FROM: http://blog.csdn.net/bigloomy/article/details/6629479
=======================================================
在此也要特地感谢下编程浪子朱云翔老师,阅读我博客后提出的宝贵意见,根据你的建议我接下来的博客中都把代码部分放到了代码框中,使得代码看起来更加的悦目。
前一篇博客中我们讲解了单链表,那么接下来还是按照我们之前的安排讲解双链表部分, 在开始讲解之前,我们先来简单的回顾下上一篇博客中的双链表,双链表是链表的一种,它的每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。所以,从双向链表中的任意一个结点开始,都可以很方便地访问它的前驱结点和后继结点。对双链表做了一个简单的回顾之后那么接下来我们就来开始讲解双链表了,在这里我们也同样遵循一个原则,就是用简单易懂的代码和文字描述来讲解,我们要突出代码的重点是在编程的过程中我们的易错点。
因为双链表的使用相对于单链表操作来说要复杂和常用些,所以在这里我采用逐渐添加功能模块的方法来进行讲解,从易到难,让读者理解起来更加轻松,同时我们在这里也使用我前面博客中提到的一些方法,学以致用嘛,学了就要在代码中尽可能的使用起来,要不然学了有什么用呢,接下来我们先来看看一个最为简单的双链表的创建。
特此说明:
1、如果在接下来的代码中发现一些不懂而我又没有给出提示信息的,如自己定义枚举型的数据结构DListReturn作为返回类型等,那么请你看我的前一篇博客《C语言的那些小秘密之链表(一)》。
2、由于文章在编辑的时候可以对代码部分使用颜色标记,但是发表后好像显示不出来,我试图修改,但还是不行,所以在此说明下,代码中被“<span style="color:#ff0000;">” 和“</span> ”框起来的部分为有色部分。读者自己在阅读代码的时候注意下,自己对比也能找到新加入的代码。
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- typedef enum _DListReturn
- {
- DLIST_RETURN_OK,
- DLIST_RETURN_FAIL
- }DListReturn;
- typedef struct _DStu
- {
- int score;
- }DStu;
- typedef struct _DListNode
- {
- struct _DListNode* prev;
- struct _DListNode* next;
- DStu* data;
- }DListNode;
- typedef struct _DList
- {
- DListNode* head;
- }DList;
- typedef DListReturn (*DListPrintFunction)(void* data);
- DListNode* dlist_node_create(void* data)
- {
- DListNode* node;
- if((node = (DListNode*) malloc(sizeof(DListNode)))==NULL)
- {
- printf("分配空间失败!");
- exit(0);
- }
- if(node != NULL)
- {
- node->prev = NULL;
- node->next = NULL;
- node->data =(DStu*)data;
- }
- return node;
- }
- DList* dlist_head_create(void)
- {
- DList* thiz;
- if((thiz = (DList*)malloc(sizeof(DList)))==NULL)
- {
- printf("分配空间失败!");
- exit(0);
- }
- if(thiz != NULL)
- {
- thiz->head = NULL;
- }
- return thiz;
- }
- DListReturn dlist_append(DList* thiz, void* data)
- {
- DListNode* node = NULL;
- DListNode* cursor = NULL;
- if((node = dlist_node_create(data)) == NULL)
- {
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- if(thiz->head == NULL)
- {
- thiz->head = node;
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- cursor = thiz->head;
- while(cursor != NULL && cursor->next != NULL)
- {
- cursor = cursor->next;
- }
- cursor->next = node;
- node->prev = cursor;
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- DListReturn dlist_print(DList* thiz, DListPrintFunction print)
- {
- DListNode* iter = thiz->head;
- while(iter != NULL)
- {
- print(iter->data);
- iter = iter->next;
- }
- printf("\n");
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- DListReturn print_int(void* data)
- {
- DStu* ss=(DStu*)data;
- printf("%d\t ", ss->score);
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- int i = 0;
- DList* dlist = dlist_head_create();
- for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
- {
- DStu* stu =(DStu*) malloc(sizeof(DStu));
- stu->score = i;
- dlist_append(dlist, (void*)stu);
- }
- dlist_print(dlist, print_int);
- return 0;
- }
运行结果为:

0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Press any key to continue
可能有的读者认为上面得代码有点复杂化了,其实不然,我们仅仅是写出了我们要讲解的双链表实现中最简单的部分,其实现的功能是创建一个链表,在链表末端添加结点,然后打印出链表中结点里存放的数据项,对代码的总体动能有了一个大概的了解之后,现在我们来逐一分析代码,为接下来添加功能模块打开思路。
