首先介绍Spring事件相关类的关系:
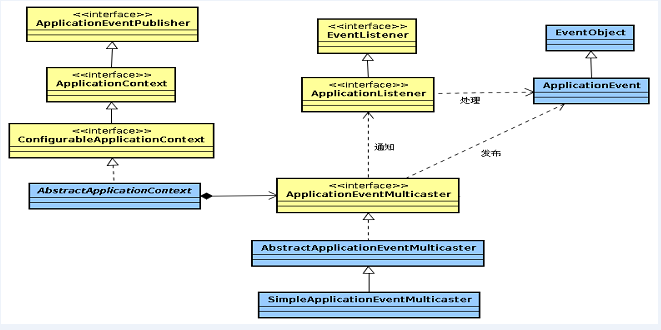
其中EventListener与EventObject均是Java SE的范畴,源码如下:
package java.util; public interface EventListener { }
package java.util; public class EventObject implements java.io.Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 5516075349620653480L; protected transient Object source; public EventObject(Object source) { if (source == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("null source"); this.source = source; } public Object getSource() { return source; } public String toString() { return getClass().getName() + "[source=" + source + "]"; } }
Spring继承以上二者,可知Spring的事件实现机制也是基于观察者模式(Observer),除此之外,Spring提供了针对Bean的事件传播功能。
事件机制三元素:发布者、接收者、事件对象;接收者也可称为监听器。Spring中、通过分别继承Java SE中的EventListener和EventObject实现了接收者、事件对象。
package org.springframework.context; import java.util.EventListener; public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener { void onApplicationEvent(E event); }
package org.springframework.context; import java.util.EventObject; public abstract class ApplicationEvent extends EventObject { private static final long serialVersionUID = 7099057708183571937L; private final long timestamp; public ApplicationEvent(Object source) { super(source); this.timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); } public final long getTimestamp() { return this.timestamp; } }
Java SE中并未提供事件发布者这一角色,在Spring中,则提供了ApplicationEventPublisher接口作为发布者,源码如下:
package org.springframework.context; public interface ApplicationEventPublisher { void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event); void publishEvent(Object event); }
至此、Spring事件机制三大角色全部构建完成。下面通过案例解析,并进一步解说发布者,代码如下:
事件对象:
package com.charles.spring.event; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent; public class HelloEvent extends ApplicationEvent{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; public HelloEvent(Object source) { super(source); } }
接收者/监听器:
package com.charles.spring.event; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; public class HelloListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> { @Override public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { if(event instanceof HelloEvent){ System.out.println("Hello World"); } } }
Spring配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:task="http://www.springframework.org/schema/task" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/task http://www.springframework.org/schema/task/spring-task-4.3.xsd "> <description>spring-configuration</description> <bean id="helloEvent" class="com.charles.spring.event.HelloEvent"> <constructor-arg index="0" value="Hello" /> </bean> <bean id="helloListener" class="com.charles.spring.event.HelloListener" /> </beans>
测试代码:
package com.charles.spring.test; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.charles.spring.event.HelloEvent; public class TestEvent { @Test @SuppressWarnings("resource") public void testHelloEvent(){ ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("config/spring-config.xml"); HelloEvent helloEvent = (HelloEvent)applicationContext.getBean("helloEvent"); applicationContext.publishEvent(helloEvent); } }
运行结果:

至此、案例代码结束,也许你尚未看到发布者的实现在哪里,其实在文章开头的类图中就ApplicationEventPublisher的继承实现作了介绍,ApplicationContext接口继承了ApplicationEventPublisher,所以我们在测试代码中,直接使用ApplicationContext作为发布者进行发布。