ServiceBean的afterPropertiesSet方法是实现了InitializingBean,还是准备先做宏观分析,然后再做细致分析。下面先宏观分析:
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
if (getProvider() == null) {
..............
//获取provider配置
} if (getApplication() == null && (getProvider() == null || getProvider().getApplication() == null)) { ...............
//获取application配置
} if (getModule() == null && (getProvider() == null || getProvider().getModule() == null)) { ...............
//获取module配置
} if ((getRegistries() == null || getRegistries().size() == 0) && (getProvider() == null || getProvider().getRegistries() == null || getProvider().getRegistries().size() == 0) && (getApplication() == null || getApplication().getRegistries() == null || getApplication().getRegistries().size() == 0)) { .................
//获取注册中心的配置
} if (getMonitor() == null && (getProvider() == null || getProvider().getMonitor() == null) && (getApplication() == null || getApplication().getMonitor() == null)) {
................ //获取monitor配置
} if ((getProtocols() == null || getProtocols().size() == 0) && (getProvider() == null || getProvider().getProtocols() == null || getProvider().getProtocols().size() == 0)) { ...............
//获取protocol配置
} if (getPath() == null || getPath().length() == 0) { //获取<dubbo:service/>的path属性,path即服务的发布路径 if (beanName != null && beanName.length() > 0 && getInterface() != null && getInterface().length() > 0 && beanName.startsWith(getInterface())) { setPath(beanName); //如果没有设置path属性,则默认会以beanName作为path } } if (! isDelay()) { //是否延迟暴露 export(); //进行服务暴露 } }
通过上面的分析对整个方法在做什么有了大致的了解, 下面进行细致分析,对里面的一段段代码分别展开分析:
1 . 获取Provider配置
//当某个<dubbo:service/>没有绑定相应的<dubbo:provider/>的时候,就会触发下面的逻辑
if (getProvider() == null) {
//在spring的IOC容器中查找所有的type为ProviderConfig.class或其子类的bean,可能会有多个provider的配置
Map<String, ProviderConfig> providerConfigMap = applicationContext == null ? null : BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, ProviderConfig.class, false, false);
if (providerConfigMap != null && providerConfigMap.size() > 0) {
//在spring的IOC容器中查找type为ProtocolConfig.class或其子类的bean
Map<String, ProtocolConfig> protocolConfigMap = applicationContext == null ? null : BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, ProtocolConfig.class, false, false);
//存在<dubbo:provider/>但不存在<dubbo:protocol/>配置的情况,也就是说旧版本的protocol配置需要从provider中提取
if ((protocolConfigMap == null || protocolConfigMap.size() == 0)&& providerConfigMap.size() > 1) { // 兼容旧版本
List<ProviderConfig> providerConfigs = new ArrayList<ProviderConfig>();
for (ProviderConfig config : providerConfigMap.values()) {
if (config.isDefault() != null && config.isDefault().booleanValue()) {
providerConfigs.add(config); // 当<dubbo:provider default="true"/>时,providerConfigs才会加入
}
}
//在配置provider的同时,也从默认的<dubbo:provider/>中提取protocol的配置
if (providerConfigs.size() > 0) {
setProviders(providerConfigs);
}
} else { //已存在<dubbo:protocol/>配置,则找出默认的<dubbo:provider/>配置
ProviderConfig providerConfig = null; for (ProviderConfig config : providerConfigMap.values()) { if (config.isDefault() == null || config.isDefault().booleanValue()) { if (providerConfig != null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate provider configs: " + providerConfig + " and " + config); } providerConfig = config; } } if (providerConfig != null) { setProvider(providerConfig); } } } }
在这里补充一下什么是默认的<dubbo:provider/>,在dubbo配置文件中,可以有多个<dubbo:provider/>配置,如果某个<dubbo:provide/>配置的default属性为true。这个默认配置只能一个。
2.获取application配置
