上一节的代码是spring-boot的入门程序,也是官方文档上的一个程序。这一节会引入spring-boot官方文档推荐的方式来开发代码,并引入我们在spring开发中service层等的调用。
1、代码结构如下

2、pom.xml

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 3 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd"> 4 5 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> 6 7 <groupId>com.xxx</groupId> 8 <artifactId>myboot</artifactId> 9 <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> 10 11 <properties> 12 <java.version>1.8</java.version><!-- 官方推荐 --> 13 </properties> 14 <!-- 引入spring-boot-starter-parent做parent是最好的方式, 15 但是有时我们可能要引入我们自己的parent,此时解决方式有两种: 16 1)我们自己的parent的pom.xml的parent设为spring-boot-starter-parent(没有做过验证,但是感觉可行) 17 2)使用springboot文档中的方式:见spring-boot-1.2.5-reference.pdf的第13页 18 --> 19 <parent> 20 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 21 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> 22 <version>1.2.5.RELEASE</version> 23 </parent> 24 25 <!-- <dependencyManagement> 26 <dependencies> 27 <dependency> 28 Import dependency management from Spring Boot 29 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 30 <artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId> 31 <version>1.2.5.RELEASE</version> 32 <type>pom</type> 33 <scope>import</scope> 34 </dependency> 35 </dependencies> 36 </dependencyManagement> --> 37 38 <!-- 引入实际依赖 --> 39 <dependencies> 40 <dependency> 41 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 42 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> 43 </dependency> 44 </dependencies> 45 46 <build> 47 <plugins> 48 <!-- 用于将应用打成可直接运行的jar(该jar就是用于生产环境中的jar) 值得注意的是,如果没有引用spring-boot-starter-parent做parent, 49 且采用了上述的第二种方式,这里也要做出相应的改动 --> 50 <plugin> 51 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 52 <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> 53 </plugin> 54 </plugins> 55 </build> 56 </project>
说明:pom.xml文件与上一节的完全一样。
3、Application.java

1 package com.xxx.firstboot; 2 3 import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; 4 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; 5 6 /** 7 * @EnableAutoConfiguration:spring boot的注解,一般只用于主类, 8 * 是无xml配置启动的关键部分,明确指定了扫描包的路径为其修饰的主类的包(这也就是为什么主类要放在根包路径下的原因) 9 * 10 * @ComponentScan 进行包的扫描,扫描路径由@EnableAutoConfiguration指定了 11 * 12 * 主类要位于根包路径下,方便之后的扫描(We generally recommend that you locate your main application class in a root package above other classes.) 13 */ 14 @SpringBootApplication //same as @Configuration+@EnableAutoConfiguration+@ComponentScan 15 public class Application { 16 /** 17 * spring boot的入口,在整个子项目在内, 18 * 只能有一个main方法,否则spring boot启动不起来 19 */ 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); 22 } 23 24 }
注意:
- 主类要位于根包路径下(例如,com.xxx.firstboot),这是推荐做法,方便扫描
- 每一个jar(即每一个子项目)都要有一个主方法,用于启动该jar(也就是一个微服务)
- 在主类上添加注解@SpringBootApplication,该注解相当于添加了如下三个注解
- @Configuration:该注解指明该类由spring容器管理
- @EnableAutoConfiguration:该注解是无xml配置启动的关键部分
- @ComponentScan:该注解指定扫描包(如果主类不是位于根路径下,这里需要指定扫描路径),类似于spring的包扫描注解
4、application.properties

1 #user info 2 user.id=1 3 user.username=zhaojigang 4 user.password=123
注意:
- application.properties文件是spring-boot的默认文件,一般各种配置(包括:数据源配置,httpclient配置等)都配在这里就好
5、User.java

