20162316刘诚昊 2017-2018-2 《Java程序设计》课下排序测试
实验要求
1 给定下列数据:90 8 7 56 123 235 9 1 653
用JDB或IDEA单步跟踪下列算法的执行过程:选择排序,插入排序,希尔排序,冒泡排序,快速排序,归并排序
2 提交每一趟的截图,要全屏,包含自己的学号信息
3 课下把代码推送到代码托管平台
过程:
1.载入书上的代码“Sorting”:
public class Sorting {
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Sorts the specified array of integers using the selection
// sort algorithm
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
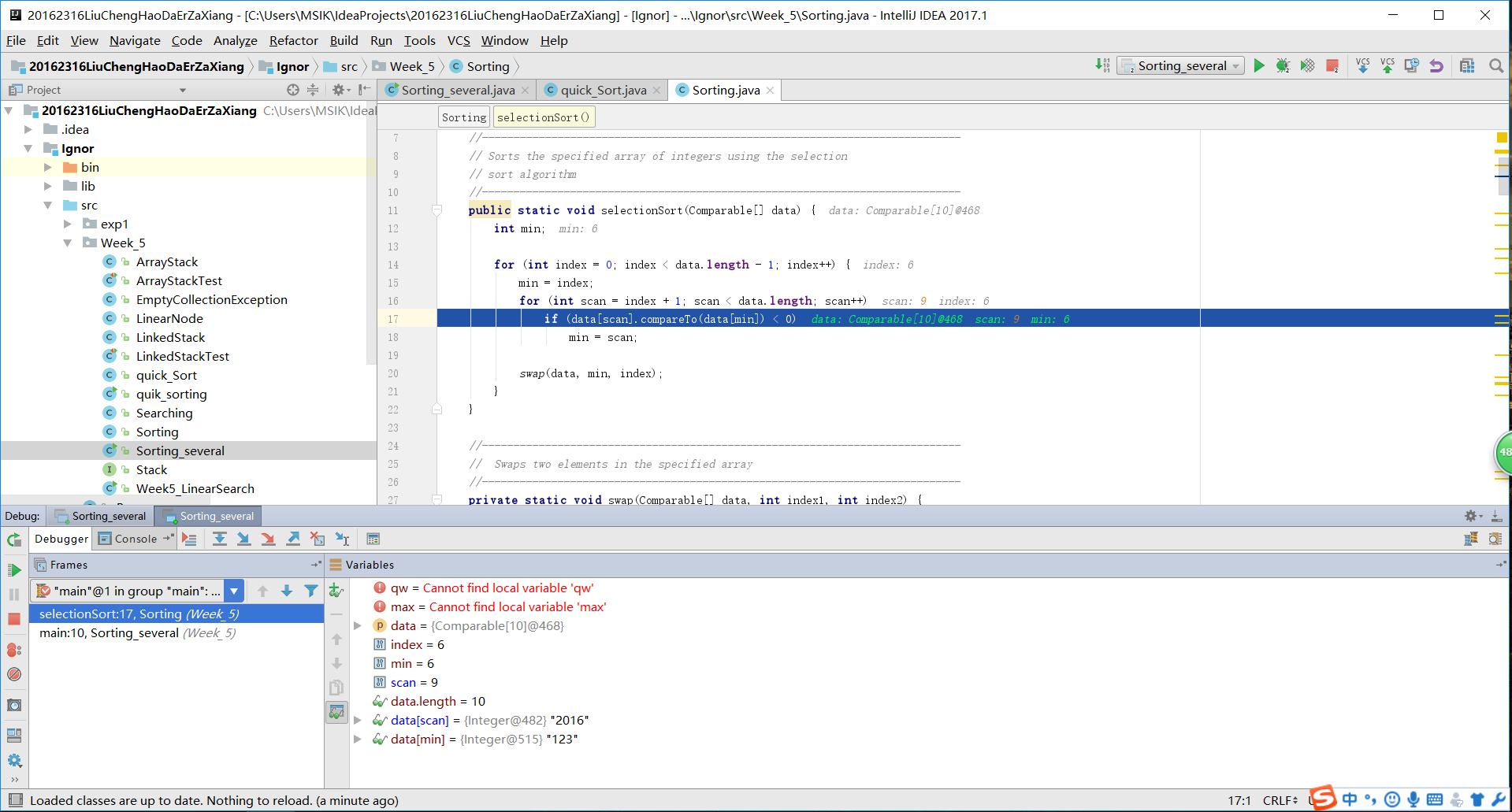
public static void selectionSort(Comparable[] data) {
int min;
for (int index = 0; index < data.length - 1; index++) {
min = index;
for (int scan = index + 1; scan < data.length; scan++)
if (data[scan].compareTo(data[min]) < 0)
min = scan;
swap(data, min, index);
}
}
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Swaps two elements in the specified array
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
