原文地址 http://blog.csdn.net/llxmedici/article/details/6282372
打算跟着友善之臂的《mini2440 linux移植开发指南》来做个LED驱动,虽然LED的原理简单得不能再简单了,但是要把kernel中针对于s3c24**的GPIO的一些数据结构,还有函数搞清楚也不是那么轻松的事,所以本文主要简单地说明下LED驱动中的相关数据结构以及函数/宏的定义,并对驱动加以验证
***************************************************************************
注意:在/arch/arm/mach-s3c2410/include/mach/gpio-fns.h源代码中有如下说明:
16/* These functions are in the to-be-removed category and it is strongly
17 * encouraged not to use these in new code. They will be marked deprecated
18 * very soon.
19 *
20 * Most of the functionality can be either replaced by the gpiocfg calls
21 * for the s3c platform or by the generic GPIOlib API.
22 *
23 * As of 2.6.35-rc, these will be removed, with the few drivers using them
24 * either replaced or given a wrapper until the calls can be removed.
25*/
该头文件包括:
static inline void s3c2410_gpio_cfgpin(unsigned int pin, unsigned int cfg)
该函数直接使用
linux/arch/arm/plat-s3c/gpio-config.c中的
int s3c_gpio_cfgpin(unsigned int pin, unsigned int config)
即可
***************************************************************************
首先看一下设备初始化程序:
85 /*
86 * 设备初始化
87 */
88 static int __init dev_init(void)
89 {
90 int ret;
91 int i;
92 for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
93 //设置 LED 对应的端口寄存器为输出(OUTPUT)
94 if (s3c_gpio_cfgpin(led_table[i], led_cfg_table[i])<0)
printk(KERN_INFO "config pin %d failed", i);
95 printk(KERN_INFO "config pin %d failed", i);
95 //设置 LED 对应的端口寄存器为低电平输出,在模块加载> 结束后,四个 LED 应该是全部都是发光
96 状态
97 s3c2410_gpio_setpin(led_table[i], 0);
98 }
99 ret = misc_register(&misc); //注册设备
100 printk (DEVICE_NAME"/tinitialized/n"); //打印初始化信息
101 return ret;
102 }
可以看到,这里涉及到两个函数,分别是s3c2410_gpio_cfgpin,s3c2410_gpio_setpin,这两个函数分别对四个LED进行配置,从函数名来看,cfgpin对引脚寄存器状态进行配置,而setpin应该是对寄存器数据值进行配置,我们在分析函数之前先弄清楚传入的参数到底是什么。
led_table[i]
28 //LED 对应的 GPIO 端口列表
29 static unsigned long led_table [] = {
30 S3C2410_GPB(5),
31 S3C2410_GPB(6),
32 S3C2410_GPB(7),
33 S3C2410_GPB(8),
34 };
这里S3C2410_GPB宏定义在mach/gpio-nrs.h中
/* GPIO bank sizes */
#define S3C2410_GPIO_A_NR (32)
#define S3C2410_GPIO_B_NR (32)
#define S3C2410_GPIO_C_NR (32)
#define S3C2410_GPIO_D_NR (32)
#define S3C2410_GPIO_E_NR (32)
#define S3C2410_GPIO_F_NR (32)
#define S3C2410_GPIO_G_NR (32)
#define S3C2410_GPIO_H_NR (32)
#define S3C2410_GPIO_J_NR (32) /* technically 16. */
