一、数据扩增
接下来将介绍常用的6类数据扩增方式,包括裁剪、平移、改变亮度、加入噪声、旋转角度以及镜像。
1、裁剪(需要改变bbox):裁剪后的图片需要包含所有的框,否则会对图像的原始标注造成破坏。

def _crop_img_bboxes(self,img,bboxes): ''' 裁剪后图片要包含所有的框 输入: img:图像array bboxes:该图像包含的所有boundingboxes,一个list,每个元素为[x_min,y_min,x_max,y_max] 要确保是数值 输出: crop_img:裁剪后的图像array crop_bboxes:裁剪后的boundingbox的坐标,list ''' #------------------ 裁剪图像 ------------------ w = img.shape[1] h = img.shape[0] x_min = w x_max = 0 y_min = h y_max = 0 for bbox in bboxes: x_min = min(x_min, bbox[0]) y_min = min(y_min, bbox[1]) x_max = max(x_max, bbox[2]) y_max = max(y_max, bbox[3]) name = bbox[4] # 包含所有目标框的最小框到各个边的距离 d_to_left = x_min d_to_right = w - x_max d_to_top = y_min d_to_bottom = h - y_max # 随机扩展这个最小范围 crop_x_min = int(x_min - random.uniform(0, d_to_left)) crop_y_min = int(y_min - random.uniform(0, d_to_top)) crop_x_max = int(x_max + random.uniform(0, d_to_right)) crop_y_max = int(y_max + random.uniform(0, d_to_bottom)) # 确保不出界 crop_x_min = max(0, crop_x_min) crop_y_min = max(0, crop_y_min) crop_x_max = min(w, crop_x_max) crop_y_max = min(h, crop_y_max) crop_img = img[crop_y_min:crop_y_max, crop_x_min:crop_x_max] #------------------ 裁剪bounding boxes ------------------ crop_bboxes = list() for bbox in bboxes: crop_bboxes.append([bbox[0]-crop_x_min, bbox[1]-crop_y_min, bbox[2]-crop_x_min, bbox[3]-crop_y_min,name]) return crop_img, crop_bboxes
2、平移(需要改变bbox):平移后的图片需要包含所有的框,否则会对图像的原始标注造成破坏。

def _shift_pic_bboxes(self, img, bboxes): ''' 平移后需要包含所有的框 参考资料:https://blog.csdn.net/sty945/article/details/79387054 输入: img:图像array bboxes:该图像包含的所有boundingboxes,一个list,每个元素为[x_min,y_min,x_max,y_max] 要确保是数值 输出: shift_img:平移后的图像array shift_bboxes:平移后的boundingbox的坐标,list ''' #------------------ 平移图像 ------------------ w = img.shape[1] h = img.shape[0] x_min = w x_max = 0 y_min = h y_max = 0 for bbox in bboxes: x_min = min(x_min, bbox[0]) y_min = min(y_min, bbox[1]) x_max = max(x_max, bbox[2]) y_max = max(x_max, bbox[3]) name = bbox[4] # 包含所有目标框的最小框到各个边的距离,即每个方向的最大移动距离 d_to_left = x_min d_to_right = w - x_max d_to_top = y_min d_to_bottom = h - y_max #在矩阵第一行中表示的是[1,0,x],其中x表示图像将向左或向右移动的距离,如果x是正值,则表示向右移动,如果是负值的话,则表示向左移动。 #在矩阵第二行表示的是[0,1,y],其中y表示图像将向上或向下移动的距离,如果y是正值的话,则向下移动,如果是负值的话,则向上移动。 x = random.uniform(-(d_to_left/3), d_to_right/3) y = random.uniform(-(d_to_top/3), d_to_bottom/3) M = np.float32([[1, 0, x], [0, 1, y]]) # 仿射变换 shift_img = cv2.warpAffine(img, M, (img.shape[1], img.shape[0])) #第一个参数表示我们希望进行变换的图片,第二个参数是我们的平移矩阵,第三个希望展示的结果图片的大小 #------------------ 平移boundingbox ------------------ shift_bboxes = list() for bbox in bboxes: shift_bboxes.append([bbox[0]+x, bbox[1]+y, bbox[2]+x, bbox[3]+y, name]) return shift_img, shift_bboxes
3、改变亮度:改变亮度比较简单,不需要处理bounding boxes

