1序列化流与反序列化流
用于从流中读取对象的操作流 ObjectInputStream 称为 反序列化流
用于向流中写入对象的操作流 ObjectOutputStream 称为 序列化流
特点:用于操作对象。可以将对象写入到文件中,也可以从文件中读取对象。
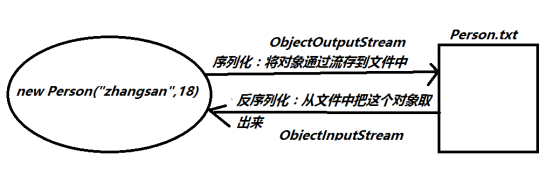
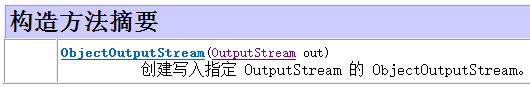
1.1对象序列化流ObjectOutputStream
例:
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Person implements Serializable{
private String name;
private int age;
public Person() {
super();
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
method01();
}
// 序列化
public static void method01() throws IOException {
Person p = new Person("zhangsan", 18);
// 明确目的地
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("E:\zyx\java\Person.txt");
// 创建序列化流
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos); // 会自动关闭fos
// 向文件中写入对象
oos.writeObject(p);
oos.close();
}
}
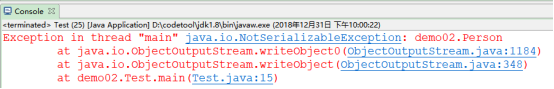
1.2序列化接口
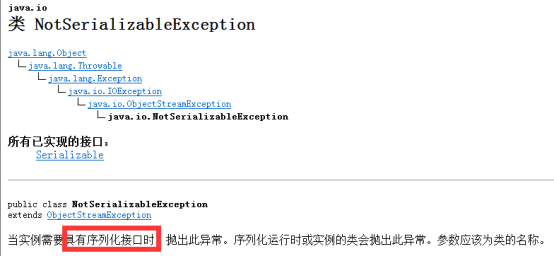
如果类都可以序列化,不安全。所以必须实现接口,才允许序列化:
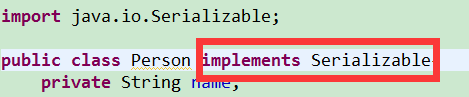
标记型接口,没有方法,不用重写,没有实际意义。
加上后再运行:

1.3对象反序列化流ObjectInputStream
例:
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
method02();
}
// 序列化
public static void method01() throws IOException {
Person p = new Person("zhangsan", 18);
// 明确目的地
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("E:\zyx\java\Person.txt");
// 创建序列化流
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos); // 会自动关闭fos
// 向文件中写入对象
oos.writeObject(p);
oos.close();
}
// 反序列化
public static void method02() throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException {
// 明确数据源
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("E:\zyx\java\Person.txt");
// 创建反序列化流
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
Object obj = ois.readObject();
Person p = (Person) obj; // 强转
System.out.println(p);
ois.close();
}
}
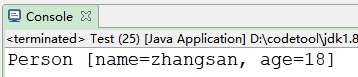
说明:
1)readObject();返回值类型是Object
所以用Object接收,再强转
2)ClassNotFoundException这个异常
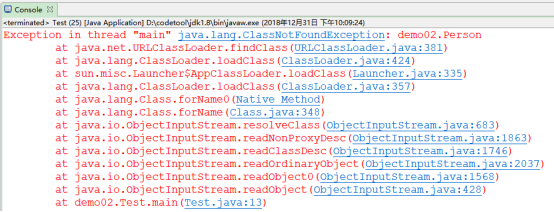
如果bin中的Person.class丢失,那么就会报这个异常

如果把age加上static
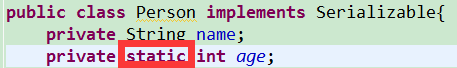
执行method01(),再执行method02(),

这说明序列化和反序列化的只是对象,静态后的属性因为不属于对象了,所以不会被序列化。
还可以加上瞬态关键字transient
1.4瞬态关键字transient

执行method01(),再执行method02(),
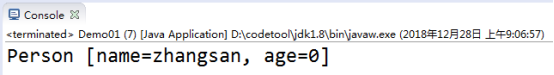
1.5序列版本号
把Person任意改一下,直接反序列化:
结果为:序列化冲突异常
图说明:
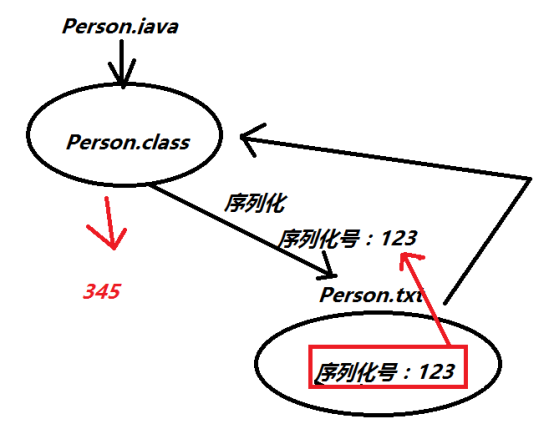
所以序列化后不要再改动Person了。
解决办法:给Person加一个序列化号:(可以直接点出来)
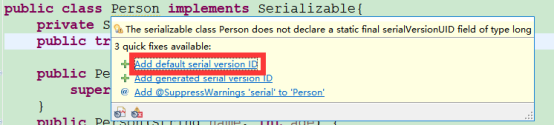
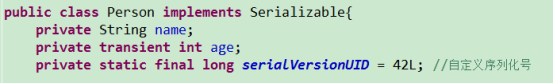
这个long值可以任意改,
加上后,再序列化,然后修改Person,再反序列化,就不会报异常了。
2打印流
只是输出流
根据流的分类:
字节打印流 PrintStream
字符打印流 PrintWriter
方法:
void print(String str): 输出任意类型的数据,
void println(String str): 输出任意类型的数据,自动写入换行操作
可以用write方法,但是走码表,而这两个是原样输出
2.1PrintStream
例:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
PrintStream ps=new PrintStream("E:\zyx\java\print.txt");
ps.print(100);
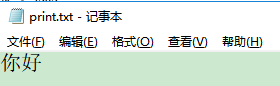
ps.println("你好");
ps.println("换行");
ps.write(100);
ps.close();
}
}
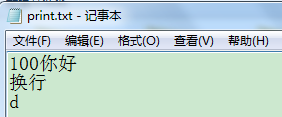
说明:
print()原样输出
println()可以换行
write()走码表
2.2续写
传一个FileOutputStream对象:
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("E:\zyx\java\print.txt",true);
PrintStream ps=new PrintStream(fos);
ps.print(100);
ps.println("你好");
ps.println("换行");
ps.write(100);
ps.close();
}
}

