The most universal layout class is the grid layout. This layout divides the space into rows and columns. To create a grid layout, we use the QtGui.QGridLayout class.
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui
"""
ZetCode PyQt4 tutorial
In this example, we create a skeleton
of a calculator using a QtGui.QGridLayout.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
last edited: July 2014
"""
class Example(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
grid = QtGui.QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(grid)
names = ['Cls', 'Bck', '', 'Close',
'7', '8', '9', '/',
'4', '5', '6', '*',
'1', '2', '3', '-',
'0', '.', '=', '+']
positions = [(i,j) for i in range(5) for j in range(4)]
for position, name in zip(positions, names):
if name == '':
continue
button = QtGui.QPushButton(name)
grid.addWidget(button, *position)
self.move(300, 150)
self.setWindowTitle('Calculator')
self.show()
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
In our example, we create a grid of buttons. To fill one gap, we add one QtGui.QLabel widget.
grid = QtGui.QGridLayout() self.setLayout(grid)
The instance of a QtGui.QGridLayout is created and set to be the layout for the application window.
names = ['Cls', 'Bck', '', 'Close',
'7', '8', '9', '/',
'4', '5', '6', '*',
'1', '2', '3', '-',
'0', '.', '=', '+']
These are the labels used later for buttons.
positions = [(i,j) for i in range(5) for j in range(4)]
We create a list of positions in the grid.
for position, name in zip(positions, names):
if name == '':
continue
button = QtGui.QPushButton(name)
grid.addWidget(button, *position)
Buttons are created and added to the layout with the addWidget() method.
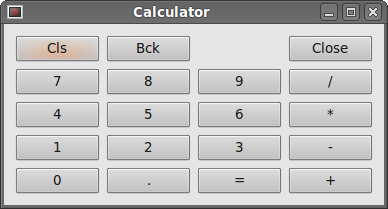 Figure: Calculator skeleton
Figure: Calculator skeleton