private static void swap(Comparable[] data, int index1, int index2) {
Comparable temp = data[index1];
data[index1] = data[index2];
data[index2] = temp;
}
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Sorts the specified array of object using an insertion
// sorts algorithm
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
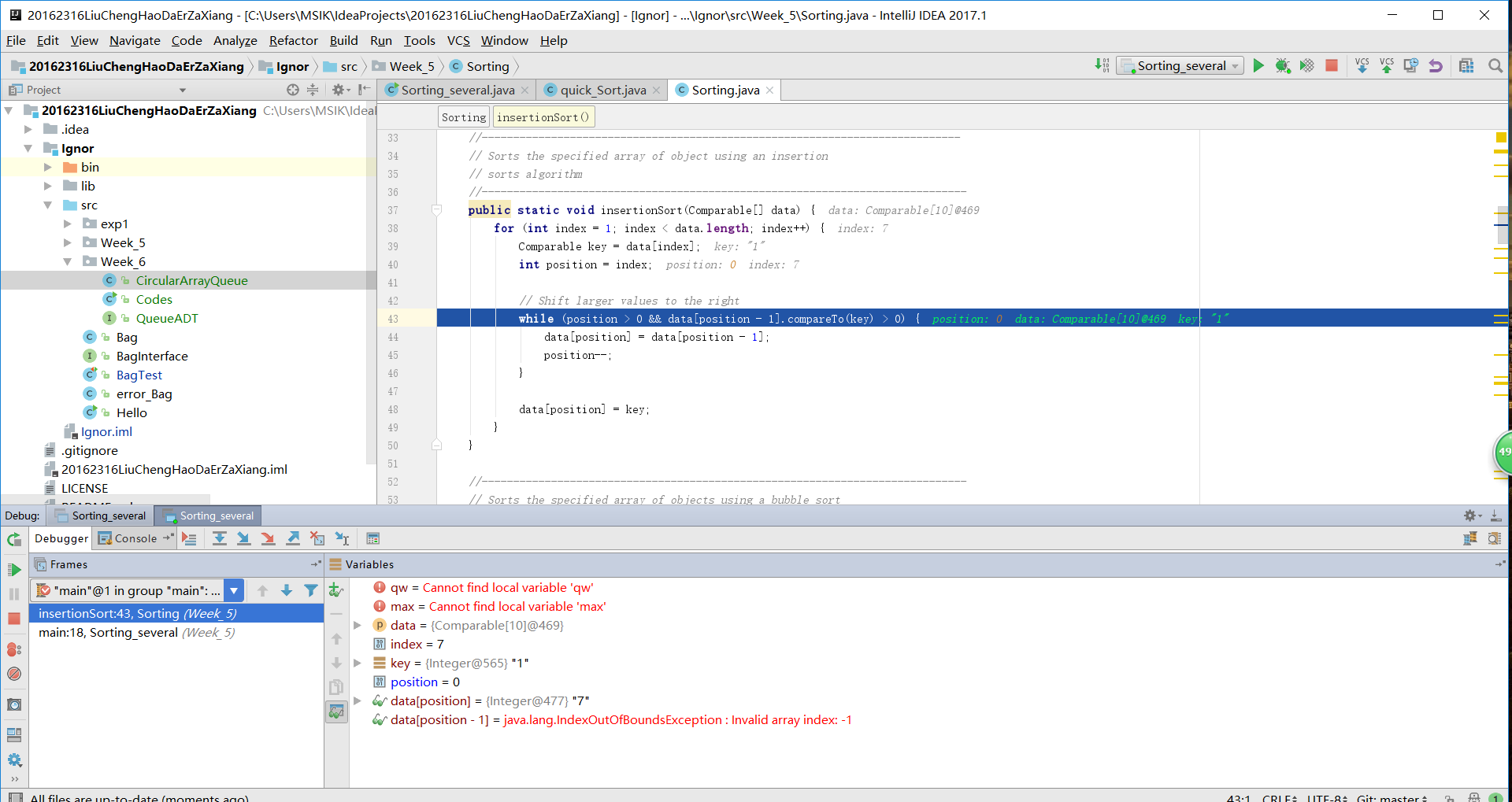
public static void insertionSort(Comparable[] data) {
for (int index = 1; index < data.length; index++) {
Comparable key = data[index];
int position = index;
// Shift larger values to the right
while (position > 0 && data[position - 1].compareTo(key) > 0) {
data[position] = data[position - 1];
position--;
}
data[position] = key;
}
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Sorts the specified array of objects using a bubble sort
// algorithm.