2.3 PrintWriter
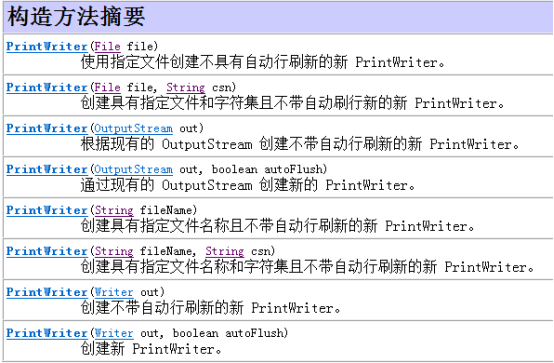
例:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter("E:\zyx\java\print.txt");
pw.println("你好");
pw.println("java");
pw.flush();
pw.close();
}
}
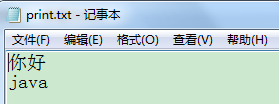
2.4自动刷新
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 字节输出流明确目的地
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("E:\zyx\java\print.txt");
// 创建自动刷新的字符打印流
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(fos, true);
pw.println("你好");
pw.println("java");
pw.close();
}
}
2.5复制
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class CopyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
copy();
}
public static void copy() throws IOException{
//明确数据源
FileReader fr=new FileReader("E:\zyx\java\print.txt");
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(fr);
//明确目的地
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("E:\zyx\java\a\print.txt");
PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(fw,true); //自动刷新
String line="";
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
pw.println(line);
}
br.close();
pw.close();
}
}
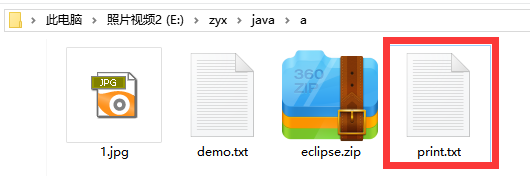
用打印流复制不用刷新和换行了
打印流总结:
1)只有输出目的地
2)不会抛IO异常
3 工具类commons-IO
3.1导入classpath
加入classpath的第三方jar包内的class文件才能在项目中使用
创建lib文件夹
将commons-io.jar拷贝到lib文件夹
右键点击commons-io.jar,Build Path→Add to Build Path
3.2 FilenameUtils
用来处理文件名的,可以轻松解决不同操作系统文件名称规范不同的问题
常用方法:
1)getExtension(String path):获取文件的扩展名;
2)getName(String filename):获取文件名;
3)isExtension(String fileName,String ext):判断fileName是否是ext后缀名;
例:
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.commons.io.FilenameUtils;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 获取文件扩展名
String ext = FilenameUtils.getExtension("E:\zyx\java\demo.txt");
System.out.println(ext);
// 获取文件名
String filename = FilenameUtils.getName("E:\zyx\java\demo.txt");
System.out.println(filename);
// 判断是否是java文件
boolean flag = FilenameUtils.isExtension("E:\zyx\java\demo.txt", "java");
System.out.println(flag);
}
}

3.3 FileUtils
常用方法:
1)readFileToString(File file):读取文件内容,并返回一个String;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
File file=new File("E:\zyx\java\print.txt");
String content=FileUtils.readFileToString(file);
System.out.println(content);
}
}

2)writeStringToFile(File file,String content):将内容content写入到file中;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
File file=new File("E:\zyx\java\print.txt");
FileUtils.writeStringToFile(file, "你好");
}
}
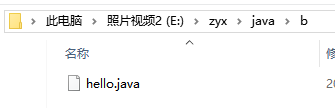
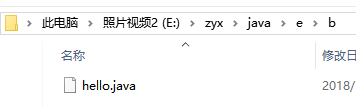
3)copyDirectoryToDirectory(File srcDir,File destDir); 文件夹复制
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 数据源
File file = new File("E:\zyx\java\b");
// 目的地
File file2 = new File("E:\zyx\java\e");
// 复制
FileUtils.copyDirectoryToDirectory(file, file2);
}
}
4)copyFile(File srcFile,File destFile); 文件复制
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 数据源
File file = new File("E:\zyx\java\eclipse.zip");
// 目的地
File file2 = new File("E:\zyx\java\f\eclipse.zip");
// 复制
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
FileUtils.copyFile(file, file2);
long end=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end-start);
}
}

练习:用常规方法复制文件夹(及文件)