前言
在Java中我们最常用的集合类毫无疑问就是Map,其中HashMap作为Map最重要的实现类在我们代码中出现的评率也是很高的。
我们对HashMap最常用的操作就是put和get了,那么你知道它是怎么实现的吗?知道HashMap的底层原理吗?你知道从jdk7到jdk8,HashMap发生了什么变化吗?
那么我们就带着这些疑问,一起来探秘HashMap。
首先声明本文这次讲的HashMap基于Jdk1.7.0_79,不同版本略有差异。Jdk1.8版本的日后讨论。
1. HashMap的数据结构
我们先从HashMap的数据结构谈起,先了解它的数据结构存储结构,后面看它的代码实现就容易多了。
HashMap底层数据结构是由数组和链表来实现对数据的存储,但数组和链表基本上是两个极端。为什么这么说咱们继续往下看。
数组
数组的存储空间是连续的,占用内存严重,即使是空的也要分配内存,故空间复杂度很大。但数组的二分查找时间复杂度小,为O(1);
数组的特点是:寻址容易,插入和删除困难;
链表
链表的存储空间是可以离散的,占用内存比较宽松,可以动态增加链表长度,故空间复杂度很小,但由于它是不连续的,查找插入删除操作会很麻烦,故时间复杂度很大,为O(N);
链表的特点是:寻址困难,插入和删除容易。
哈希表
那么我们能不能综合两者的优点,设计出一种寻址容易,插入删除也容易的数据结构?答案是肯定的,这就是我们要讲的哈希表。
哈希表((Hash table)既满足了数据的查找方便,同时不占用太多的内容空间,使用也十分方便。
哈希表有多种不同的实现方式,接下来我们探讨的是最常用的一种实现方式--拉链法,我们可以理解为“链表的数组” ,如图:
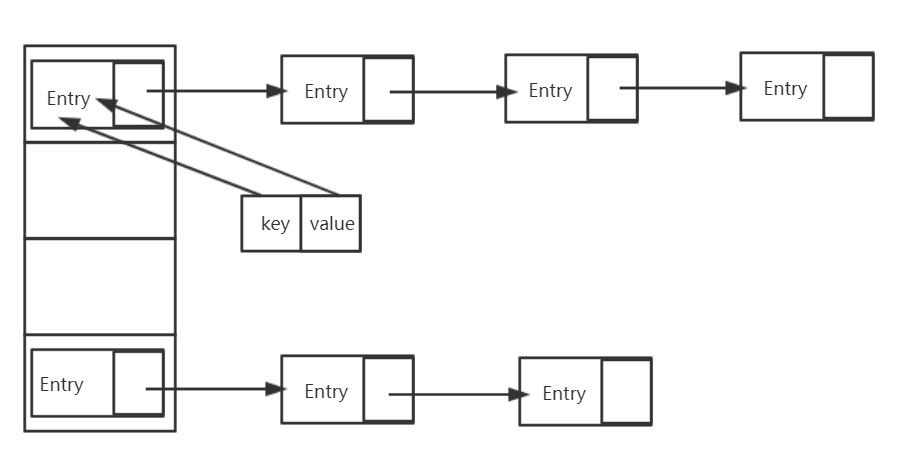
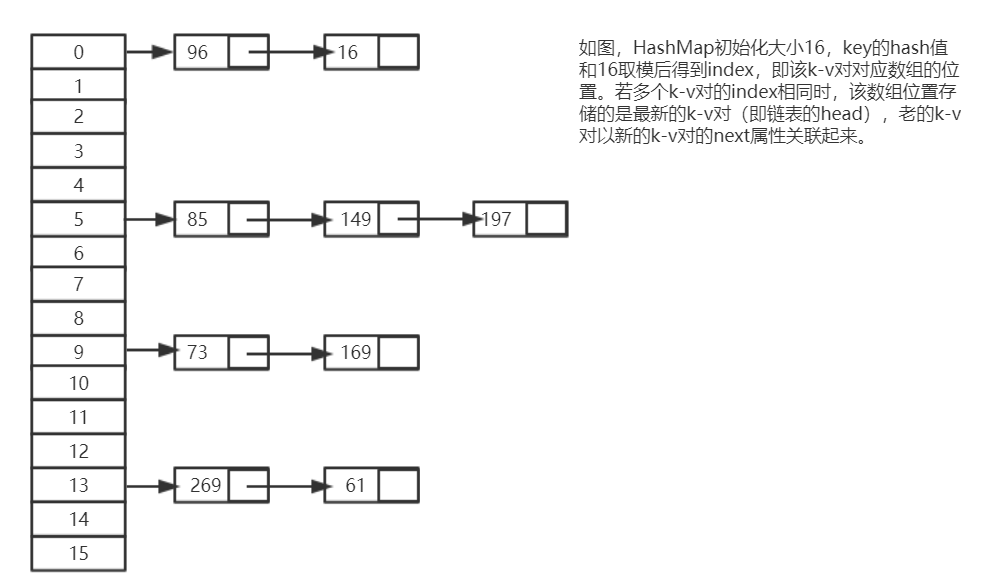
从上图我们可以发现哈希表是由数组+链表组成的,在一个长度为16的数组中,每个元素存储的是一个链表的头结点。
那么这些元素是按照什么样的规则存储到数组中呢?