这个相对比较容易,只是说明几点,用户可以通过<dubbo:application/>的形式来配置application,也可以直接以bean的形式去配,这个bean对应的Class就是ApplicationConfig.class
if (getApplication() == null && (getProvider() == null || getProvider().getApplication() == null)) { Map<String, ApplicationConfig> applicationConfigMap = applicationContext == null ? null : BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, ApplicationConfig.class, false, false); if (applicationConfigMap != null && applicationConfigMap.size() > 0) { ApplicationConfig applicationConfig = null; for (ApplicationConfig config : applicationConfigMap.values()) { if (config.isDefault() == null || config.isDefault().booleanValue()) { if (applicationConfig != null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate application configs: " + applicationConfig + " and " + config); } applicationConfig = config; } } if (applicationConfig != null) { setApplication(applicationConfig); } } }
3. 获取Module,同上
4. 获取Registries,同上
5. 获取Monitor , 同上
6. 获取Protocols ,同上
7. 获取path(服务路径)
if (getPath() == null || getPath().length() == 0) { if (beanName != null && beanName.length() > 0 && getInterface() != null && getInterface().length() > 0 && beanName.startsWith(getInterface())) { setPath(beanName); } }
上面代码说明如果<dubbo:service/>没有配path属性,dubbo将会设置一个默认的path属性,默认值就是beanName,而beanName是ServiceBean实现了BeanNameAware接口,由spring的IOC容器传入进来的。通过上文对dubbo配置的解析的源码分析可知,一般情况这个path属性就是服务接口的类的全路径名。
8. 判断该服务是否延迟发布
if (! isDelay()) {
export(); //服务暴露的方法
}
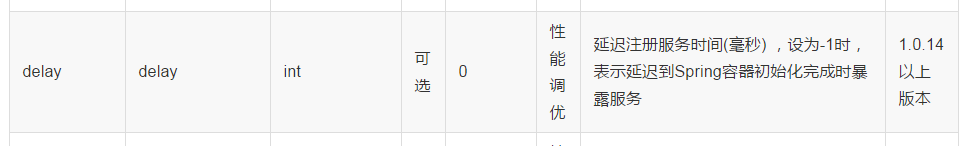
<dubbo:service/>上会有一个delay的配置属性(官方的说明:)
private boolean isDelay() { Integer delay = getDelay(); ProviderConfig provider = getProvider(); if (delay == null && provider != null) { delay = provider.getDelay(); } return supportedApplicationListener && (delay == null || delay.intValue() == -1); }
上面为判断该服务是否延迟的方法的源码,说明如果<dubbo:service/>没有配delay属性或将其配置为-1都会延迟发布服务,而这个supportedApplicationListener属性在ServiceBean实现ApplicationContextAware接口的setApplicationContext方法中设置为true的。
下面再看一下setApplicationContext方法的源码,主要作用是为了兼容Spring2.0.1的版本,为了向前兼容spring的事件机制
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) { this.applicationContext = applicationContext; SpringExtensionFactory.addApplicationContext(applicationContext); if (applicationContext != null) { SPRING_CONTEXT = applicationContext; try { Method method = applicationContext.getClass().getMethod("addApplicationListener", new Class<?>[]{ApplicationListener.class}); // 兼容Spring2.0.1 method.invoke(applicationContext, new Object[] {this}); supportedApplicationListener = true; } catch (Throwable t) { if (applicationContext instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) { try { Method method = AbstractApplicationContext.class.getDeclaredMethod("addListener", new Class<?>[]{ApplicationListener.class}); // 兼容Spring2.0.1 if (! method.isAccessible()) { method.setAccessible(true); } method.invoke(applicationContext, new Object[] {this}); supportedApplicationListener = true; } catch (Throwable t2) { } } } } }
根据这个源码可知,通常我们的dubbo服务的配置:<dubbo:service interface="com.xxx.Yxxx" ref="userService" protocol="dubbo" retries="0" /> ,在这样的情况下 isDelay()方法返回true,所以我们的暴露将会发生在下面的方法中
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { if (ContextRefreshedEvent.class.getName().equals(event.getClass().getName())) { if (isDelay() && ! isExported() && ! isUnexported()) { if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("The service ready on spring started. service: " + getInterface()); } export(); } } }
至此,这个初始化的方法就分析完了。下文将开始分析 处理服务暴露的方法(export()方法)。