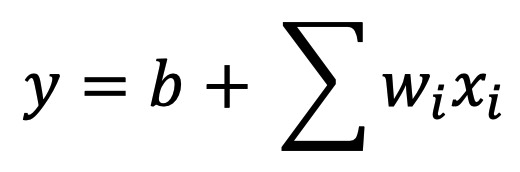#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: utf-8
import torch
import time
# init variable a, b as 1000 dimension vector
n = 1000
a = torch.ones(n)
b = torch.ones(n)
# define a timer class to record time
class Timer(object):
"""Record multiple running times."""
def __init__(self):
self.times = []
self.start()
def start(self):
# start the timer
self.start_time = time.time()
def stop(self):
# stop the timer and record time into a list
self.times.append(time.time() - self.start_time)
return self.times[-1]
def avg(self):
# calculate the average and return
return sum(self.times)/len(self.times)
def sum(self):
# return the sum of recorded time
return sum(self.times)
timer = Timer()
c = torch.zeros(n)
for i in range(n):
c[i] = a[i] + b[i]
'%.5f sec' % timer.stop()
timer.start()
d = a + b
'%.5f sec' % timer.stop()
# import packages and modules
get_ipython().run_line_magic('matplotlib', 'inline')
import torch
from IPython import display
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import random
print(torch.__version__)
# ### 线性回归模型从零开始的实现
# set input feature number
num_inputs = 2
# set example number
num_examples = 1000
# set true weight and bias in order to generate corresponded label
true_w = [2, -3.4]
true_b = 4.2
features = torch.randn(num_examples, num_inputs,
dtype=torch.float32)
labels = true_w[0] * features[:, 0] + true_w[1] * features[:, 1] + true_b
labels += torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0, 0.01, size=labels.size()),
dtype=torch.float32)
# ### 使用图像来展示生成的数据
plt.scatter(features[:, 1].numpy(), labels.numpy(), 1);
# ### 读取数据集
def data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
num_examples = len(features)
indices = list(range(num_examples))
random.shuffle(indices) # random read 10 samples
for i in range(0, num_examples, batch_size):
j = torch.LongTensor(indices[i: min(i + batch_size, num_examples)]) # the last time may be not enough for a whole batch
yield features.index_select(0, j), labels.index_select(0, j)
batch_size = 10
for X, y in data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
print(X, '
', y)
break
# ### 模型初始化
w = torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0, 0.01, (num_inputs, 1)), dtype=torch.float32)
b = torch.zeros(1, dtype=torch.float32)
w.requires_grad_(requires_grad=True)
b.requires_grad_(requires_grad=True)
# ### 定义模型
# 定义用来训练参数的训练模型:
# $$ mathrm{price} = w_{mathrm{area}} cdot mathrm{area} + w_{mathrm{age}} cdot mathrm{age} + b $$
# In[19]:
def linreg(X, w, b):
return torch.mm(X, w) + b
# ### 定义损失函数
# 我们使用的是均方误差损失函数:
# $$l^{(i)}(mathbf{w}, b) = frac{1}{2} left(hat{y}^{(i)} - y^{(i)}
ight)^2,$$
# In[16]:
def squared_loss(y_hat, y):
return (y_hat - y.view(y_hat.size())) ** 2 / 2
# ### 定义优化函数
# 在这里优化函数使用的是小批量随机梯度下降:
# $$(mathbf{w},b) leftarrow (mathbf{w},b) - frac{eta}{|mathcal{B}|} sum_{i in mathcal{B}} partial_{(mathbf{w},b)} l^{(i)}(mathbf{w},b)$$
# In[17]:
def sgd(params, lr, batch_size):
for param in params:
param.data -= lr * param.grad / batch_size # ues .data to operate param without gradient track
# ### 训练
# 当数据集、模型、损失函数和优化函数定义完了之后就可来准备进行模型的训练了。
# In[20]:
# super parameters init
lr = 0.03
num_epochs = 5
net = linreg
loss = squared_loss
# training
for epoch in range(num_epochs): # training repeats num_epochs times
# in each epoch, all the samples in dataset will be used once
# X is the feature and y is the label of a batch sample
for X, y in data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