def _changeLight(self,img): ''' adjust_gamma(image, gamma=1, gain=1)函数: gamma>1时,输出图像变暗,小于1时,输出图像变亮 输入: img:图像array 输出: img:改变亮度后的图像array ''' flag = random.uniform(0.5, 1.5) ##flag>1为调暗,小于1为调亮 return exposure.adjust_gamma(img, flag)
4、加入噪声:加入噪声也比较简单,不需要处理bounding boxes

def _addNoise(self,img): ''' 输入: img:图像array 输出: img:加入噪声后的图像array,由于输出的像素是在[0,1]之间,所以得乘以255 ''' return random_noise(img, mode='gaussian', clip=True) * 255
5、旋转:旋转后的图片需要包含所有的框,否则会对图像的原始标注造成破坏。需要注意的是,旋转时图像的一些边角可能会被切除掉,需要避免这种情况。

def _rotate_img_bboxes(self, img, bboxes, angle=5, scale=1.): ''' 参考:https://blog.csdn.net/saltriver/article/details/79680189 https://www.ctolib.com/topics-44419.html 关于仿射变换:https://www.zhihu.com/question/20666664 输入: img:图像array,(h,w,c) bboxes:该图像包含的所有boundingboxs,一个list,每个元素为[x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max],要确保是数值 angle:旋转角度 scale:默认1 输出: rot_img:旋转后的图像array rot_bboxes:旋转后的boundingbox坐标list ''' #---------------------- 旋转图像 ---------------------- w = img.shape[1] h = img.shape[0] # 角度变弧度 rangle = np.deg2rad(angle) # 计算新图像的宽度和高度,分别为最高点和最低点的垂直距离 nw = (abs(np.sin(rangle)*h) + abs(np.cos(rangle)*w))*scale nh = (abs(np.cos(rangle)*h) + abs(np.sin(rangle)*w))*scale # 获取图像绕着某一点的旋转矩阵 # getRotationMatrix2D(Point2f center, double angle, double scale) # Point2f center:表示旋转的中心点 # double angle:表示旋转的角度 # double scale:图像缩放因子 #参考:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1425373 rot_mat = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((nw*0.5, nh*0.5), angle, scale) # 返回 2x3 矩阵 # 新中心点与旧中心点之间的位置 rot_move = np.dot(rot_mat,np.array([(nw-w)*0.5, (nh-h)*0.5,0])) # the move only affects the translation, so update the translation # part of the transform rot_mat[0,2] += rot_move[0] rot_mat[1,2] += rot_move[1] # 仿射变换 rot_img = cv2.warpAffine(img, rot_mat, (int(math.ceil(nw)), int(math.ceil(nh))), flags=cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4) # ceil向上取整 #---------------------- 矫正boundingbox ---------------------- # rot_mat是最终的旋转矩阵 # 获取原始bbox的四个中点,然后将这四个点转换到旋转后的坐标系下 rot_bboxes = list() for bbox in bboxes: x_min = bbox[0] y_min = bbox[1] x_max = bbox[2] y_max = bbox[3] name = bbox[4] point1 = np.dot(rot_mat, np.array([(x_min+x_max)/2, y_min,1])) point2 = np.dot(rot_mat, np.array([x_max, (y_min+y_max)/2, 1])) point3 = np.dot(rot_mat, np.array([(x_min+x_max)/2, y_max, 1])) point4 = np.dot(rot_mat, np.array([x_min, (y_min+y_max)/2, 1])) # 合并np.array concat = np.vstack((point1, point2,point3,point4)) # 在竖直方向上堆叠 # 改变array类型 concat = concat.astype(np.int32) # 得到旋转后的坐标 rx, ry, rw, rh = cv2.boundingRect(concat) rx_min = rx ry_min = ry rx_max = rx+rw ry_max = ry+rh # 加入list中 rot_bboxes.append([rx_min, ry_min, rx_max, ry_max,name]) return rot_img, rot_bboxes
6、镜像:旋转后的图片需要包含所有的框,否则会对图像的原始标注造成破坏。这里只介绍两种镜像方式:水平翻转和垂直翻转