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public static void bubbleSort(Comparable[] data) {
int position, scan;
for (position = data.length - 1; position >= 0; position--) {
for (scan = 0; scan <= position - 1; scan++)
if (data[scan].compareTo(data[scan + 1]) > 0)
swap(data, scan, scan + 1);
}
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Sorts the specified array of objects using the quick sort algorithm.
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public static void quickSort(Comparable[] data, int min, int max){
int pivot;
if (min < max){
pivot = partition (data, min, max); //make partitions
quickSort(data, min, pivot-1); //sort left partition
quickSort(data, pivot+1, max);
}
}
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Creates the partitions needed fof quick sort.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
private static int partition(Comparable[] data, int min, int max){
//Use first element as the partiton value.
Comparable partitionValue = data[min];
int left = min;
int right = max;
while (left < right){
// Search for an element that is > the partition element
while (data[left].compareTo(partitionValue) <= 0 && left < right)
left++;
// Search for an element that is < the partition element
while (data[right].compareTo(partitionValue) >0)
right--;
if (left < right)
swap(data, left, right);
}
// Move the partition element to its fianl position
swap(data, min, right);
return right;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Sorts the speceified array of objects using the merge sort algorithm
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public static void mergeSort(Comparable[] data, int min, int max){
if (min < max){
int mid = (min + max) / 2;
mergeSort(data, min, mid);
mergeSort(data, mid+1, max);
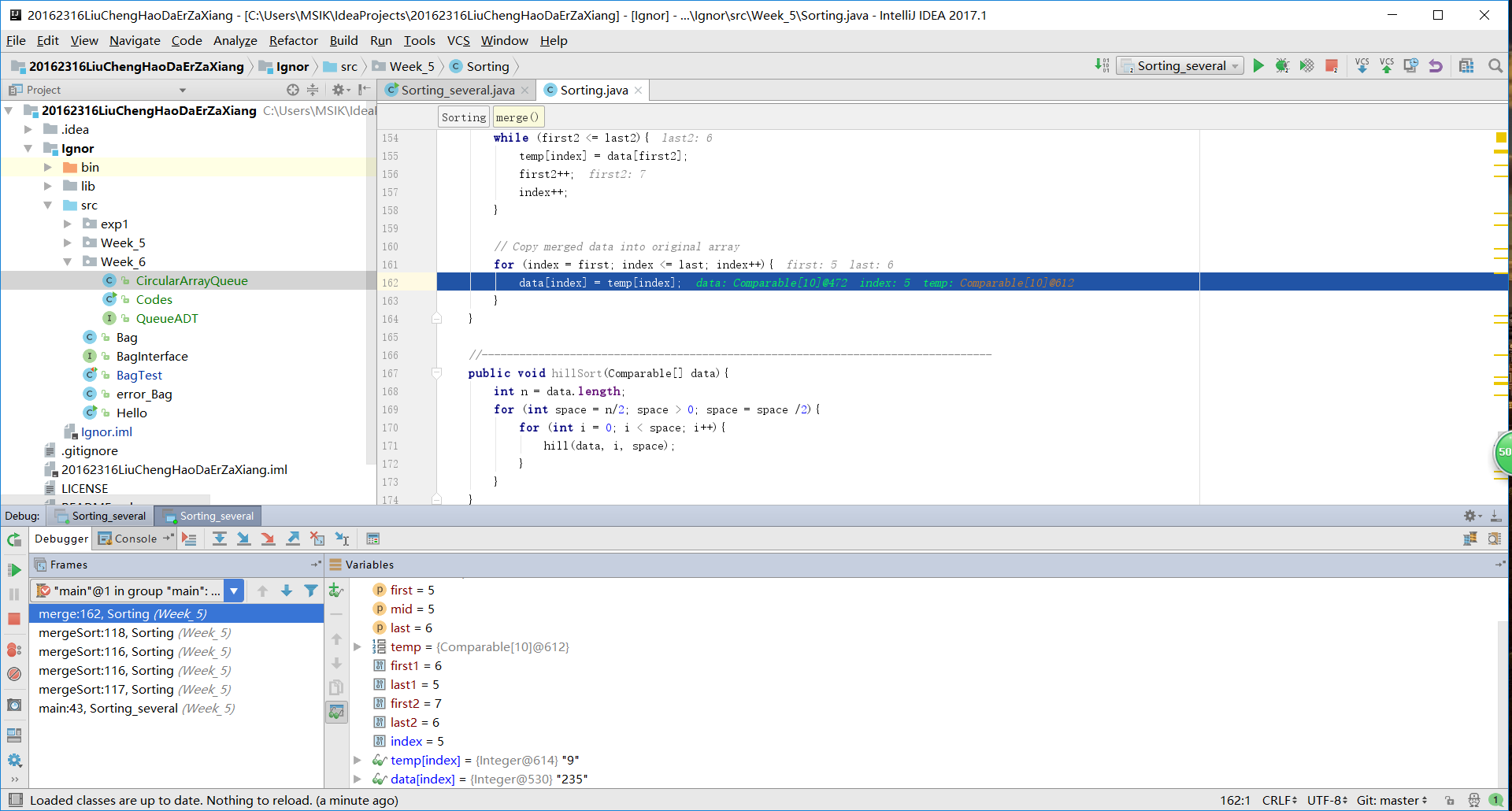
merge (data, min, mid, max);
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Sorts the specified array of objects using the merge sort algorithm.
