上一篇讲的是容器工厂的原型。
我们可以不必通过new关键之创建实例,可以直接取容器里面的实例。
我们可以发现,在对比他们的地址值的时候,他们是相同的为true。
如果我们需要的是不一样的呢。也就是有一些特殊的操作需要到的是单例地址。
下面让我们看看如何创建一个可以随意切换原型&单例的容器工厂吧。
我们在上一篇原型的容器工厂上稍微做一下改造就OK了!
添加一个描述bean的类,封装了配置文件bean的类
public class Definition { //bean的唯一标识 private String id; //bean的完整类名 private String className; //bean的创建方式 private String scope = "singleton"; public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getClassName() { return className; } public void setClassName(String className) { this.className = className; } public String getScope() { return scope; } public void setScope(String scope) { this.scope = scope; } }
第二,我们需要在容器工厂的类里面做出稍稍的改动。
如下:
public class ContainerFactoryTwo { //单例的容器(Singleton) private static Map<String,Object> singleton = new HashMap<String,Object>(); //原型的容器(prototype) private static Map<String,Definition> prototype = new HashMap<String,Definition>(); //初始化 public ContainerFactoryTwo(String resourcePath){ initPrototype(resourcePath); initSingleton(); } public void initPrototype(String resourcePath){ //创建SAX解析器 SAXReader reader = new SAXReader(); try { Document document = reader.read(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(resourcePath)); Element root = document.getRootElement(); List<Element> list = root.elements(); for (Element e:list){ String id = e.attributeValue("id"); String className = e.attributeValue("class"); String scope = e.attributeValue("scope"); //构建bean的定义 Definition def = new Definition(); def.setId(id); def.setClassName(className); if(scope!=null){ def.setScope(scope); } prototype.put(id,def); } } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } /** * 初始化单利容器 */ private void initSingleton(){ //遍历prototype里面的值做出判断 for (String key : prototype.keySet()) { Definition def = prototype.get(key); //如果是判断是否是singleton if("singleton".equals(def.getScope())){ try { //将实例化对象保存到singleton的map里 singleton.put(key, Class.forName(def.getClassName()).newInstance()); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } } public Object getBean(String name){ return getContainerBean(name); } public <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> clazz){ return (T)getContainerBean(name); } private Object getContainerBean(String name){ //获取作用域属性 String scope = prototype.get(name).getScope(); try { //三目运算,singleton在scope里面?是的话就之前前者(K对应的已经是一个Object对象)否则执行后者,通过类加载返回一个对象 return ("singleton".equals(scope))?singleton.get(name): Class.forName(prototype.get(name).getClassName()).newInstance(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }
测试:
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建工厂 ContainerFactoryTwo factory = new ContainerFactoryTwo("beans.xml"); Phone phone1 = factory.getBean("OppoPhone", Phone.class);//singleton Phone phone2 = factory.getBean("OppoPhone", Phone.class);//singleton Pad pad1 = (Pad) factory.getBean("OppoPad", Pad.class);//prototype Pad pad2 = (Pad) factory.getBean("OppoPad", Pad.class);//prototype System.out.println(phone1==phone2); System.out.println(pad1==pad2); //phone1.call(); } }
结果为:
true
false
注意:在XML文件里面的scope
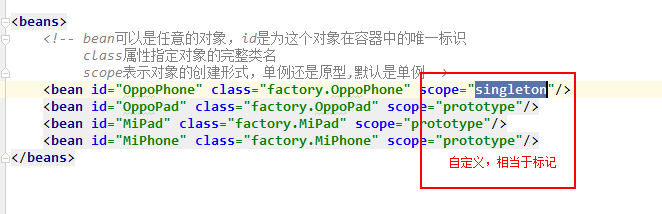
决定单例或者是原型容器在于Map