# 镜像 def _flip_pic_bboxes(self, img, bboxes): ''' 参考:https://blog.csdn.net/jningwei/article/details/78753607 镜像后的图片要包含所有的框 输入: img:图像array bboxes:该图像包含的所有boundingboxs,一个list,每个元素为[x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max],要确保是数值 输出: flip_img:镜像后的图像array flip_bboxes:镜像后的bounding box的坐标list ''' # ---------------------- 镜像图像 ---------------------- import copy flip_img = copy.deepcopy(img) if random.random() < 0.5: horizon = True else: horizon = False h, w, _ = img.shape if horizon: # 水平翻转 flip_img = cv2.flip(flip_img, -1) else: flip_img = cv2.flip(flip_img, 0) # ---------------------- 矫正boundingbox ---------------------- flip_bboxes = list() for bbox in bboxes: x_min = bbox[0] y_min = bbox[1] x_max = bbox[2] y_max = bbox[3] name = bbox[4] if horizon: flip_bboxes.append([w-x_max, y_min, w-x_min, y_max, name]) else: flip_bboxes.append([x_min, h-y_max, x_max, h-y_min, name]) return flip_img, flip_bboxes
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/lky-learning/p/11653861.html
二、early stopping
早停法是一种被广泛使用的方法,在很多案例上都比正则化的方法要好。是在训练中计算模型在验证集上的表现,当模型在验证集上的表现开始下降的时候,停止训练,这样就能避免继续训练导致过拟合的问题。其主要步骤如下:
- 将原始的训练数据集划分成训练集和验证集
- 只在训练集上进行训练,并每隔一个周期计算模型在验证集上的误差
- 当模型在验证集上(权重的更新低于某个阈值;预测的错误率低于某个阈值;达到一定的迭代次数),则停止训练
- 使用上一次迭代结果中的参数作为模型的最终参数
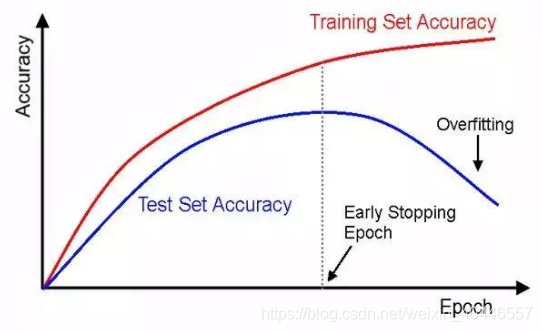 如图之后的某个epoch,模型的验证误差逐渐上升,模型出现过拟合,所以需要提前停止训练,早停法主要是训练时间和泛化错误之间的权衡。不同的停止标准也是给我们带来不同的效果。
如图之后的某个epoch,模型的验证误差逐渐上升,模型出现过拟合,所以需要提前停止训练,早停法主要是训练时间和泛化错误之间的权衡。不同的停止标准也是给我们带来不同的效果。
代码如下:

#使用Early Stopping训练模型 def train_model(model, batch_size, patience, n_epochs): # 在模型训练时跟踪训练损失 train_losses = [] # 在模型训练时跟踪验证损失 valid_losses = [] # 跟踪模型训练时每个历元的平均训练损失 avg_train_losses = [] # to track the average validation loss per epoch as the model trains avg_valid_losses = [] # initialize the early_stopping object early_stopping = EarlyStopping(patience=patience, verbose=True) for epoch in range(1, n_epochs + 1): ################### # train the model # ################### model.train() # prep model for training for batch, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader, 1): # clear the gradients of all optimized variables optimizer.zero_grad() # forward pass: compute predicted outputs by passing inputs to the model output = model(data) # calculate the loss loss = criterion(output, target) # backward pass: compute gradient of the loss with respect to model parameters loss.backward() # perform a single optimization step (parameter update) optimizer.step() # record training loss train_losses.append(loss.item()) ###################### # validate the model # ###################### model.eval() # prep model for evaluation for data, target in valid_loader: # forward pass: compute predicted outputs by passing inputs to the model output = model(data) # calculate the loss loss = criterion(output, target) # record validation loss valid_losses.append(loss.item()) # print training/validation statistics # calculate average loss over an epoch train_loss = np.average(train_losses) valid_loss = np.average(valid_losses) avg_train_losses.append(train_loss) avg_valid_losses.append(valid_loss) epoch_len = len(str(n_epochs)) print_msg = (f'[{epoch:>{epoch_len}}/{n_epochs:>{epoch_len}}] ' + f'train_loss: {train_loss:.5f} ' + f'valid_loss: {valid_loss:.5f}') print(print_msg) # clear lists to track next epoch train_losses = [] valid_losses = [] # early_stopping needs the validation loss to check if it has decresed, # and if it has, it will make a checkpoint of the current model early_stopping(valid_loss, model) if early_stopping.early_stop: print("Early stopping") break # load the last checkpoint with the best model model.load_state_dict(torch.load('checkpoint.pt')) return model, avg_train_losses, avg_valid_losses
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40446557/article/details/103387629
