

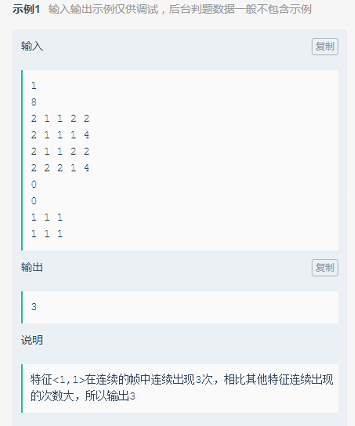
使用map的递推,java对象做key需要重写equeal,hashCode方法,使拥有相同属性值的对象被识别为同一对象。
import java.util.*; class Cat{ public Integer f1; public Integer f2; public Cat(int f11,int f22){ f1 = f11; f2 = f22; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj)return true; if(obj == null||getClass()!=obj.getClass()){ return false; } Cat p = (Cat)obj; if(f1!=null?!f1.equals(p.f1):p.f1!=null){ return false; } if(f2!=null?!f2.equals(p.f2):p.f2!=null){ return false; } return true; } @Override public int hashCode() { return f1!=null&&f2!=null?f1.hashCode()+ f2.hashCode():0; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); int n = in.nextInt(); for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ int m = in.nextInt(); Map<Cat, Integer> map = new HashMap<Cat, Integer>(); int res = 0; for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ int o = in.nextInt(); Map<Cat, Integer> map1 = new HashMap<Cat, Integer>(); map1.clear(); for(int k=0;k<o;k++){ int f1 = in.nextInt(); int f2 = in.nextInt(); Cat cat = new Cat(f1,f2); int step=0; if(map.get(cat) == null) step = 1; else step = map.get(cat)+1; map1.put(cat, step); res = Math.max(res, step); } map = map1; } System.out.println(res); } return; } }