概述
Skip list是平衡树的一种替代的数据结构,但是和红黑树不相同的是,跳表对于树的平衡的实现是基于一种随机化的算法的,这样也就是说跳表的插入和删除的工作是比较简单的。并且是Redis、LevelDB、nessDB、SkipDB等的底层结构,学习skip list为后面学习levelDB打下基础。
核心思想
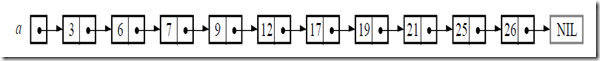
如果是一个简单的链表,如图1,那么我们知道在链表中查找一个元素I的话,需要将整个链表遍历一次。
图 1
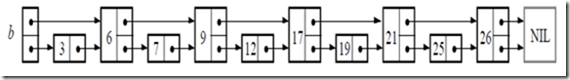
如果是说链表是排序的,并且节点中还存储了指向前面第二个节点的指针的话,如图2,那么在查找一个节点时,仅仅需要遍历N/2个节点即可。
图 2
这基本上就是跳表的核心思想,其实也是一种通过“空间来换取时间”的一个算法,通过在每个节点中增加了向前的指针,从而提升查找的效率。
跳表数据存储模型
我们定义:
如果一个基点存在k个向前的指针的话,那么陈该节点是k层的节点。
一个跳表的层MaxLevel定义为跳表中所有节点中最大的层数。
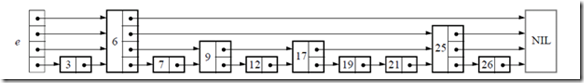
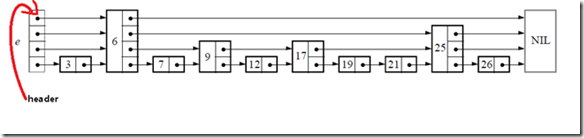
下面给出一个完整的跳表的图示:
那么我们该如何将该数据结构使用二进制存储呢?通过上面的跳表的很容易设计这样的数据结构:
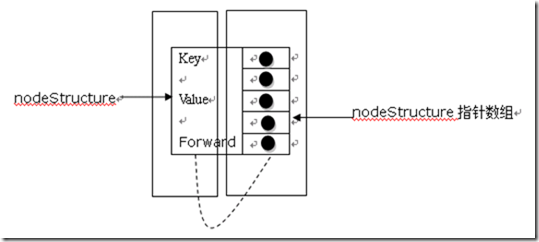
定义每个节点类型:
typedef struct NodeStructure *Node;
typedef struct NodeStructure
{
keyType key; // key值
valueType value; // value值
// 向前指针数组,根据该节点层数的不同指向不同大小的数组
NodeStructure *forward[1];
上面的每个结构体对应着图中的每个节点,如果一个节点是一层的节点的话(如7,12等节点),那么对应的forward将指向一个只含一个元素的数组,以此类推。
定义跳表数据类型:
// 定义跳表数据类型
typedef struct SkipList{
int level; /* Maximum level of the list
(1 more than the number of levels in the list) */
Node header; /* pointer to header */
} * SkipList;跳表数据类型中包含了维护跳表的必要信息,level表明跳表的层数,header如下所示:
定义辅助变量:
#define MAX_LEVEL 10
定义辅助方法:
创建节点
Node CreateNode(int level,int key,int value)
{
Node node=(NodeStructure *)malloc(sizeof(NodeStructure)+level*sizeof(NodeStructure*));
node->key=key;
node->value=value;
return node;
}
好的基本的数据结构定义已经完成,接下来来分析对于跳表的一个操作。
跳表代码实现
1 初始化
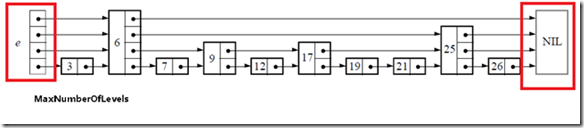
初始化的过程很简单,仅仅是生成下图中红线区域内的部分,也就是跳表的基础结构:
SkipList CreateSkiplist()
{
SkipList skiplist=(SkipList *)malloc(sizeof(struct SkipList));
skiplist->level=0;
skiplist->header=CreateNode(MAX_LEVEL-1,0,0);
for(int i=0;i<MAX_LEVEL;i++)
{
skiplist->header->forward[i]=NULL;
}
return skiplist;
}
2 查找
//搜索指定key的value
int Search(SkipList skiplist,int key)
{
Node pre,now=NULL;
pre=skiplist->header;
//从最高层开始搜
int k=skiplist->level;
for(int i=k-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
while((now=pre->forward[i])&&(now->key<=key))
{
if(now->key == key)
{
return now->value;
}
pre=now;
}
}
return NULL;
}
3 插入操作
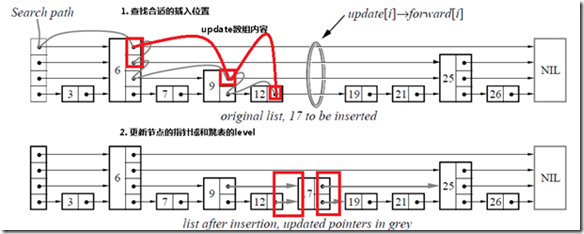
由于跳表数据结构整体上是有序的,所以在插入时,需要首先查找到合适的位置,然后就是修改指针(和链表中操作类似),然后更新跳表的level变量。
//随机产生层数
int randomLevel()
{
int k=1;
while (rand()%2)
k++;
k=(k<MAX_LEVEL)?k:MAX_LEVEL;
return k;
}
//插入节点
bool Insert(SkipList *skiplist,int key,int value)
{
