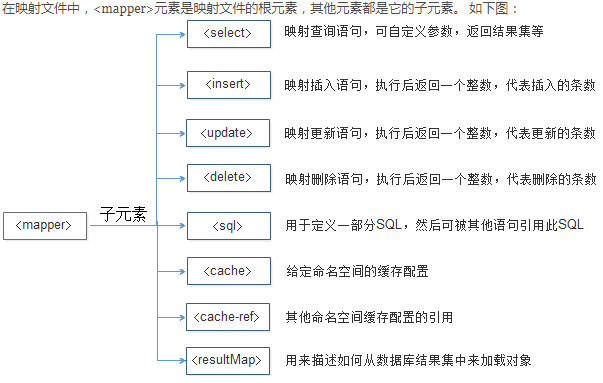
映射文件是mybatis框架中十分重要的文件,可以说,mybatis框架的强大之处就体现在映射文件的编写上。mapper.xml映射文件主要是用来编写sql语句的,以及一些结果集的映射关系的编写,还有就是缓存的一些配置等等。
一、select元素
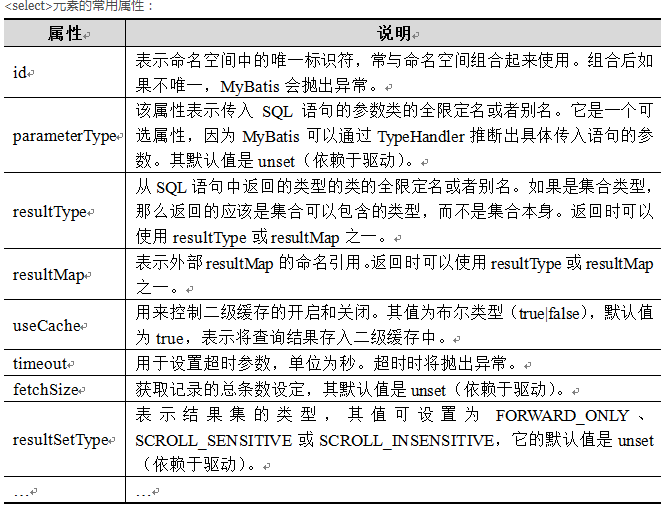
<select>元素就是sql查询语句。可以执行一些简单的查询操作,也可以是复杂的查询操作。例如:
<select id="findCustomerById" parameterType="Integer" resultType="com.itheima.po.Customer">
select * from t_customer where id = #{id}
</select>
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| statementType | 用于设置mybatis使用哪个JDBC的Statement工作,其值为statement、prepared(默认值)或callable,分别对应JDBC中的Statement、PreparedStatement和CallableStatement |
二、insert元素
<insert>元素用于映射插入语句,在执行完元素中定义的SQL语句后,会返回一个表示插入记录数的整数。
<insert>元素的配置示例如下:
<insert
id="addCustomer"
parameterType="com.itheima.po.Customer"
flushCache="true"
statementType="PREPARED"
keyProperty=""
keyColumn=""
useGeneratedKeys=""
timeout="20">

执行插入操作后,很多时候需要返回插入成功的数据生成的主键值,此时就可以通过上面讲解的3个属性来实现。
1、对于支持主键自助增长的数据库(如MySQL),可以通过如下配置实现:
<insert id="addCustomer" parameterType="com.itheima.po.Customer" keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true" >
insert into t_customer(username,jobs,phone) values(#{username},#{jobs},#{phone})
</insert>
使用以上配置后,执行插入后会返回插入成功的行数,以及插入行的主键值。
2、对于不支持主键自助增长的数据库(如Oracle),或者支持增长的数据库取消了主键自动增长的规则时,可以通过如下配置实现自定义生成主键:
<insert id="insertCustomer" parameterType="com.itheima.po.Customer">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="Integer" order="BEFORE">
select if(max(id) is null, 1, max(id) +1) as newId from t_customer
</selectKey>
insert into t_customer(id,username,jobs,phone) values(#{id},#{username},#{jobs},#{phone})
</insert>
解析:在执行以上配置时,selectKey元素会首先执行,它会通过自定义的语句来设置数据表中的主键(如果t_customer表中没有记录,则将id设置为1,否则就将id的最大值加1来作为新的主键),然后调用插入语句。
<selectKey
keyProperty="id"
resultType="Integer"
order="BEFORE"
statementType="Prepared" (默认的)
>
其中orde属性可以设置为before或者after。当设置为before时,那么它会首先执行selectkey元素中的配置来设置主键,然后在执行插入语句;如果设置为after,则相反。
三、update和delete元素
<update>和<delete>元素的使用比较简单,它们的属性配置也基本相同。
1、<update>和<delete>元素的常用属性如下:
<update
id="updateCustomer"
parameterType="com.itheima.po.Customer"
flushCache="true"
statementType="PREPARED"
timeout="20">
<delete
id="deleteCustomer"