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public static void merge(Comparable[] data, int first, int mid, int last){
Comparable[] temp = new Comparable[data.length];
int first1 = first, last1 = mid; // endpoints of first subarray
int first2 = mid+1, last2 = last; // endpoints of second subarray
int index = first1; // next index open in temp array
// Copy smaller item from each subarray intp temp until one
// of the subarray is exhausted
while (first1 <= last1 && first2 <= last2){
if (data[first1].compareTo(data[first2]) < 0){
temp[index] = data[first1];
first1++;
}
else{
temp[index] = data[first2];
first2++;
}
index++;
}
// Copy remaining elements from first subarray, if any
while (first1 <= last1){
temp[index] = data[first1];
first1++;
index++;
}
// Copy remaining elements from second subarray, if any
while (first2 <= last2){
temp[index] = data[first2];
first2++;
index++;
}
// Copy merged data into original array
for (index = first; index <= last; index++){
data[index] = temp[index];
}
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public void hillSort(Comparable[] data){
int n = data.length;
for (int space = n/2; space > 0; space = space /2){
for (int i = 0; i < space; i++){
hill(data, i, space);
}
}
}
public void hill(Comparable[] data, int index, int space){
for (int i = index + space; i < data.length; i += space){
Comparable obj = data[i];
for (int j = i; j > index; j -= space){
if (obj.compareTo(data[j]) < 0)
data[j + space] = data[j];
data[j] = obj;
}
}
}
}
2.写实现代码,并验证是否处理正确:
public class Sorting_several {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sorting q = new Sorting();
Comparable[] num1 = {90, 8, 7, 56, 123, 235, 9, 1, 653, 2016};
q.selectionSort(num1);
System.out.println("选择排序结果:");
for(Comparable element : num1){
System.out.print(element + " ");
}
System.out.println();
Comparable[] num2 = {90, 8, 7, 56, 123, 235, 9, 1, 653, 2016};