Node update[MAX_LEVEL];
Node p, q = NULL;
p=skiplist->header;
int k=skiplist->level;
//从最高层往下查找需要插入的位置
//填充update
for(int i=k-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
//q!=NULL
while((q=p->forward[i])&&(q->key<key))
{
p=q;
}
update[i]=p;
}
// 这里已经查找到了合适的位置,并且update数组已经
// 填充好了元素
//不能插入相同的key
if(q&&q->key==key)
{
return false;
}
//产生一个随机层数K
//新建一个待插入节点q
//一层一层插入
k=randomLevel();
// 如果新生成的层数比跳表的层数大的话
// 增加整个跳表的层数
if(k>(skiplist->level))
{
for(int i=skiplist->level; i < k; i++)
{
// 在update数组中将新添加的层指向skiplist->header
update[i] = skiplist->header;
}
skiplist->level=k;
}
q=CreateNode(k,key,value);
//逐层更新节点的指针,和普通列表插入一样
for(int i=0;i<k;i++)
{
q->forward[i]=update[i]->forward[i];
update[i]->forward[i]=q;
}
return true;
}
4 删除某个节点
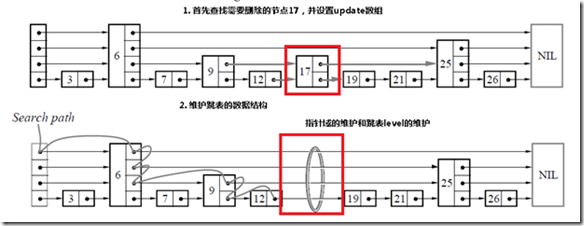
和插入是相同的,首先查找需要删除的节点,如果找到了该节点的话,那么只需要更新指针域,如果跳表的level需要更新的话,进行更新。
//删除指定的key
bool Delete(SkipList skiplist,int key)
{
Node update[MAX_LEVEL];
Node p,q=NULL;
p=skiplist->header;
//从最高层开始搜
int k=skiplist->level;
for(int i=k-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
while((q=p->forward[i])&&(q->key<key))
{
p=q;
}
update[i]=p;
}
if(q&&q->key==key)
{
//逐层删除,和普通列表删除一样
for(int i=0; i<skiplist->level; i++)
{
if(update[i]->forward[i]==q)
{
update[i]->forward[i]=q->forward[i];
}
}
free(q);
//如果删除的是最大层的节点,那么需要重新维护跳表的
for(int i=skiplist->level - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if(skiplist->header->forward[i]==NULL)
{
skiplist->level--;
}
}
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
5 参考文献
ftp://ftp.cs.umd.edu/pub/skipLists/skiplists.pdf
#define MAX_LEVEL 10
typedef struct NodeStructure *Node;
typedef struct NodeStructure
{
keyType key; // key值
valueType value; // value值
// 向前指针数组,根据该节点层数的不同指向不同大小的数组
NodeStructure *forward[1];
}NodeStructure;
typedef struct SkipList{
int level; /* Maximum level of the list
(1 more than the number of levels in the list) */
Node header; /* pointer to header */
} * SkipList;
Node CreateNode(int level,int key,int value)
{
Node node=(NodeStructure *)malloc(sizeof(NodeStructure)+level*sizeof(NodeStructure*));
node->key=key;
node->value=value;
return node;
}
SkipList CreateSkiplist()
{
SkipList skiplist=(SkipList *)malloc(sizeof(struct SkipList));
skiplist->level=0;
skiplist->header=CreateNode(MAX_LEVEL-1,0,0);
for(int i=0;i<MAX_LEVEL;i++)
{
skiplist->header->forward[i]=NULL;
}
return skiplist;
}
//搜索指定key的value