1 package com.xxx.firstboot.domain; 2 3 import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; 4 import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; 5 6 /** 7 * @ConfigurationProperties(prefix="user") 8 * 自动读取application.properties(是spring-boot默认查找的文件)文件中的user.*的属性 9 * 在没有使用@ConfigurationProperties的情况下,可以使用@Value("${user.id}")来一个个指定属性的值 10 * 11 * 注意:如果要使用@ConfigurationProperties和@Value,需要将该bean添加@Component, 12 * 因为在后边的对该类的使用中,需要直接将该类使用@Autowire注解注入,这样这些属性的自动注入才起作用, 13 * 具体使用查看"UserService" 14 */ 15 @Component 16 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix="user") 17 public class User { 18 19 //@Value("${user.id}") 20 private int id; 21 22 //@Value("wangna") 23 private String username; 24 25 private String password; 26 27 public int getId() { 28 return id; 29 } 30 31 public void setId(int id) { 32 this.id = id; 33 } 34 35 public String getUsername() { 36 return username; 37 } 38 39 public void setUsername(String username) { 40 this.username = username; 41 } 42 43 public String getPassword() { 44 return password; 45 } 46 47 public void setPassword(String password) { 48 this.password = password; 49 } 50 51 }
注意:
- 该类就是一个普通的model,在ssm框架中我们并没有将这样的model归给spring容器去管理,在这里使用@Component注解将其交由spring容器去处理,这样在之后的使用中,就可以直接将该model注入到其使用类中。
- 在该类上添加了@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="user")注解,这样的意思就是可以自动扫描application.properties文件相关前缀的配置,并根据名称配置到该类的每一个属性上去
- 也可以在属性上使用@Value注解单独复值,当然前提是没有配置@ConfigurationProperties,如果配置了,@Value注解失效
6、UserService.java

1 package com.xxx.firstboot.service; 2 3 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; 4 import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; 5 6 import com.xxx.firstboot.domain.User; 7 8 @Service 9 public class UserService { 10 11 @Autowired 12 private User user; 13 14 public User getUser(){ 15 return user; 16 } 17 18 }
注意:
- 这里直接注入了User,这和类正是上边的那个model
7、UserController.java

1 package com.xxx.firstboot.web; 2 3 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; 4 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; 5 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; 6 7 import com.xxx.firstboot.domain.User; 8 import com.xxx.firstboot.service.UserService; 9 /** 10 * @RestController:spring mvc的注解, 11 * 相当于@Controller与@ResponseBody的合体,可以直接返回json 12 */ 13 @RestController 14 @RequestMapping("/user") 15 public class UserController { 16 17 @Autowired 18 private UserService userService; 19 20 @RequestMapping("/getUser") 21 public User getUser() { 22 return userService.getUser(); 23 } 24 25 }
说明:
- 这个类其实就是开发中,开发一个spring-boot程序的最基本最常用的方式。(在微服务应用中,用到类似于"Java企业应用开发实践"系列中的父子模块开发,之后再说)
- 相对于ssm而言,spring-boot的读取属性文件的方式也相当容易,读取属性文件常用的三种方式
- 使用FileUtil去读:见第一章 属性文件操作工具类
- 使用如上的注解实现(最推荐的方式)
- 使用Environment这个类来获取就行(这个可能写错类名了)
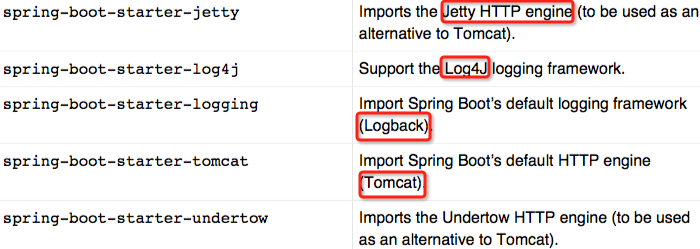
对于spring-boot而言,其本身有很多集成的jar包(见下边),我们可以根据自己的需求引入相应的jar,但是暂无与mybatis集成的jar。
spring-boot相关的依赖包(可以根据需求自己引入):