从main()函数开始,通过 DList* dlist = dlist_head_create();我们创建了一个头节点。值得注意的是,为了链表更加通用和符合实际需求,我们在此创建的链表存放的是结构,因为现实中在使用链表时,绝大部分都是存放结构的,而前一篇文章中我们创建单链表时我们存放的是数据,所以这一点读者是要引起注意的,接下来是一个for循环语句,在for循环语句中我们首先使用DStu* stu =(DStu*) malloc(sizeof(DStu));为stu分配了空间,这也是很多读者的一个易错点,不分配就使用下面的stu->score = i;语句,从而导致出错,如果读者对于指针还不是很了解的话可以看看我前面的文章《C语言的那些小秘密之指针》,在往下看dlist_append(dlist, (void*)stu);语句,从函数名称我们也可以看出它的功能是在链表的末端添加结点的,在函数里面我们使用了一个if判断语句来看分配的结点是否成功,如果成功继续往下执行,如果失败则返回DLIST_RETURN_FAIL。对于第一次分配的节点我们使用了 thiz->head = node;语句使其变为头结点,在第二次调用dlist_append(dlist, (void*)stu)函数分配结点之后,由于头结点已经不再为空,那么跳过if(thiz->head == NULL)语句,执行以下语句:
cursor = thiz->head;
while(cursor != NULL && cursor->next != NULL)
{ cursor = cursor->next; }
其功能为查找末端结点,然后使用 cursor->next = node; node->prev = cursor;语句来将刚刚创建的新结点node作为尾结点。main()函数中的for循环语句执行完之后就轮到了调用dlist_print(dlist, print_int)函数打印我们创建的双向链表保存的数据值了,在这里的时候我们用了前面我博客中提到的函数指针作为参数的使用,如果有对函数指针不熟悉的读者可以参考我之前写的一篇博客《C语言的那些小秘密之函数指针》,到此读者应该都理解了上面的代码,但是其中有个值得注意的地方,那就是main()函数中使用dlist_append(dlist, (void*)stu);的时候,我们传递的是一个无类型的指针,在创建新结点的时候,我们使用了一句node->data =(DStu*)data;进行一个强制转换,使得链表中的数据域指向的就是我们使用DStu* stu =(DStu*) malloc(sizeof(DStu));所创建的空间。创建了空间之后当然要释放掉,所以接下来我们就添加一个释放功能模块。新添加的代码我们用红色部分来标记。以便于读者的阅读
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- typedef enum _DListReturn
- {
- DLIST_RETURN_OK,
- DLIST_RETURN_FAIL
- }DListReturn;
- typedef struct _DStu
- {
- int score;
- }DStu;
- typedef struct _DListNode
- {
- struct _DListNode* prev;
- struct _DListNode* next;
- DStu* data;
- }DListNode;
- typedef struct _DList
- {
- DListNode* head;
- }DList;
- typedef DListReturn (*DListPrintFunction)(void* data);
- DListNode* dlist_node_create(void* data)
- {
- DListNode* node;
- if((node = (DListNode*) malloc(sizeof(DListNode)))==NULL)
- {
- printf("分配空间失败!");
- exit(0);
- }
- if(node != NULL)
- {
- node->prev = NULL;
- node->next = NULL;
- node->data =(DStu*)data;
- }
- return node;
- }
- DList* dlist_head_create(void)
- {
- DList* thiz;
- if((thiz = (DList*)malloc(sizeof(DList)))==NULL)
- {
- printf("分配空间失败!");
- exit(0);
- }
- if(thiz != NULL)
- {
- thiz->head = NULL;
- }
- return thiz;
- }
- DListReturn dlist_append(DList* thiz, void* data)
- {
- DListNode* node = NULL;
- DListNode* cursor = NULL;
- if((node = dlist_node_create(data)) == NULL)
- {
- return DLIST_RETURN_FAIL;
- }
- if(thiz->head == NULL)
- {
- thiz->head = node;
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- cursor = thiz->head;
- while(cursor != NULL && cursor->next != NULL)
- {
- cursor = cursor->next;
- }
- cursor->next = node;
- node->prev = cursor;
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- DListReturn dlist_prepend(DList* thiz, void* data)
- {
- DListNode* node = NULL;
- DListNode* cursor = NULL;
- if((node = dlist_node_create(data)) == NULL)
- {
- return DLIST_RETURN_FAIL;
- }
- if(thiz->head == NULL)
- {
- thiz->head = node;
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- cursor = thiz->head;
- if(thiz->head == cursor)
- thiz->head = node;
- node->next = cursor;
- cursor->prev = node;
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- DListReturn dlist_print(DList* thiz, DListPrintFunction print)
- {
- DListNode* iter = thiz->head;
- while(iter != NULL)
- {
- print(iter->data);
- iter = iter->next;
- }
- printf("\n");
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- DListReturn print_int(void* data)
- {
- DStu* ss=(DStu*)data;
- printf("%d\t ", ss->score);
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- DListReturn dlist_node_destroy(DListNode* node)
- {
- if(node != NULL)
- {
- node->next = NULL;
- node->prev = NULL;
- free(node);
- }
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- DListReturn dlist_destroy(DList* thiz)
- {
- DListNode* iter = thiz->head;
- DListNode* next = NULL;
- while(iter != NULL)
- {
- next = iter->next;
- dlist_node_destroy(iter);
- iter = next;
- }
- thiz->head = NULL;
- free(thiz);
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- int i = 0;
- int n = 10;
- DList* dlist = dlist_head_create();
- DStu* stu[7];
- for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
- {
- stu[i] =(DStu*) malloc(sizeof(DStu));
- stu[i]->score = i;
- dlist_append(dlist, (void*)stu[i]);
- }
- dlist_print(dlist, print_int);
- for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
- {
- free(stu[i]);
- }
- return 0;
- }
在使用dlist_append(dlist, (void*)stu[i]);语句的时候我们传递的是stu[i]的指针,所以在创建结点的时候我们使用的node->data =(DStu*)data;语句使得data强制转换为了DStu结构类型指针,即在结点创建函数中我们仅仅是使数据域的结构指针data指向了stu[i]所分配的存储空间,和stu[i]指向的是同一个空间,但是在释放结点时,我们仅仅是释放掉了存放data指针变量的空间,并没有释放掉data所指向的空间,所以我们在main函数中我们最后使用了一个for循环语句来释放data所指向的存储空间。在此也讲讲之前我给出的以下代码和我们双链表释放方式的区别。
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- int main()
- {
- int *pointer_1=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
- int *pointer_2=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
- pointer_1=pointer_2;
- printf("%d\n",pointer_1);
- printf("%d\n",pointer_2);
- printf("%d\n",&pointer_1);
- printf("%d\n",&pointer_2);
- //free(pointer_1);
- free(pointer_2);
- return 0;
- }
运行结果为:

3674136
3674136
1245052
1245048
Press any key to continue
虽然两个指针变量存放在不同的单元,但是它们都指向同一个存储单元,所以在释放的时候只能释放一次,如果释放两次就会出错。注意切不可同时使用free(pointer_1);和 free(pointer_2);,否则将会出现内存错误。对出错原因不懂的可以参考我前面的文章《C语言的那些小秘密之指针》。这个代码和我们双链表的最大区别是它只能使用free()函数进行一次释放,而我们双链表中看似使用了两次,但实则一次而已。原因就在于我们在对头结点分配空间的时候分配的是存放data指针变量的存储空间(注意:所有的指针变量在分配的时候均分配4字节大小的存储空间,如果有什么疑惑可以参考我之前写的《C语言的那些小秘密之指针》)。所以释放的时候也是释放的存放指针变量data的存储空间,并没有释放掉指针变量data所指向的存储空间。所以在释放data指向的存储空间时,我们只需要在main()函数中对stu[i]所指向的存储空间使用free()函数即可,因为data和它指向的是同一个存储空间。
接下来我们来添加一个在头结点添加结点的模块。
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- typedef enum _DListReturn
- {
- DLIST_RETURN_OK,
- DLIST_RETURN_FAIL
- }DListReturn;
- typedef struct _DStu
- {
- int score;
- }DStu;
- typedef struct _DListNode
- {
- struct _DListNode* prev;
- struct _DListNode* next;
- DStu* data;
- }DListNode;
- typedef struct _DList
- {
- DListNode* head;
- }DList;
- typedef DListReturn (*DListPrintFunction)(void* data);
- DListNode* dlist_node_create(void* data)
- {
- DListNode* node;
- if((node = (DListNode*) malloc(sizeof(DListNode)))==NULL)
- {
- printf("分配空间失败!");
- exit(0);
- }
- if(node != NULL)
- {
- node->prev = NULL;
- node->next = NULL;
- node->data =(DStu*)data;
- }
- return node;
- }
