刚开始自学数据结构,感觉就是理论的部分都很好理解,但是代码就是另一回事了,昨天琢磨了很久二叉树重构这个题,又回顾了一下视频讲解,酝酿了好久终于写出来了
题目:
Description
In general, given the preorder traversal sequence and postorder traversal sequence of a binary tree, we cannot determine the binary tree.
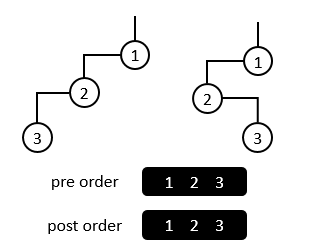
Figure 1
In Figure 1 for example, although they are two different binary tree, their preorder traversal sequence and postorder traversal sequence are both of the same.
But for one proper binary tree, in which each internal node has two sons, we can uniquely determine it through its given preorder traversal sequence and postorder traversal sequence.
Label n nodes in one binary tree using the integers in [1, n], we would like to output the inorder traversal sequence of a binary tree through its preorder and postorder traversal sequence.
Input
The 1st line is an integer n, i.e., the number of nodes in one given binary tree,
The 2nd and 3rd lines are the given preorder and postorder traversal sequence respectively.
Output
The inorder traversal sequence of the given binary tree in one line.
Example
Input
5 1 2 4 5 3 4 5 2 3 1
Output
4 2 5 1 3
Restrictions
For 95% of the estimation, 1 <= n <= 1,000,00
For 100% of the estimation, 1 <= n <= 4,000,000
The input sequence is a permutation of {1,2...n}, corresponding to a legal binary tree.
Time: 2 sec
Memory: 256 MB
Hints
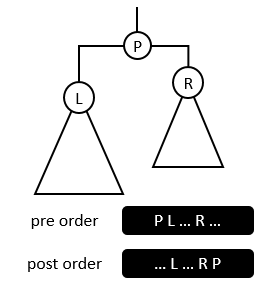
Figure 2
In Figure 2, observe the positions of the left and right children in preorder and postorder traversal sequence.
ac代码:

#include <cmath> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #define MAX_N 4000000 struct node{ node *lchild,*rchild; int val; }; int pre[MAX_N],post[MAX_N]; node *Build(int s1,int e1,int s2,int e2){ node *root=new node; root->val=pre[s1]; root->lchild=root->rchild=NULL; int pos,left_num; if(s2==e2) return root; // 后续范围长度为0时返回此时节点 for(int i=s2;i<=e2;i++){ if(pre[s1+1]==post[i]){ pos=i; break; // 找到左子树的根节点在后续排列中的位置; } } left_num=pos-s2+1; root->lchild=Build(s1+1,s1+left_num,s2,pos); root->rchild=Build(s1+left_num+1,e1,pos+1,e2-1); return root; } void solve(node *root){ if(!root) return; solve(root->lchild); printf("%d ",root->val); solve(root->rchild); } int main(void){ int n; scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&pre[i]); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&post[i]); node *R=Build(0,n-1,0,n-1); solve(R); return 0; }