l = loss(net(X, w, b), y).sum()
# calculate the gradient of batch sample loss
l.backward()
# using small batch random gradient descent to iter model parameters
sgd([w, b], lr, batch_size)
# reset parameter gradient
w.grad.data.zero_()
b.grad.data.zero_()
train_l = loss(net(features, w, b), labels)
print('epoch %d, loss %f' % (epoch + 1, train_l.mean().item()))
# In[21]:
w, true_w, b, true_b
# ### 线性回归模型使用pytorch的简洁实现
# In[22]:
import torch
from torch import nn
import numpy as np
torch.manual_seed(1)
print(torch.__version__)
torch.set_default_tensor_type('torch.FloatTensor')
# ### 生成数据集
# 在这里生成数据集跟从零开始的实现中是完全一样的。
# In[23]:
num_inputs = 2
num_examples = 1000
true_w = [2, -3.4]
true_b = 4.2
features = torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0, 1, (num_examples, num_inputs)), dtype=torch.float)
labels = true_w[0] * features[:, 0] + true_w[1] * features[:, 1] + true_b
labels += torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0, 0.01, size=labels.size()), dtype=torch.float)
# ### 读取数据集
# In[24]:
import torch.utils.data as Data
batch_size = 10
# combine featues and labels of dataset
dataset = Data.TensorDataset(features, labels)
# put dataset into DataLoader
data_iter = Data.DataLoader(
dataset=dataset, # torch TensorDataset format
batch_size=batch_size, # mini batch size
shuffle=True, # whether shuffle the data or not
num_workers=2, # read data in multithreading
)
# In[27]:
for X, y in data_iter:
print(X, '
', y)
break
# ### 定义模型
# In[28]:
class LinearNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature):
super(LinearNet, self).__init__() # call father function to init
self.linear = nn.Linear(n_feature, 1) # function prototype: `torch.nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias=True)`
def forward(self, x):
y = self.linear(x)
return y
net = LinearNet(num_inputs)
print(net)
# In[29]:
# ways to init a multilayer network
# method one
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(num_inputs, 1)
# other layers can be added here
)
# method two
net = nn.Sequential()
net.add_module('linear', nn.Linear(num_inputs, 1))
# net.add_module ......
# method three
from collections import OrderedDict
net = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
('linear', nn.Linear(num_inputs, 1))
# ......
]))
print(net)
print(net[0])
# ### 初始化模型参数
# In[30]:
from torch.nn import init
init.normal_(net[0].weight, mean=0.0, std=0.01)
init.constant_(net[0].bias, val=0.0) # or you can use `net[0].bias.data.fill_(0)` to modify it directly
# In[31]:
for param in net.parameters():
print(param)
# ### 定义损失函数
# In[32]:
loss = nn.MSELoss() # nn built-in squared loss function
# function prototype: `torch.nn.MSELoss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')`
# ### 定义优化函数
# In[33]:
import torch.optim as optim
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.03) # built-in random gradient descent function
print(optimizer) # function prototype: `torch.optim.SGD(params, lr=, momentum=0, dampening=0, weight_decay=0, nesterov=False)`
# In[34]:
##trainning
num_epochs = 3
for epoch in range(1, num_epochs + 1):
for X, y in data_iter:
output = net(X)
l = loss(output, y.view(-1, 1))
optimizer.zero_grad() # reset gradient, equal to net.zero_grad()
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
print('epoch %d, loss: %f' % (epoch, l.item()))
# In[35]:
# result comparision
dense = net[0]
print(true_w, dense.weight.data)
print(true_b, dense.bias.data)
# In[ ]: