Given a binary tree
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Follow up:
- You may only use constant extra space.
- Recursive approach is fine, you may assume implicit stack space does not count as extra space for this problem.
Example 1:
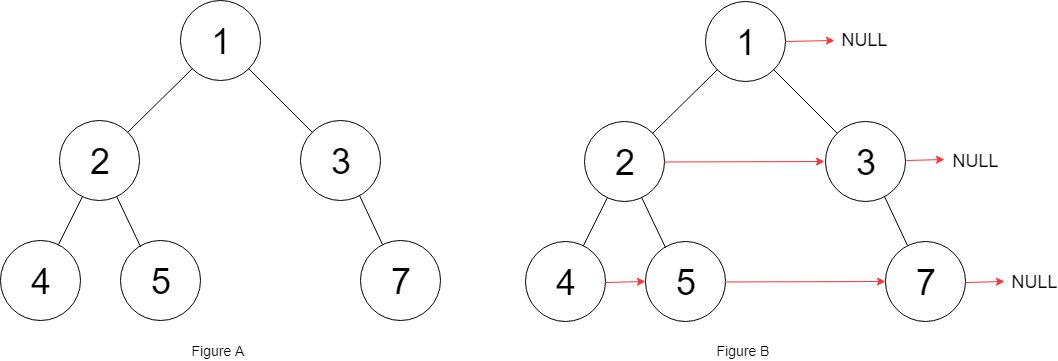
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7]
Output: [1,#,2,3,#,4,5,7,#]
Explanation: Given the above binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B. The serialized output is in level order as connected by the next pointers, with '#' signifying the end of each level.
把bfs基本模版改了改:
本层拿出来,不是放到level中,而是连接到下一个元素
if (i < count - 1) cur.next = q.peek();
如何保证是下一个元素:利用q本身的性质。先左后右按顺序放的,所以peek的就是紧接着的下一个。因为不需要加level了,所以不加。

class Solution { public Node connect(Node root) { if (root == null) return root; Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>(); q.offer(root); while (!q.isEmpty()) { int count = q.size(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { Node cur = q.poll(); //本层拿出来,不是放到level中,而是连接到下一个元素 //先左后右按顺序放的,所以peek的就是紧接着的下一个 if (i < count - 1) cur.next = q.peek(); if (cur.left != null) q.offer(cur.left); if (cur.right != null) q.offer(cur.right); } } return root; } }
另附上recursive的做法,参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/springfor/p/3889327.html

public void connect(TreeLinkNode root) { 2 if (root == null) 3 return; 4 5 TreeLinkNode p = root.next; 6 /* 7 因此,这道题目首要是找到右孩子的第一个有效的next链接节点,然后再处理左孩子。然后依次递归处理右孩子,左孩子 8 */ 9 while (p != null) { 10 if (p.left != null) { 11 p = p.left; 12 break; 13 } 14 if (p.right != null) { 15 p = p.right; 16 break; 17 } 18 p = p.next; 19 } 20 21 if (root.right != null) { 22 root.right.next = p; 23 } 24 25 if (root.left != null) { 26 if(root.right!=null) 27 root.left.next = root.right; 28 else 29 root.left.next = p; 30 } 31 32 connect(root.right); 33 connect(root.left); 34 }