q.insertionSort(num2);
System.out.println("插入排序结果:");
for(Comparable element : num2) {
System.out.print(element + " ");
}
System.out.println();
Comparable[] num3 = {90, 8, 7, 56, 123, 235, 9, 1, 653, 2016};
q.bubbleSort(num3);
System.out.println("冒泡排序结果:");
for(Comparable element : num3){
System.out.print(element + " ");
}
System.out.println();
Comparable[] num4 = {90, 8, 7, 56, 123, 235, 9, 1, 653, 2016};
System.out.println("快速排序结果:");
q.quickSort(num4,0,num4.length-1);
for(Comparable element : num4){
System.out.print(element + " ");
}
System.out.println();
Comparable[] num5 = {90, 8, 7, 56, 123, 235, 9, 1, 653, 2016};
System.out.println("归并排序结果:");
q.mergeSort(num5,0,num5.length-1);
for(Comparable element : num5){
System.out.print(element + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
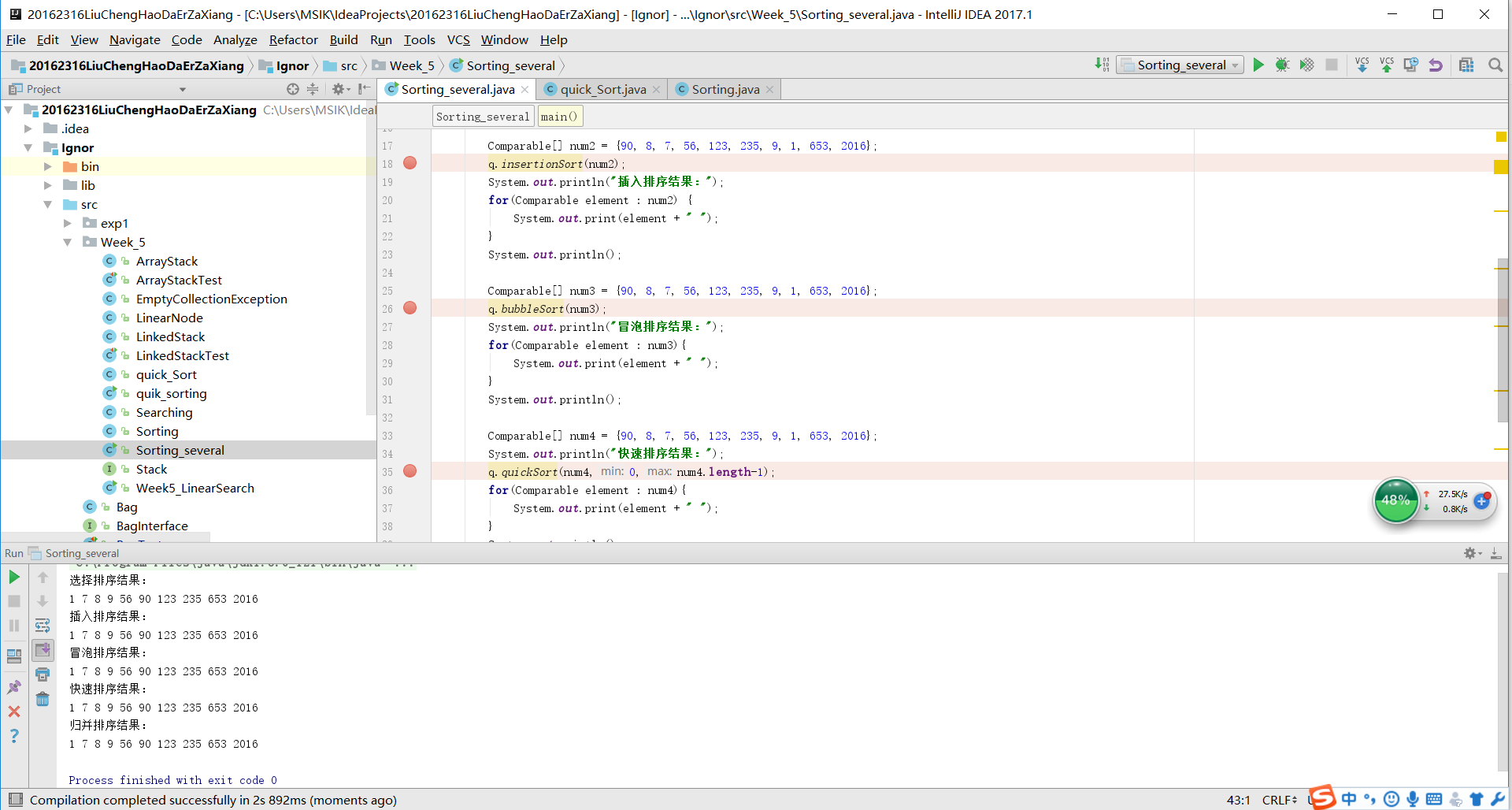
3.Debug 单步跟踪:
选择排序:
插入排序:
冒泡排序:
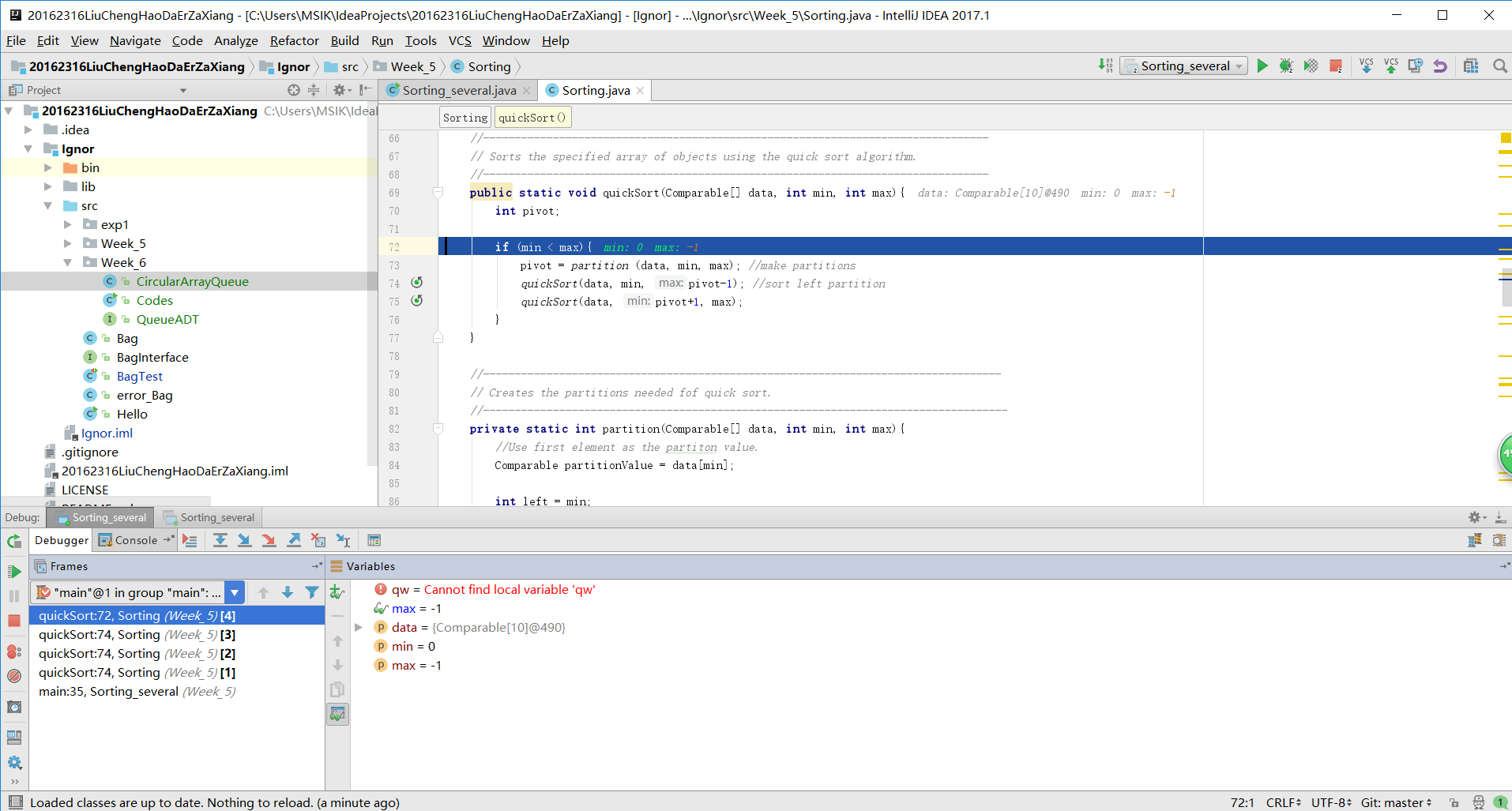
快速排序:
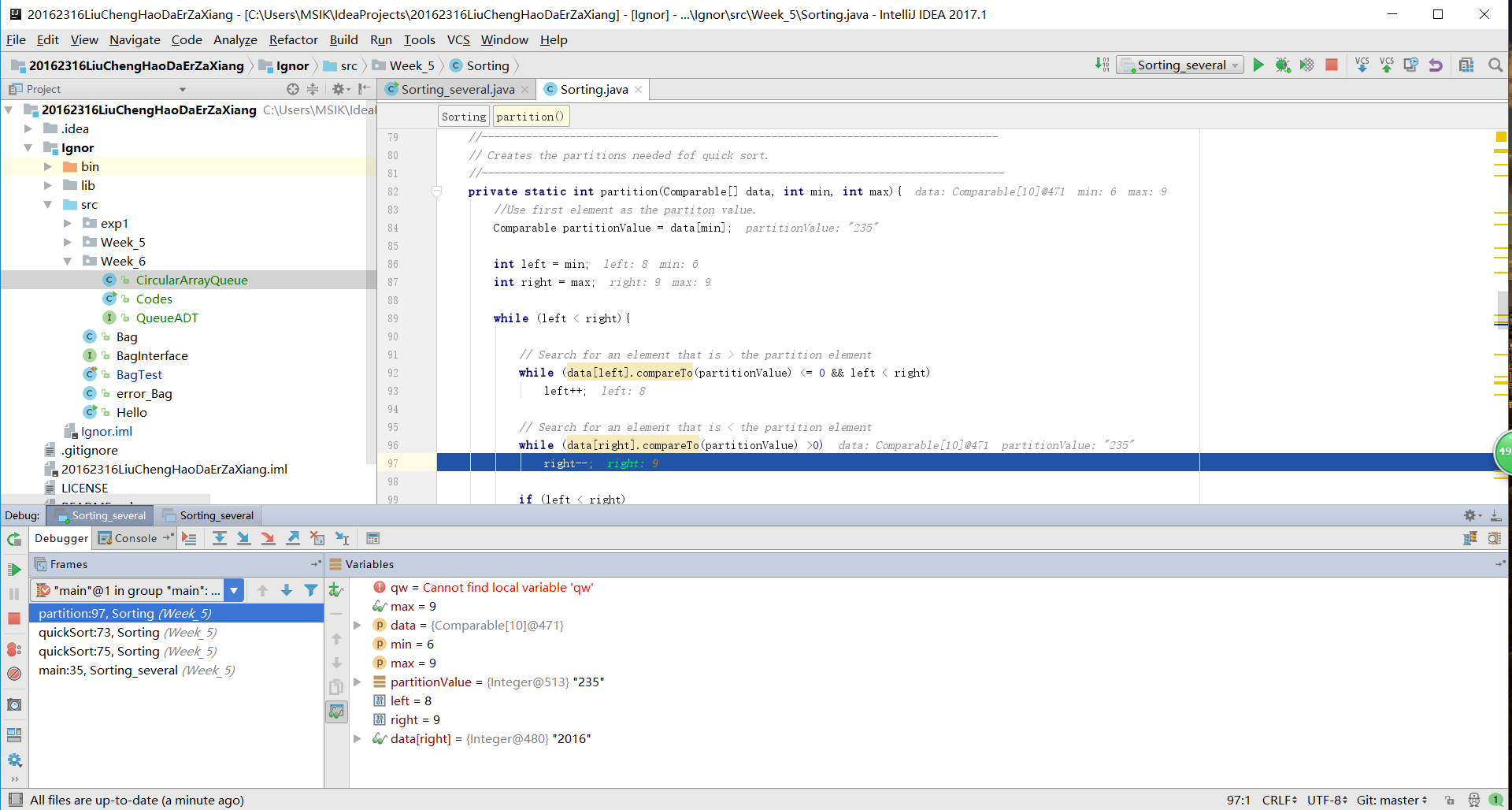
归并排序: