SYNOPSIS
ln [OPTION]... [-T] TARGET LINK_NAME (1st form)
ln [OPTION]... TARGET (2nd form)
ln [OPTION]... TARGET... DIRECTORY (3rd form)
ln [OPTION]... -t DIRECTORY TARGET... (4th form)
- form1:创建一个名为LINK_NAME 的连接文件指向原文件TARGET
- form2:在当前目录中创建一个与TARGET同名的链接文件(TARGET不能在当前目录,目标可以是绝对路径,也可以是相对路径)
- form3 | form4:在指定的目录DIRECTORY中,为每一个原文件TARGET创建一个链接文件。
硬链接与软链接(-s)的联系与区别(默认是建立硬链接)
我们知道文件都有文件名与数据,这在 Linux 上被分成两个部分:用户数据 (user data) 与元数据 (metadata)。用户数据,即文件数据块 (data block),数据块是记录文件真实内容的地方;而元数据则是文件的附加属性,如文件大小、创建时间、所有者等信息。在 Linux 中,元数据中的 inode 号(inode 是文件元数据的一部分但其并不包含文件名,inode 号即索引节点号)才是文件的唯一标识而非文件名。文件名仅是为了方便人们的记忆和使用,系统或程序通过 inode 号寻找正确的文件数据块。图 1.展示了程序通过文件名获取文件内容的过程。
图 1. 通过文件名打开文件
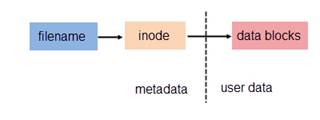
由于硬链接是有着相同 inode 号仅文件名不同的文件,因此硬链接存在以下几点特性:
- 文件有相同的 inode 及 data block;
- 只能对已存在的文件进行创建;
- 不能交叉文件系统进行硬链接的创建;
- 不能对目录进行创建,只可对文件创建;
- 删除一个硬链接文件并不影响其他有相同 inode 号的文件。
可选参数如下
--backup[=CONTROL]
make a backup of each existing destination file
-b like --backup but does not accept an argument
-d, -F, --directory
allow the superuser to attempt to hard link directories (note: will probably fail
due to system restrictions, even for the superuser)
-f, --force
remove existing destination files
-i, --interactive
prompt whether to remove destinations
-L, --logical
dereference TARGETs that are symbolic links
-n, --no-dereference
treat LINK_NAME as a normal file if it is a symbolic link to a directory
-P, --physical
make hard links directly to symbolic links
-r, --relative
create symbolic links relative to link location
-s, --symbolic
make symbolic links instead of hard links
-S, --suffix=SUFFIX
override the usual backup suffix
-t, --target-directory=DIRECTORY
specify the DIRECTORY in which to create the links
-T, --no-target-directory
treat LINK_NAME as a normal file always
-v, --verbose
print name of each linked file
--help display this help and exit
--version
output version information and exit
每个文件存在两个计数器:i_count 与 i_nlink,即引用计数与硬链接计数。结构体 inode 中的 i_count 用于跟踪文件被访问的数量,而 i_nlink 则是上述使用 ls -l 等命令查看到的文件硬链接数。或者说 i_count 跟踪文件在内存中的情况,而 i_nlink 则是磁盘计数器。当文件被删除时,则 i_nlink 先被设置成 0。文件的这两个计数器使得 Linux 系统升级或程序更新变的容易。系统或程序可在不关闭的情况下(即文件 i_count 不为 0),将新文件以同样的文件名进行替换,新文件有自己的 inode 及 data block,旧文件会在相关进程关闭后被完整的删除。
查看文件是否是硬链接
$ touch file1 # 创建新文件 file1
$ touch file2 # 创建新文件 file2
$ ln file1 file3 # 为 file1 创建硬链接 file3
$ ls -l
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 2 root root 0 Aug 12 16:59 file1
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Aug 12 17:00 file2
-rw-r--r-- 2 root root 0 Aug 12 16:59 file3
结果的第二列数字就是指向该文件的硬链接数. 注意, 硬链接和原文件是无法区分的. 所以 file3 是 file1 的硬链接也可以看作 file1 是 file3 的硬链接. 所以该数字大于 2 即说明该文件是硬链接.
查看文件的 inode number
ls -i # 可以与 ls -l 一起使用, 即 ls -il
$ ls -il
total 0
267105 -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 0 Aug 12 16:59 file1
267106 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Aug 12 17:00 file2
267105 -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 0 Aug 12 16:59 file3
这时结果的第一列就是文件的 inode number, 可以看出由于 file1 和 file3 互为硬链接, 所以他们的 inode number 相同.
如何找出所有硬链接到某个文件的文件?
首先使用
1
ls -i
查看文件的 inode number
然后使用
find -inum
查找所有指向该 inode 的文件
例子:
$ find . -inum 267105
./file3
./file1
ref :https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-cn-hardandsymb-links/