#define S3C2410_GPIO_K_NR (32) /* technically 16. */
#define S3C2410_GPIO_L_NR (32) /* technically 15. */
#define S3C2410_GPIO_M_NR (32) /* technically 2. */
#if CONFIG_S3C_GPIO_SPACE != 0
#error CONFIG_S3C_GPIO_SPACE cannot be zero at the moment
#endif
#define S3C2410_GPIO_NEXT(__gpio) /
((__gpio##_START) + (__gpio##_NR) + CONFIG_S3C_GPIO_SPACE + 0)
//##是粘贴的意思,即把前面的()里面的内容粘贴在这里
//这里的CONFIG_S3C_GPIO_SPAC是内核配置选项,在.config中可以找到,我的配置为:
CONFIG_S3C_GPIO_SPACE = 0
enum s3c_gpio_number {
S3C2410_GPIO_A_START = 0,
S3C2410_GPIO_B_START = S3C2410_GPIO_NEXT(S3C2410_GPIO_A),
S3C2410_GPIO_C_START = S3C2410_GPIO_NEXT(S3C2410_GPIO_B),
S3C2410_GPIO_D_START = S3C2410_GPIO_NEXT(S3C2410_GPIO_C),
S3C2410_GPIO_E_START = S3C2410_GPIO_NEXT(S3C2410_GPIO_D),
S3C2410_GPIO_F_START = S3C2410_GPIO_NEXT(S3C2410_GPIO_E),
S3C2410_GPIO_G_START = S3C2410_GPIO_NEXT(S3C2410_GPIO_F),
S3C2410_GPIO_H_START = S3C2410_GPIO_NEXT(S3C2410_GPIO_G),
S3C2410_GPIO_J_START = S3C2410_GPIO_NEXT(S3C2410_GPIO_H),
S3C2410_GPIO_K_START = S3C2410_GPIO_NEXT(S3C2410_GPIO_J),
S3C2410_GPIO_L_START = S3C2410_GPIO_NEXT(S3C2410_GPIO_K),
S3C2410_GPIO_M_START = S3C2410_GPIO_NEXT(S3C2410_GPIO_L),
};
#define S3C2410_GPB(_nr) (S3C2410_GPIO_B_START + (_nr))
因此,以S3C2410_GPB(5)为例,其宏展开为:
S3C2410_GPIO_NEXT(S3C2410_GPIO_A) +5 =>
(S3C2410_GPIO_A_START +S3C2410_GPIO_A_NR + CONFIG_S3C_GPIO_SPACE + 0) +5 =>
很显然, S3C2410_GPB(5)就是从GPA的首地址+GPA个数+GPB的offset就是当前GPB的IO偏移量,即
0+32+5=37, 同理
S3C2410_GPB(0) 相当于 32
30 S3C2410_GPB(5) 相当于 37
31 S3C2410_GPB(6) 相当于 38
32 S3C2410_GPB(7) 相当于 39
33 S3C2410_GPB(8) 相当于 40
***************************************************************************
led_cfg_table[i]
36 //LED 对应端口将要输出的状态列表
37 static unsigned int led_cfg_table [] = {
38 S3C2410_GPIO_OUTPUT,
39 S3C2410_GPIO_OUTPUT,
40 S3C2410_GPIO_OUTPUT,
41 S3C2410_GPIO_OUTPUT,
42 };
S3C2410_GPIO_OUTPUT定义在mach/regs-gpio.h
#define S3C2410_GPIO_LEAVE (0xFFFFFFFF) // 最后两位是设置,11表示RESERVE
#define S3C2410_GPIO_INPUT (0xFFFFFFF0) /* not available on A */ // 最后两位是设置,00表示INPUT
#define S3C2410_GPIO_OUTPUT (0xFFFFFFF1) // 最后两位是设置,01表示OUTPUT
#define S3C2410_GPIO_IRQ (0xFFFFFFF2) /* not available for all */
#define S3C2410_GPIO_SFN2 (0xFFFFFFF2) /* bank A => addr/cs/nand */
#define S3C2410_GPIO_SFN3 (0xFFFFFFF3) /* not available on A */
