目录
平均池化
最大值池化
参考资料
|
平均池化 |
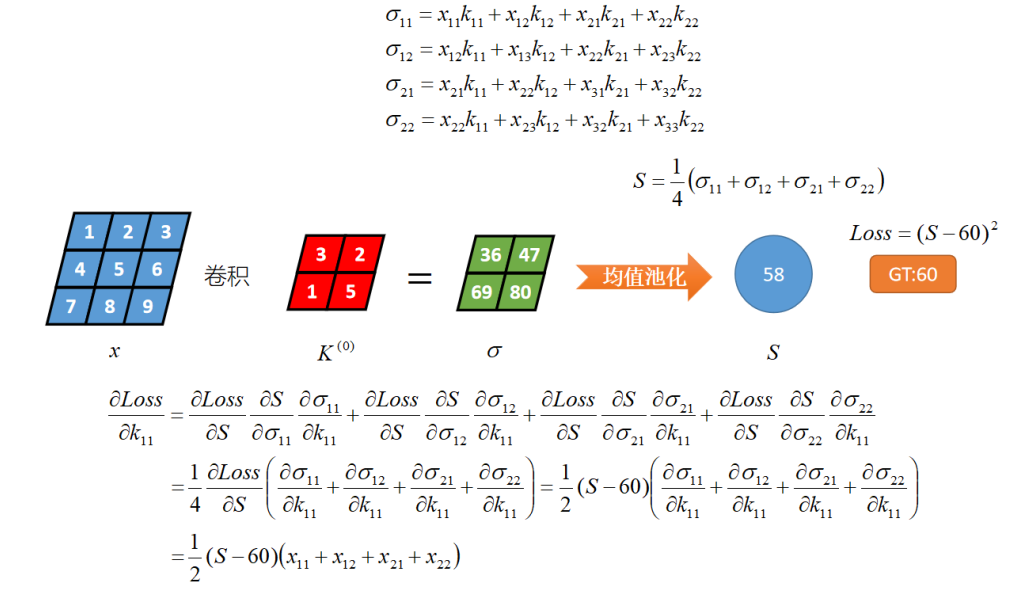
x和卷积核K做卷积运算,得到σ,对σ的做平均池化,得到S,然后S与GT计算MSE损失。
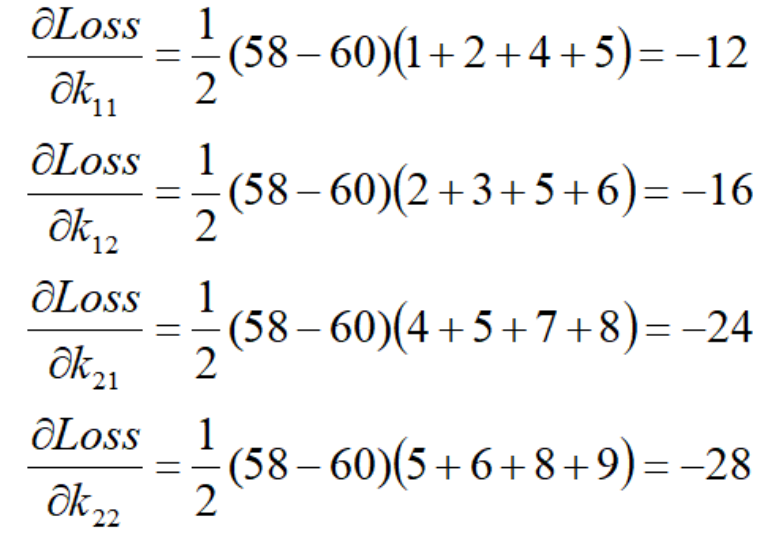
对应代码

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F class Net(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(Net, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 1, 2, bias=False) # 默认padding=0 即valid卷积 def forward(self, x): # Max pooling over a (2, 2) window x = self.conv1(x) x = F.avg_pool2d(x, 2) # x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2) return x if __name__ == '__main__': net = Net() print("网络结构为:") print(net) print() weight1 = torch.tensor([3., 2., 1., 5.]) weight1 = weight1.view(1, 1, 2, 2) net.conv1._parameters['weight'].data = weight1 # 自定义卷积核 input = torch.tensor([[1., 2., 3.], # 自定义输入 [4., 5., 6.], [7., 8., 9.]]) input = input.view(1, 1, 3, 3) output = net(input) print("前向传播输出:") print(output) print() # Loss Function target = torch.tensor(60.) criterion = nn.MSELoss() loss = criterion(output, target) print("MSE loss:", loss) print() # Backprop net.zero_grad() # zeroes the gradient buffers of all parameters loss.backward() print("卷积核的梯度:") print(net.conv1.weight.grad) print() use_module = True if not use_module: # Update the weights weight = weight - learning_rate * gradient learning_rate = 0.01 for f in net.parameters(): f.data.sub_(f.grad.data * learning_rate) print("手动更新") print(list(net.parameters())) """ tensor([[[[2.5200, 1.3600], [0.0400, 3.8800]]]], requires_grad=True)] """ else: # However, as you use neural networks, you want to use various different update rules such as SGD, # Nesterov-SGD, Adam, RMSProp, etc. To enable this, we built a small package: torch.optim that # implements all these methods. Using it is very simple: import torch.optim as optim # create your optimizer optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.01) # in your training loop: optimizer.zero_grad() # zero the gradient buffers output = net(input) loss = criterion(output, target) loss.backward() optimizer.step() # Does the update print("optim更新") print(list(net.parameters())) """ tensor([[[[2.5200, 1.3600], [0.0400, 3.8800]]]], requires_grad=True)] """
|
最大值池化 |

对应代码

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F class Net(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(Net, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 1, 2, bias=False) # 默认padding=0 即valid卷积 def forward(self, x): # Max pooling over a (2, 2) window x = self.conv1(x) # x = F.avg_pool2d(x, 2) x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2) return x if __name__ == '__main__': net = Net() print("网络结构为:") print(net) print() weight1 = torch.tensor([3., 2., 1., 5.]) weight1 = weight1.view(1, 1, 2, 2) net.conv1._parameters['weight'].data = weight1 # 自定义卷积核 input = torch.tensor([[1., 2., 3.], # 自定义输入 [4., 5., 6.], [7., 8., 9.]]) input = input.view(1, 1, 3, 3) output = net(input) print("前向传播输出:") print(output) print() # Loss Function target = torch.tensor(60.) criterion = nn.MSELoss() loss = criterion(output, target) print("MSE loss:", loss) print() # Backprop net.zero_grad() # zeroes the gradient buffers of all parameters loss.backward() print("卷积核的梯度:") print(net.conv1.weight.grad) print() use_module = True if not use_module: # Update the weights weight = weight - learning_rate * gradient learning_rate = 0.01 for f in net.parameters(): f.data.sub_(f.grad.data * learning_rate) print("手动更新") print(list(net.parameters())) """ tensor([[[[2.5200, 1.3600], [0.0400, 3.8800]]]], requires_grad=True)] """ else: # However, as you use neural networks, you want to use various different update rules such as SGD, # Nesterov-SGD, Adam, RMSProp, etc. To enable this, we built a small package: torch.optim that # implements all these methods. Using it is very simple: import torch.optim as optim # create your optimizer optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.01) # in your training loop: optimizer.zero_grad() # zero the gradient buffers output = net(input) loss = criterion(output, target) loss.backward() optimizer.step() # Does the update print("optim更新") print(list(net.parameters())) """ tensor([[[[2.5200, 1.3600], [0.0400, 3.8800]]]], requires_grad=True)] """
|
参考资料 |