int Search(SkipList skiplist,int key)
{
Node pre,now=NULL;
pre=skiplist->header;
//从最高层开始搜
int k=skiplist->level;
for(int i=k-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
while((now=pre->forward[i])&&(now->key<=key))
{
if(now->key == key)
{
return now->value;
}
pre=now;
}
}
return NULL;
}
//随机产生层数
int randomLevel()
{
int k=1;
while (rand()%2)
k++;
k=(k<MAX_LEVEL)?k:MAX_LEVEL;
return k;
}
//插入节点
bool Insert(SkipList skiplist,int key,int value)
{
Node update[MAX_LEVEL];
Node p, q = NULL;
p=skiplist->header;
int k=skiplist->level;
//从最高层往下查找需要插入的位置
//填充update
for(int i=k-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
//q!=NULL
while((q=p->forward[i])&&(q->key<key))
{
p=q;
}
update[i]=p;
}
// 这里已经查找到了合适的位置,并且update数组已经
// 填充好了元素
//不能插入相同的key
if(q&&q->key==key)
{
return false;
}
//产生一个随机层数K
//新建一个待插入节点q
//一层一层插入
k=randomLevel();
// 如果新生成的层数比跳表的层数大的话
// 增加整个跳表的层数
if(k>(skiplist->level))
{
for(int i=skiplist->level; i < k; i++)
{
// 在update数组中将新添加的层指向skiplist->header
update[i] = skiplist->header;
}
skiplist->level=k;
}
q=CreateNode(k,key,value);
//逐层更新节点的指针,和普通列表插入一样
for(int i=0;i<k;i++)
{
q->forward[i]=update[i]->forward[i];
update[i]->forward[i]=q;
}
return true;
}
//删除指定的key
bool Delete(SkipList skiplist,int key)
{
Node update[MAX_LEVEL];
Node p,q=NULL;
p=skiplist->header;
//从最高层开始搜
int k=skiplist->level;
for(int i=k-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
while((q=p->forward[i])&&(q->key<key))
{
p=q;
}
update[i]=p;
}
if(q&&q->key==key)
{
//逐层删除,和普通列表删除一样
for(int i=0; i<skiplist->level; i++)
{
if(update[i]->forward[i]==q)
{
update[i]->forward[i]=q->forward[i];
}
}
free(q);
//如果删除的是最大层的节点,那么需要重新维护跳表的
for(int i=skiplist->level - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if(skiplist->header->forward[i]==NULL)
{
skiplist->level--;
}
}
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
void Print(SkipList skiplist)
{
//从最高层开始打印
nodeStructure *p,*q=NULL;
//从最高层开始搜
int k=skiplist->level;
for(int i=k-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
p=skiplist->header;
while(q=p->forward[i])
{
printf("%d -> ",p->value);
p=q;
}
printf("
");
}
printf("
");
}
int main()
{
SkipList skiplist=CreateSkiplist();
for(int i=1;i<=19;i++)
{
Insert(skiplist,i,i*2);
}
Print(skiplist);
//搜索
int i=Search(skiplist,4);
printf("i=%d
",i);
//删除
bool b=Delete(skiplist,4);
if(b)
printf("删除成功
");
Print(skiplist);
system("pause");
return 0;
}