2019-10-05 23:40:13
一、定义
割点:去掉一个顶点及其相邻的边,图的连通分量增加。
割边:去掉一条边,图的连通分量增加。
两者关系
- 有割点不一定有割边,有割边一定存在割点
- 割边一定是割点依附的边
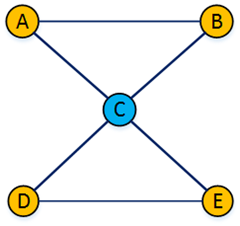
如下图,点C是割点,但是图中不存在割边。
二、Tarjan算法
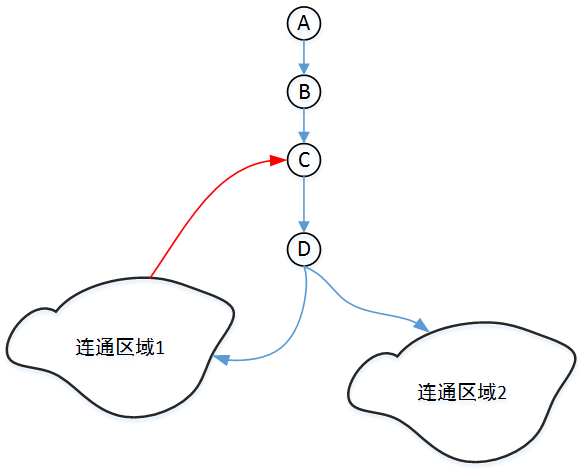
使用Tarjan算法可以在一次dfs里得到所有的割边。
- 为所有节点按照dfs遍历顺序打上时间戳
- 为所有节点记录非父节点能到达的最小的时间戳(包括自己)
- 如果一个节点不通过父节点可以通向比父节点时间戳更小的节点,那么父节点必不是割点
- 如果一个节点的子节点能到达的最小的时间戳比自己小,那么这两点可以构成割边
三、例题
- Critical Connections in a Network
问题描述:
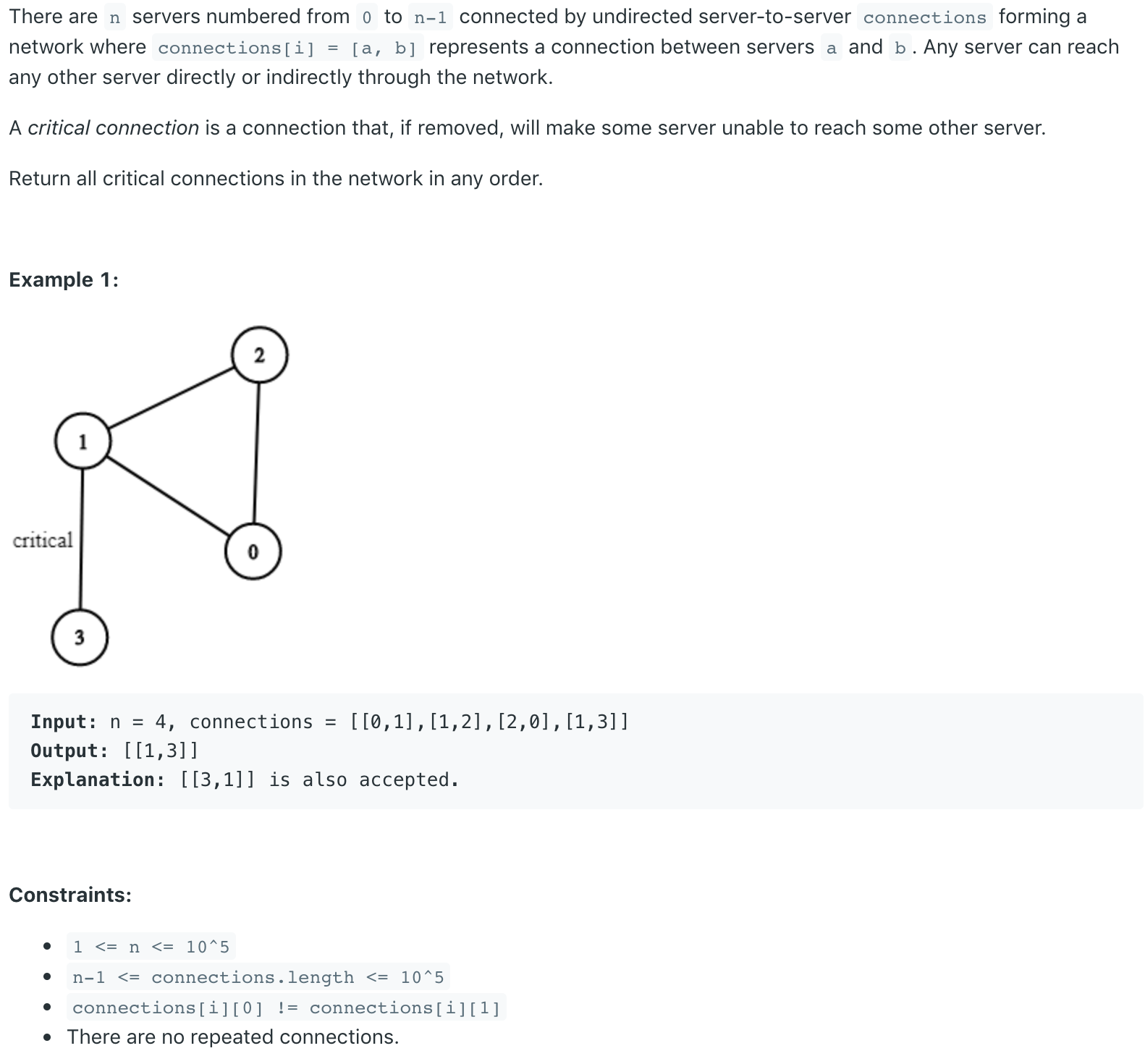
问题求解:
Tarjan算法,可以在O(n + e)的时间复杂度求解。
int time = 0;
public List<List<Integer>> criticalConnections(int n, List<List<Integer>> connections) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
int[] ts = new int[n];
int[] lo = new int[n];
List<Integer>[] graph = new List[n];
Arrays.fill(ts, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for (List<Integer> con : connections) {
graph[con.get(0)].add(con.get(1));
graph[con.get(1)].add(con.get(0));
}
dfs(graph, 0, -1, ts, lo, res);
return res;
}
private void dfs(List<Integer>[] graph, int node, int prev, int[] ts, int[] lo, List<List<Integer>> res) {
ts[node] = time;
lo[node] = time;
time = time + 1;
for (int next : graph[node]) {
if (next == prev) continue;
if (ts[next] == -1) {
dfs(graph, next, node, ts, lo, res);
if (lo[next] > ts[node]) res.add(Arrays.asList(node, next));
}
lo[node] = Math.min(lo[node], lo[next]);
}
}