArrayQueue() { arr = new String[5]; } /** * 入队 */ public boolean put(String data) { if (head == (tail + 1) % arr.length) { //说明队满 return false; } arr[tail] = data; tail = (tail + 1) % arr.length; return true; } /** * 出队 */ public String pull() { if (head == tail) { return null; } String result = arr[head]; arr[head] = null; head = (head + 1) % arr.length; return result; } /** * 获取队首元素,不出队 */ public String peek() { if (head == tail) { return null; } return arr[head]; } /** * 判断是否为空 * * @return */ public boolean isEmpty() { return head == tail; } /** * 判断是否为满 * * @return */ public boolean isFull() { return head == (tail + 1) % arr.length; } /** * 获取队列中的元素个数 * * @return */ public int getsize() { if (tail >= head) { return tail - head; } else { return (tail + arr.length) - head; } } }
测试

@Test public void test() { ArrayQueue myQueue = new ArrayQueue(); System.out.println("原始队列 head=" + myQueue.head + ",tail=" + myQueue.tail); //入队 System.out.println("入队A="+myQueue.put("A")); System.out.println("入队B="+myQueue.put("B")); System.out.println("入队C="+myQueue.put("C")); //出队 String pullResultA = myQueue.pull(); String pullResultB = myQueue.pull(); System.out.println("出队元素=" + pullResultA + pullResultB + ",head=" + myQueue.head + ",tail=" + myQueue.tail); //入队 System.out.println("入队D="+myQueue.put("D")); System.out.println("入队E="+myQueue.put("E")); System.out.println("head=" + myQueue.head + ",tail=" + myQueue.tail); } }
测试输出结果
 View Code
View Code4 代码实现(单向链表实现队列)

package com.differ.jackyun.examples.javabasisc.datastructure; import org.junit.Test; /** * 队列 * * @author hup * @data 2020-06-17 21:44 **/ public class ListQueue { /** * 头 * 用于出队 */ public Node head; /** * 尾 * 用于入队 */ public Node tail; /** * 队列长度 */ public int size; /** * 入队 */ public boolean put(int data) { Node nodeNew = new Node(data); if (head == null) { head = nodeNew; tail = head; size++; return true; } size++; tail.next = nodeNew; tail = tail.next; return true; } /** * 出队 */ public int pull() { //队列为空 if (head == tail) { return 0; } //只有头一个元素 if (head.next == null) { int reault = head.data; head.data = 0; size--; return reault; } //返回值 int reault = head.data; head.data = head.next.data; head.next = head.next.next; size--; return reault; } /** * 获取队首元素,不出队 */ public int peek() { //队列为空 if (head == null) { return 0; } return head.data; } /** * 判断是否为空 * * @return */ public boolean isEmpty() { return head == tail; } /** * 获取队列中的元素个数 * * @return */ public int getsize() { return size; } }
测试

@Test public void test() { ListQueue myQueue = new ListQueue(); System.out.println("原始队列 head=" + myQueue.head + ",tail=" + myQueue.tail); //入队 System.out.println("入队1=" + myQueue.put(1)); System.out.println("入队2=" + myQueue.put(2)); System.out.println("队列 head=" + myQueue.head + ",tail=" + myQueue.tail + ";队列中元素个数=" + myQueue.getsize()); System.out.println(); //出队 int pullResult1 = myQueue.pull(); System.out.println("出队元素=" + pullResult1 + ",head=" + myQueue.head + ",tail=" + myQueue.tail + ";队列中元素个数=" + myQueue.getsize()); System.out.println(); //入队 System.out.println("入队3=" + myQueue.put(3)); System.out.println("入队4=" + myQueue.put(4)); System.out.println("队列 head=" + myQueue.head + ",tail=" + myQueue.tail + ";队列中元素个数=" + myQueue.getsize()); }
测试输出结果

原始队列 head=null,tail=null 入队1=true 入队2=true 队列 head=Node{next=Node{next=null, data=2}, data=1},tail=Node{next=null, data=2};队列中元素个数=2 出队元素=1,head=Node{next=null, data=2},tail=Node{next=null, data=2};队列中元素个数=1 入队3=true 入队4=true 队列 head=Node{next=null, data=2},tail=Node{next=null, data=4};队列中元素个数=3
可以看到,队列生效
5 队列的应用场景
队列先入先出的特点,使得其应用非常广泛,比如队列作为“缓冲区”,可以解决计算机和外设速度不匹配的问题,FIFO的特点保证了数据传输的顺序;
除此之外队列在后面树的层序遍历中也有应用,FIFO的特点保证了处理顺序不会出错。