parameterType="com.itheima.po.Customer"
flushCache="true"
statementType="PREPARED"
timeout="20">
2、<update>和<delete>元素的使用示例如下:
<update id="updateCustomer" parameterType="com.itheima.po.Customer">
update t_customer
set username=#{username},jobs=#{jobs},phone=#{phone}
where id=#{id}
</update>
<delete id="deleteCustomer" parameterType="Integer">
delete from t_customer where id=#{id}
</delete>
四、sql片段元素
sql片段,可以在mapper文件中的任何地方引用,主要作用是减少代码量,复用重复的字段。
例如:
<sql id="customerColumns">id,username,jobs,phone</sql>
定义sql片段,通过<include>元素的refid属性引用id为customerColumns的代码片段。
例如:
<select id="findCustomerById" parameterType="Integer" resultType="com.itheima.po.Customer">
select
<include refid="customerColumns"/>
from tableName
where id = #{id}
</select>
五、resultMap 结果集映射元素
<resultMap>元素表示结果映射集,是MyBatis中最重要也是最强大的元素。它的主要作用是定义映射规则、级联的更新以及定义类型转化器等。<resultMap>元素中包含了一些子元素,它的元素结构如下所示:
<resultMap type="" id="">
<constructor> <!-- 类在实例化时,用来注入结果到构造方法中-->
<idArg/> <!-- ID参数;标记结果作为ID-->
<arg/> <!-- 注入到构造方法的一个普通结果-->
</constructor>
<id/> <!-- 用于表示哪个列是主键-->
<result/> <!-- 注入到字段或JavaBean属性的普通结果-->
<association property="" /> <!-- 用于一对一关联 -->
<collection property="" /> <!-- 用于一对多关联 -->
<discriminator javaType=""> <!-- 使用结果值来决定使用哪个结果映射-->
<case value="" /> <!-- 基于某些值的结果映射 -->
</discriminator>
</resultMap>
<resultMap>元素的type属性表示需要映射的POJO,id属性是这个resultMap的唯一标识。它的子元素<constructor>用于配置构造方法(当一个POJO中未定义无参的构造方法时就可以使用<constructor>元素进行配置)。子元素<id>用于表示那个列是主键,而<result>用于表示POJO和数据表中普通列的映射关系。 <association>和<collection>用于处理多表时的关联关系,而<discriminator>元素主要用于处理一个单独的数据库查询返回很多不同数据类型结果集的情况。
在默认情况下,mybatis程序在运行时会自动的将查询到的数据与需要返回的对象的属性进行匹配赋值(需要表中的列名与对象的属性名称完全一致),然而在实际开发中属性名和列名可能不一致,这个时候就需要使用resultMap元素进行映射处理。
例如:简单的结果集映射
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="cn.jason.bootmybatis.model.Tests">
<id column="id" property="id" jdbcType="BIGINT"/>
<result column="name" property="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result column="age" property="age" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectByPrimaryKey" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select
<include refid="Base_Column_List"/>
from tests
where id = #{id,jdbcType=BIGINT}
</select>