一般情况是通过hash(key)%len获得,也就是计算出元素的key的哈希值,然后用哈希值对数组长度取模得到的即为该元素存储到数组中的index。
比如上述哈希表中,85%16=5,149%16=5,197%16=5。
所以hash值为85、149、197的k-v对都存储在数组下标为5的位置。
HashMap底层数据结构的原理就是使用的上述的哈希表,HashMap其实也是一个线性的数组实现的,所以可以理解为其存储数据的容器就是一个线性数组。
这可能让我们很不解,一个线性的数组怎么实现按键值对来存取数据呢?
如上图所示,HashMap做了一些处理。
首先HashMap里面实现了一个静态内部类Entry,其重要的属性有 key , value, next,从属性key,value我们就能很明显的看出来Entry就是HashMap键值对实现的一个基础bean。
我们上面说到HashMap的基础就是一个线性数组,这个数组就是Entry[],Map里面的内容都保存在Entry[]里面。
这数组里存的其实是每一个链表的head节点,然后根据Entry的next属性关联链表的每个节点。
/**
* The table, resized as necessary. Length MUST Always be a power of two.
*/
transient Entry[] table;
2. HashMap的存取实现
既然是线性数组,为什么能随机存取?这里HashMap用了一个小算法,利用hash算法散列,大致是这样实现的:
// 存储时:
// 这个hashCode方法这里不详述,只要理解每个key的hash是一个固定的int值
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = hash % Entry[].length;
Entry[index] = value;
// 取值时:
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = hash % Entry[].length;
return Entry[index];
1)put
疑问:如果两个key通过hash%Entry[].length得到的index相同,会不会有覆盖的危险?
答案是不会,因为这里HashMap里面也用到了链式数据结构的一个概念。形如上面我们提到过Entry类里面有一个next属性,作用是指向下一个Entry。
举个例子, 第一个键值对A进来,通过计算其key的hash得到的index=0,记做:Entry[0] = A。
一会后又进来一个键值对B,通过计算其index也等于0,现在怎么办?
HashMap会这样做:B.next = A,Entry[0] = B,如果又进来C,index也等于0,那么C.next = B,Entry[0] = C;
这样我们发现index=0的地方其实存了A,B,C三个键值对,他们通过next这个属性链接在一起。所以疑问不用担心。
也就是说数组中存储的是最后插入的元素,相同位置的其他元素用next属性关联。即,通过散列后计算得到相同index的元素会在一条链上,并通过next属性连接。
到这里为止,HashMap的大致实现,我们应该已经清楚了。具体代码如下:
public V put(K key, V value) {
if(table == EMPTY_TABLE){
inflateTable(threshold);
}
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value); //null总是放在数组的第一个链表中
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
//确定当前元素所在的链表,遍历链表
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
//如果key在链表中已存在,则替换为新value
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//如果size超过threshold,则扩充table大小。hash(key)%new length再散列
if((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])){
resize(2*table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash,table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bunketIndex);
}
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bunketIndex){
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e); //参数e, 是Entry.next
size++;
}
当然HashMap里面也包含一些优化方面的实现,这里也说一下。
比如:Entry[]的长度一定后,随着map里面数据的越来越长,这样同一个index的链就会很长,肯定会影响性能。
所以HashMap里面设置了一个增长因子,随着map的size越来越大,Entry[]会以一定的规则加长长度。
这个就是上面代码注释里提到的如果size超过threshold,则扩充table大小。hash(key)%new length再散列,这个一会儿在下面详细说明。
2)get
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
/**
* Returns the entry associated with the specified key in the
* HashMap. Returns null if the HashMap contains no mapping
* for the key.
*/
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}
3)null key的存取
null key总是存放在Entry[]数组的第一个元素。
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(0, null, value, 0);
return null;
}
private V getForNullKey() {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null)
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
4)确定数组index:hashcode % table.length取模
HashMap存取时,都需要计算当前key应该对应Entry[]数组哪个元素,即计算数组下标;算法如下:
/**
* Returns index for hash code h.
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}
按位取并,作用上相当于取模mod或者取余%。
这意味着数组下标相同,并不表示hashCode相同。
5)table初始大小
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial
* capacity and load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = initialCapacity;
init();
}
/**
* Inflates the table.
*/
private void inflateTable(int toSize) {
// Find a power of 2 >= toSize
int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize);
threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
table = new Entry[capacity];
initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity);
}
Jdk1.7和之前的版本不同的是我们推迟初始化直到我们确实需要它。即并没有在new的时候就初始化数组,在put的时候判断数组为空时再调用inflateTable初始化HashMap。
另外需要注意的是table初始大小并不是构造函数中的initialCapacity!!
而是 >= initialCapacity的2的n次幂!!!——为什么这么设计呢?——
另外,调用无参构造时的初始化大小是16,增长因子是0.75
3. 解决hash冲突的办法
*开放定址法(线性探测再散列,二次探测再散列,伪随机探测再散列)
*再哈希法
*链地址法
*建立一个公共溢出区
Java中HashMap的解决办法就是采用的链地址法。
4. 再散列rehash过程
从上面的代码addEntry方法可以看出,每次都会判断size是不是已经超过threshold,即当哈希表的容量超过默认容量时,必须调整table的大小,对数组进行扩容。
当容量已经达到最大可能值时,那么该方法就将容量调整到Integer.MAX_VALUE返回。
扩容时,需要创建一张新表,将原表的映射到新表中。具体代码如下:
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));//把原来的数组放到新数组里
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);//新的阈值
}
/**
* Transfers all entries from current table to newTable.
*/
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {
while(null != e) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
//根据新的数组长度重新计算index
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
}
}
}
由于篇幅原因,将在下一篇探秘jdk1.8的HashMap。
参考:
jdk1.7.0_79源码
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/44478231