***************************************************************************
根据前面的分析,s3c2410传入了当前GPIO的偏移地址,以及OUTPUT状态
现在我们深入前面的两个函数:
定义在linux/arch/arm/plat-s3c/gpio-config.c
int s3c_gpio_cfgpin(unsigned int pin, unsigned int config)
{
struct s3c_gpio_chip *chip = s3c_gpiolib_getchip(pin); //得到对应GPIO结构体首指针,里面包含了该GPIO的各种参数
unsigned long flags;
int offset;
int ret;
if (!chip)
return -EINVAL; // 没找到的话,返回invalid
offset = pin - chip->chip.base; // 否则offset等于该GPIO引脚相对于GPX(0)的偏移量,每个偏移1
s3c_gpio_lock(chip, flags); // 自旋锁锁住该GPIO,通过chip指针指向lock,看下面的define和图
ret = s3c_gpio_do_setcfg(chip, offset, config); //设置该GPIO状态寄存器的数值为config
s3c_gpio_unlock(chip, flags); // 解锁
// 自旋锁操作
/* locking wrappers to deal with multiple access to the same gpio bank */
//#define s3c_gpio_lock(_oc, _fl) spin_lock_irqsave(&(_oc)->lock, _fl)
//#define s3c_gpio_unlock(_oc, _fl) spin_unlock_irqrestore(&(_oc)->lock, _fl)
//s3c_gpio_do_setcfg操作
static inline int s3c_gpio_do_setcfg(struct s3c_gpio_chip *chip,
unsigned int off, unsigned int config)
{
return (chip->config->set_config)(chip, off, config);
}
//这里的set_config是一个函数指针,由后面的分析知道,如果针对GPA,该函数指针指向s3c_gpio_setcfg_s3c24xx_a ,如果针对GPX应该是指向s3c_gpio_setcfg_s3c24xx——但发现,如果是其他GPX,根本没有定义set_config!!!(这个问题已经解决,见后文s3c24xx_gpiolib_init函数,事实上,其余的config的确指向s3c_gpio_do_setcfg函数)
struct s3c_gpio_cfg s3c24xx_gpiocfg_default = {
.set_config = s3c_gpio_setcfg_s3c24xx,
.get_config = s3c_gpio_getcfg_s3c24xx,
};
int s3c_gpio_setcfg_s3c24xx_a(struct s3c_gpio_chip *chip, unsigned int off, unsigned int cfg)
{
void __iomem *reg = chip->base; // GPXCON的物理基地址
unsigned int shift = off; // 每个GPA对应一位
u32 con;
if (s3c_gpio_is_cfg_special(cfg)) { //OUTPUT状态是否为(0xfffffffX),是,返回1
cfg &= 0xf; // cfg = 0xX
/* Map output to 0, and SFN2 to 1 */ 本实验不会运行到这
cfg -= 1;
if (cfg > 1)
return -EINVAL;
cfg <<= shift;
}
con = __raw_readl(reg); // 先读出该GPXCON的值,32位
con &= ~(0x1 << shift); //
con |= cfg; //
__raw_writel(con, reg); // 将新值写入GPXCON
PS:
#define __raw_writeb(v,a) (__chk_io_ptr(a), *(volatile unsigned char __force *)(a) = (v))
#define __raw_writew(v,a) (__chk_io_ptr(a), *(volatile unsigned short __force *)(a) = (v))
#define __raw_writel(v,a) (__chk_io_ptr(a), *(volatile unsigned int __force *)(a) = (v))
#define __raw_readb(a) (__chk_io_ptr(a), *(volatile unsigned char __force *)(a))