- DList* dlist_head_create(void)
- {
- DList* thiz;
- if((thiz = (DList*)malloc(sizeof(DList)))==NULL)
- {
- printf("分配空间失败!");
- exit(0);
- }
- if(thiz != NULL)
- {
- thiz->head = NULL;
- }
- return thiz;
- }
- DListReturn dlist_append(DList* thiz, void* data)
- {
- DListNode* node = NULL;
- DListNode* cursor = NULL;
- if((node = dlist_node_create(data)) == NULL)
- {
- return DLIST_RETURN_FAIL;
- }
- if(thiz->head == NULL)
- {
- thiz->head = node;
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- cursor = thiz->head;
- while(cursor != NULL && cursor->next != NULL)
- {
- cursor = cursor->next;
- }
- cursor->next = node;
- node->prev = cursor;
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- <span style="color:#ff0000;">DListReturn dlist_prepend(DList* thiz, void* data)
- {
- DListNode* node = NULL;
- DListNode* cursor = NULL;
- if((node = dlist_node_create(data)) == NULL)
- {
- return DLIST_RETURN_FAIL;
- }
- if(thiz->head == NULL)
- {
- thiz->head = node;
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- cursor = thiz->head;
- if(thiz->head == cursor)
- thiz->head = node;
- node->next = cursor;
- cursor->prev = node;
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- </span>DListReturn dlist_print(DList* thiz, DListPrintFunction print)
- {
- DListNode* iter = thiz->head;
- while(iter != NULL)
- {
- print(iter->data);
- iter = iter->next;
- }
- printf("\n");
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- DListReturn print_int(void* data)
- {
- DStu* ss=(DStu*)data;
- printf("%d\t ", ss->score);
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- DListReturn dlist_node_destroy(DListNode* node)
- {
- if(node != NULL)
- {
- node->next = NULL;
- node->prev = NULL;
- free(node);
- }
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- DListReturn dlist_destroy(DList* thiz)
- {
- DListNode* iter = thiz->head;
- DListNode* next = NULL;
- while(iter != NULL)
- {
- next = iter->next;
- dlist_node_destroy(iter);
- iter = next;
- }
- thiz->head = NULL;
- free(thiz);
- return DLIST_RETURN_OK;
- }
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- int i = 0;
- DList* dlist = dlist_head_create();
- for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
- {
- DStu* stu =(DStu*) malloc(sizeof(DStu));
- stu->score = i;
- dlist_append(dlist, (void*)stu);
- }
- <span style="color:#ff0000;"> for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
- {
- DStu* stu =(DStu*) malloc(sizeof(DStu));
- stu->score = i;
- dlist_prepend(dlist, (void*)stu);
- }</span>
- dlist_print(dlist, print_int);
- dlist_destroy(dlist);
- return 0;
- }
注意:红色部分为新加入的代码。
我们在上一段代码添加了红色部分代码后,使得其在已经生成的双链表的头结点处添加结点,运行结果如下:
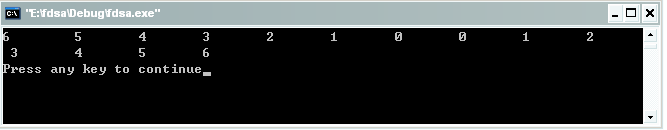
6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 1 2
3 4 5 6
Press any key to continue
可以看出结果与我们的要求完全符合。如果你认真分析了代码的话你就会发现,我们的两种添加方式中有公共代码出现,那就说明我们的代码可以继续改进,把公共代码放到一个函数中,读者可以另外编写一个函数来实现,使得我们编写的代码得到充分的利用。
篇幅似乎有些过长了,接下来我就不再一一讲解了,我在这里只是想起一个引路的作用,读者完全可以在此基础之上继续编写双链表其余部分的功能,其他的功能模块读者可以在此基础上一一添加上去,到下一篇的时候我们将走进linux内核链表,继续链表之旅的最后一站。由于本人水平有限,博客中的不妥或错误之处在所难免,殷切希望读者批评指正。同时也欢迎读者共同探讨相关的内容,如果乐意交流的话请留下你宝贵的意见。
=======================================================