#define __raw_readw(a) (__chk_io_ptr(a), *(volatile unsigned short __force *)(a))
#define __raw_readl(a) (__chk_io_ptr(a), *(volatile unsigned int __force *)(a))
return 0;
}
如果针对GPX情况
int s3c_gpio_setcfg_s3c24xx(struct s3c_gpio_chip *chip,
unsigned int off, unsigned int cfg)
{
void __iomem *reg = chip->base;
unsigned int shift = off * 2; // 每个GPX对应2位
u32 con;
if (s3c_gpio_is_cfg_special(cfg)) {
cfg &= 0xf;
if (cfg > 3)
return -EINVAL;
cfg <<= shift; // 将cfg的0,1两位左移offset
}
con = __raw_readl(reg); // 读对应的GPXCON值
con &= ~(0x3 << shift); // 将GPXCON(pin)的两bits请0
con |= cfg; // 设置config值
__raw_writel(con, reg); // 写入新的GPXCON
return 0;
}
return ret;
} // end s3c_gpio_cfgpin
这里涉及到了一个重要的数据结构,s3c_gpio_chip,此数据结构比较复杂,我贴出这个数据结构的结构图:
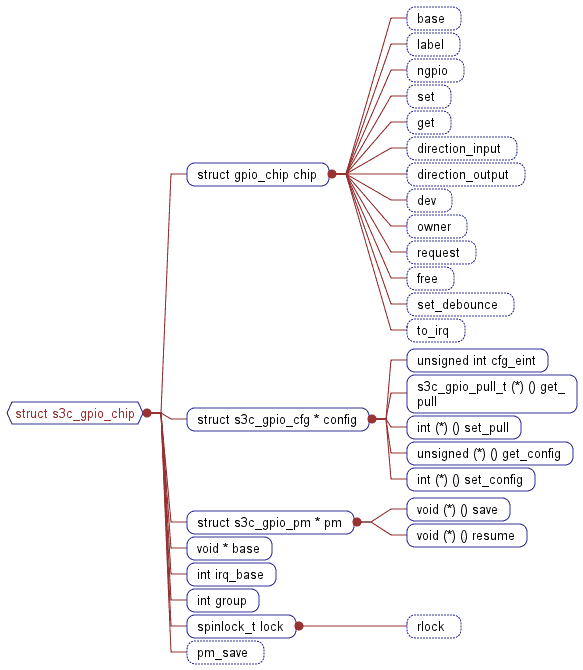 、
、
这个重要的数据结构中可以记录每个GPIO所需要的所有数据,后面会遇到的s3c24xx_gpios[]结构体就是该结构体的集合,描述了芯片中所有的GPIO端口,之后我们需要时时回头看看这个结构。
我们先来看s3c_gpiolib_getchip,它实现了返回对应pin值的GPIO结构体首指针的功能
#include<mach/gpio-core.h>
static inline struct s3c_gpio_chip *s3c_gpiolib_getchip(unsigned int pin)
{
struct s3c_gpio_chip *chip;
if (pin > S3C_GPIO_END) //如果超过GPJ(32)就return NULL
return NULL;
chip = &s3c24xx_gpios[pin/32]; //根据偏移,计算出对应pin的GPIO结构体指针
return ((pin - chip->chip.base) < chip->chip.ngpio) ? chip : NULL;
// 这里验证,如果pin偏移超过了GPIO的个数,说明出错了,否则就返回该GPIO的结构体指针
}
回想以下之前s3c2410_gpio_cfgpin中,我们传入的参数是led_table[i]和 led_cfg_table[i],
/* GPIO sizes for various SoCs:
*
* 2442
* 2410 2412 2440 2443 2416
* ---- ---- ---- ---- ----
* A 23 22 25 16 25
* B 11 11 11 11 9
* C 16 15 16 16 16
* D 16 16 16 16 16
* E 16 16 16 16 16
* F 8 8 8 8 8
* G16 16 16 16 8
* H 11 11 9 15 15
* J -- -- 13 16 --
* K -- -- -- -- 16
* L -- -- -- 15 7
* M -- -- -- 2 2
*/
struct s3c_gpio_chip s3c24xx_gpios[] = {
[0] = {
.base = S3C2410_GPACON, // datasheet上地址为0x56000000
//#define S3C2410_GPACON S3C2410_GPIOREG(0x00)
#define S3C2410_GPIOREG(x) ((x) + S3C24XX_VA_GPIO)
#define S3C24XX_VA_GPIO ((S3C24XX_PA_GPIO - S3C24XX_PA_UART) + S3C24XX_VA_UART)
S3C24XX_PA_GPIO相当于(0x15600000)
S3C24XX_PA_UART相当于(0x15000000)
#define S3C_VA_UART S3C_ADDR(0x01000000) /* UART */
#define S3C_ADDR_BASE 0xF6000000
#ifndef __ASSEMBLY__
#define S3C_ADDR(x) ((void __iomem __force *)S3C_ADDR_BASE + (x))
#else
#define S3C_ADDR(x) (S3C_ADDR_BASE + (x))
#endif
0x15600000-15000000+F7000000这里的S3C2410_GPACON应该怎么算?
.pm = __gpio_pm(&s3c_gpio_pm_1bit),
.config = &s3c24xx_gpiocfg_banka, // 设置GPIO的函数指针
static struct s3c_gpio_cfg s3c24xx_gpiocfg_banka = {
.set_config = s3c_gpio_setcfg_s3c24xx_a,
.get_config = s3c_gpio_getcfg_s3c24xx_a,
};
.chip = {
.base = S3C2410_GPA(0), //基地址,也是偏移量
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.label = "GPIOA",
.ngpio = 24,
.direction_input = s3c24xx_gpiolib_banka_input,
.direction_output = s3c24xx_gpiolib_banka_output,
},
},
[1] = {
.base = S3C2410_GPBCON,
.pm = __gpio_pm(&s3c_gpio_pm_2bit),
.chip = {
.base = S3C2410_GPB(0),
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.label = "GPIOB",
.ngpio = 16,
},
},
[2] = {
.base = S3C2410_GPCCON,
.pm = __gpio_pm(&s3c_gpio_pm_2bit),
.chip = {
.base = S3C2410_GPC(0),
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.label = "GPIOC",
.ngpio = 16,
},
},
[3] = {
.base = S3C2410_GPDCON,
.pm = __gpio_pm(&s3c_gpio_pm_2bit),
.chip = {
.base = S3C2410_GPD(0),
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.label = "GPIOD",
.ngpio = 16,
},
},
[4] = {
.base = S3C2410_GPECON,
.pm = __gpio_pm(&s3c_gpio_pm_2bit),
.chip = {
.base = S3C2410_GPE(0),
.label = "GPIOE",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.ngpio = 16,
},
},
[5] = {
.base = S3C2410_GPFCON,
.pm = __gpio_pm(&s3c_gpio_pm_2bit),
.chip = {
.base = S3C2410_GPF(0),
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.label = "GPIOF",
.ngpio = 8,
.to_irq = s3c24xx_gpiolib_bankf_toirq,
},
},
[6] = {
.base = S3C2410_GPGCON,
.pm = __gpio_pm(&s3c_gpio_pm_2bit),
.irq_base = IRQ_EINT8,
.chip = {
.base = S3C2410_GPG(0),
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.label = "GPIOG",
.ngpio = 16,
.to_irq = samsung_gpiolib_to_irq,
},
}, {
.base = S3C2410_GPHCON,
.pm = __gpio_pm(&s3c_gpio_pm_2bit),
.chip = {
.base = S3C2410_GPH(0),
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.label = "GPIOH",
.ngpio = 11,
},
},
/* GPIOS for the S3C2443 and later devices. */2440用不到
{
.base = S3C2440_GPJCON,
.pm = __gpio_pm(&s3c_gpio_pm_2bit),
.chip = {
.base = S3C2410_GPJ(0),
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.label = "GPIOJ",
.ngpio = 16,
},
}, {
.base = S3C2443_GPKCON,
.pm = __gpio_pm(&s3c_gpio_pm_2bit),
.chip = {
.base = S3C2410_GPK(0),
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.label = "GPIOK",
.ngpio = 16,
},
}, {
.base = S3C2443_GPLCON,
.pm = __gpio_pm(&s3c_gpio_pm_2bit),
.chip = {
.base = S3C2410_GPL(0),
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.label = "GPIOL",
.ngpio = 15,
},
}, {
.base = S3C2443_GPMCON,
.pm = __gpio_pm(&s3c_gpio_pm_2bit),
.chip = {
.base = S3C2410_GPM(0),
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.label = "GPIOM",
.ngpio = 2,
},
},
};
***************************************************************************
下面分析第二个函数,先看一下相关结构体
gpio_desc和gpio_chip结构图
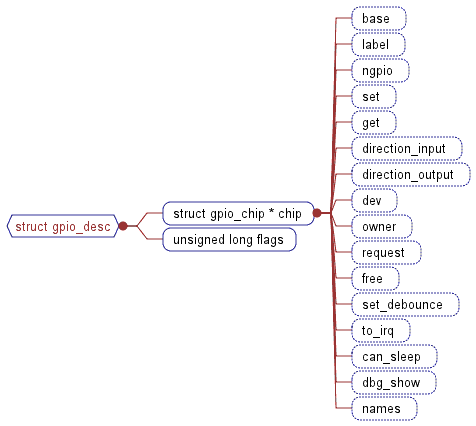
void s3c2410_gpio_setpin(unsigned int pin, unsigned int to)
{
/* do this via gpiolib until all users removed */
gpio_request(pin, "temporary");
gpio_set_value(pin, to);
gpio_free(pin);
}
又出现了三个函数,我们一一说明:
1169/* These "optional" allocation calls help prevent drivers from stomping
1170 * on each other, and help provide better diagnostics in debugfs.
1171 * They're called even less than the "set direction" calls.
1172 */
PS:static struct gpio_desc gpio_desc[ARCH_NR_GPIOS];
其中ARCH_NR_GPIOS在arch/arm/mach-s3c2410/include/mach/gpio.h中定义
#define ARCH_NR_GPIOS (32 * 9 + CONFIG_S3C24XX_GPIO_EXTRA)
因此,每个引脚都分配了一个gpio_desc数据结构
1173int gpio_request(unsigned gpio, const char *label) // 这个函数还不是很明白
1174{
1175 struct gpio_desc *desc;
1176 struct gpio_chip *chip;
1177 int status = -EINVAL;
1178 unsigned long flags;
1179
1180 spin_lock_irqsave(&gpio_lock, flags); // gpio_lock是自旋锁,上锁,保存FLAG在flags变量中
1181
1182 if (!gpio_is_valid(gpio)) // 不符合要求,跳转到done
1183 goto done;
1184 desc = &gpio_desc[gpio]; // desc = &gpio_desc[pin]
1185 chip = desc->chip;
1186 if (chip == NULL) // gpio_desc.chip指向NULL,跳转到done
1187 goto done;
1188
1189 if (!try_module_get(chip->owner)) // 该函数用于增加模块使用计数;若返回为0,表示调用失败,希望使用的模块没有被加载或正在被卸载中
1190 goto done;
1191
1192 /* NOTE: gpio_request() can be called in early boot,
1193 * before IRQs are enabled, for non-sleeping (SOC) GPIOs.
1194 */
1195
1196 if (test_and_set_bit(FLAG_REQUESTED, &desc->flags) == 0) { // 原子操作,将flags的第FLAG_REQUESTED位置1,并返回其原值
1197 desc_set_label(desc, label ? : "?"); // 如果原来的值是0, 执行desc_set_label, 对desc->chip.label赋值,如果label有定义,直接用定义,比如上面的“temporary”,否则用“?”
static inline void desc_set_label(struct gpio_desc *d, const char *label)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_FS
d->label = label; // 为什么不是d->chip.label = label; ?
#endif
}
1198 status = 0;
1199 } else { // 如果flags的第FLAG_REQUESTED位原来的值是1
1200 status = -EBUSY;
1201 module_put(chip->owner); // 该函数用于减少模块使用计数
1202 goto done;
1203 }
1204
1205 if (chip->request) { // chip->request在linux初始化时是没有指向的,可以见后面s3c_gpiolib_add
1206 /* chip->request may sleep */
1207 spin_unlock_irqrestore(&gpio_lock, flags); // 如果chip->request不为0, 解锁,因为后面调用的chip->request有可能睡眠
1208 status = chip->request(chip, gpio - chip->base);
1209 spin_lock_irqsave(&gpio_lock, flags); // 执行完后,继续上锁
1210
1211 if (status < 0) { // status返回负数,说明出错
1212 desc_set_label(desc, NULL);
1213 module_put(chip->owner);
1214 clear_bit(FLAG_REQUESTED, &desc->flags);
1215 }
1216 }
1217
1218done:
1219 if (status)
1220 pr_debug("gpio_request: gpio-%d (%s) status %d/n", gpio, label ? : "?", status);
1221 // 如果状态不为0, 打印gpio-pin"****"的状态
1222 spin_unlock_irqrestore(&gpio_lock, flags); // 解锁
1223 return status; // 返回状态
1224}
***************************************************************************
下面先分析gpio_free函数
void gpio_free(unsigned gpio) // 待分析
{
unsigned long flags;
struct gpio_desc *desc;
struct gpio_chip *chip;
might_sleep();
if (!gpio_is_valid(gpio)) {
WARN_ON(extra_checks);
return;
}
gpio_unexport(gpio);
spin_lock_irqsave(&gpio_lock, flags);
desc = &gpio_desc[gpio];
chip = desc->chip;
if (chip && test_bit(FLAG_REQUESTED, &desc->flags)) {
if (chip->free) {
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&gpio_lock, flags);
might_sleep_if(chip->can_sleep);
chip->free(chip, gpio - chip->base);
spin_lock_irqsave(&gpio_lock, flags);
}
desc_set_label(desc, NULL);
module_put(desc->chip->owner);
clear_bit(FLAG_ACTIVE_LOW, &desc->flags);
clear_bit(FLAG_REQUESTED, &desc->flags);
} else
WARN_ON(extra_checks);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&gpio_lock, flags);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(gpio_free);
***************************************************************************
arch/arm/mach-s3c2410/include/mach/gpio.h
#define gpio_set_value __gpio_set_value
void __gpio_set_value(unsigned gpio, int value)
{
struct gpio_chip *chip;
chip = gpio_to_chip(gpio); // 返回对应于pin的gpio_desc[pin].chip指针
WARN_ON(chip->can_sleep);
chip->set(chip, gpio - chip->base, value); // 这里调用的是s3c_gpiolib_set函数!!!
}
/* caller holds gpio_lock *OR* gpio is marked as requested */
static inline struct gpio_chip *gpio_to_chip(unsigned gpio)
{
return gpio_desc[gpio].chip;
}
看到这里,一直有个问题让我百思不得其解,这里的chip按理说应该是s3c_gpio_chip中的chip成员,但是之前都没有代码交代他们是如何联系到一起的,s3c_gpio_chip与gpio_desc结构体如何联系在一起,也没有函数交代,并且这里的chip->set函数指针也没有实现的代码,但是,经实验确认没有问题后,我开始查找plat-s3c24xx/gpiolib.c中的函数希望能有些线索,果然,找到了这么一个函数:
static __init int s3c24xx_gpiolib_init(void)
{
struct s3c_gpio_chip *chip = s3c24xx_gpios;
int gpn;
for (gpn = 0; gpn < ARRAY_SIZE(s3c24xx_gpios); gpn++, chip++) {
if (!chip->config)
chip->config = &s3c24xx_gpiocfg_default; // 原来chip->config默认函数也是在这里!!!
s3c_gpiolib_add(chip); // 之前的疑惑都在这里实现!!!
}
return 0;
}
core_initcall(s3c24xx_gpiolib_init);
但是,这个s3c24xx_gpiolib_init函数又是在什么时候执行的呢?可以看到,在该函数的下面,有一句:core_initcall(s3c24xx_gpiolib_init);查阅相关资料发现, 在linux初始化的过程中,内核采用了一种initcall的机制,它利用gcc的扩展功能以及ld的连接控制脚本实现了在内核初始化的过程中通过简单的循环就实现了相关驱动的初始化
也就是说,在linux初始化期间,就已经执行了s3c24xx_gpiolib_init,现在我们可以分析下s3c_gpiolib_add(chip);这个函数了,
__init void s3c_gpiolib_add(struct s3c_gpio_chip *chip)
{
struct gpio_chip *gc = &chip->chip;
int ret;
BUG_ON(!chip->base);
BUG_ON(!gc->label);
BUG_ON(!gc->ngpio);
spin_lock_init(&chip->lock); // 初始化s3c_gpio_chip的自旋锁
if (!gc->direction_input)
gc->direction_input = s3c_gpiolib_input; // direction_input 函数指针
if (!gc->direction_output)
gc->direction_output = s3c_gpiolib_output; // direction_output 函数指针
if (!gc->set)
gc->set = s3c_gpiolib_set; // set函数指针
if (!gc->get)
gc->get = s3c_gpiolib_get; // get函数指针
#ifdef CONFIG_PM
if (chip->pm != NULL) {
if (!chip->pm->save || !chip->pm->resume)
printk(KERN_ERR "gpio: %s has missing PM functions/n", gc->label);
} else
printk(KERN_ERR "gpio: %s has no PM function/n", gc->label);
#endif
/* gpiochip_add() prints own failure message on error. */
ret = gpiochip_add(gc);
if (ret >= 0)
s3c_gpiolib_track(chip);
}
gpiochip_add函数分析:
/**
* gpiochip_add() - register a gpio_chip
* @chip: the chip to register, with chip->base initialized
* Context: potentially before irqs or kmalloc will work
*
* Returns a negative errno if the chip can't be registered, such as
* because the chip->base is invalid or already associated with a
* different chip. Otherwise it returns zero as a success code.
*
* When gpiochip_add() is called very early during boot, so that GPIOs
* can be freely used, the chip->dev device must be registered before
* the gpio framework's arch_initcall(). Otherwise sysfs initialization
* for GPIOs will fail rudely.
*
* If chip->base is negative, this requests dynamic assignment of
* a range of valid GPIOs.
*/
int gpiochip_add(struct gpio_chip *chip) // 在gpio_desc[]中分配空间,并链接chip结构
{
unsigned long flags;
int status = 0;
unsigned id;
int base = chip->base;
if ((!gpio_is_valid(base) || !gpio_is_valid(base + chip->ngpio - 1))
&& base >= 0) {
status = -EINVAL;
goto fail;
}
spin_lock_irqsave(&gpio_lock, flags); // 上锁
if (base < 0) {
base = gpiochip_find_base(chip->ngpio); // 这个函数在gpiolib.c中,在gpio_desc[]中分配chip->ngpio个空间(从最后往前分配),返回第一个index
if (base < 0) { // 分配不到
status = base;
goto unlock; // 解锁退出
}
chip->base = base; // gpio_chip *chip->base = i (i是gpio_desc[i]中的index)
}
/* these GPIO numbers must not be managed by another gpio_chip */
for (id = base; id < base + chip->ngpio; id++) {
if (gpio_desc[id].chip != NULL) {
status = -EBUSY;
break;
}
}
if (status == 0) { // 分配到空间,正常情况下
for (id = base; id < base + chip->ngpio; id++) {
gpio_desc[id].chip = chip; // 这里将gpio_desc与s3c_gpio_chip联系起来,他们的chip成员指向的是同一个数据结构
/* REVISIT: most hardware initializes GPIOs as
* inputs (often with pullups enabled) so power
* usage is minimized. Linux code should set the
* gpio direction first thing; but until it does,
* we may expose the wrong direction in sysfs.
*/
gpio_desc[id].flags = !chip->direction_input ? (1 << FLAG_IS_OUT) : 0; // 设置flags
}
} // end if
of_gpiochip_add(chip); // 没操作
unlock:
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&gpio_lock, flags); // 解锁
if (status)
goto fail;
status = gpiochip_export(chip); //×××××××××××××××待分析
if (status)
goto fail;
return 0;
fail:
/* failures here can mean systems won't boot... */
pr_err("gpiochip_add: gpios %d..%d (%s) failed to register/n",
chip->base, chip->base + chip->ngpio - 1,
chip->label ? : "generic");
return status; // 返回状态
}
下面是s3c_gpiolib_track函数
#ifdef CONFIG_S3C_GPIO_TRACK
struct s3c_gpio_chip *s3c_gpios[S3C_GPIO_END];
static __init void s3c_gpiolib_track(struct s3c_gpio_chip *chip) // 没完全理解,待分析
{
unsigned int gpn;
int i;
gpn = chip->chip.base;
for (i = 0; i < chip->chip.ngpio; i++, gpn++) {
BUG_ON(gpn >= ARRAY_SIZE(s3c_gpios));
s3c_gpios[gpn] = chip;
}
}
#endif /* CONFIG_S3C_GPIO_TRACK */
***************************************************************************
好,现在我们开始分析设备注册与卸载函数,在初始化程序中,有如下语句:
ret = misc_register(&misc); //注册设备
其中的misc_register就是杂项设备的注册函数,首先关注下这里的参数misc数据结构
75 /*
76 * 把 LED 驱动注册为 MISC 设备
77 */
78 static struct miscdevice misc = {
79 .minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR, //动态设备号
80 .name = DEVICE_NAME,
81 .fops = &dev_fops,
82 };
miscdevice的数据结构如图所示:
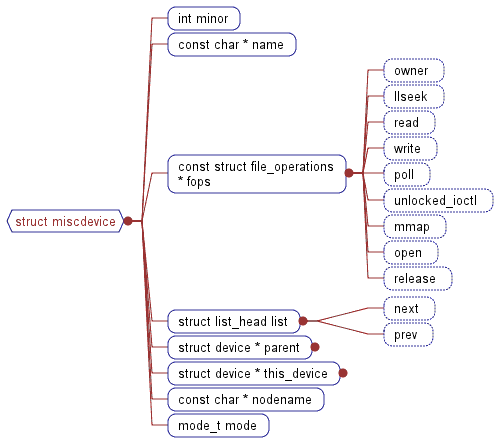
/**
* misc_register - register a miscellaneous device
* @misc: device structure
*
* Register a miscellaneous device with the kernel. If the minor
* number is set to %MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR a minor number is assigned
* and placed in the minor field of the structure. For other cases
* the minor number requested is used.
*
* The structure passed is linked into the kernel and may not be
* destroyed until it has been unregistered.
*
* A zero is returned on success and a negative errno code for
* failure.
*/
int
misc_register(struct miscdevice * misc)
{
struct miscdevice *c;
dev_t dev;
int err = 0;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&misc->list); // 初始化链表头,将misc->list的next和pre都指向自己
mutex_lock(&misc_mtx); // 获取互斥锁, or睡眠
list_for_each_entry(c, &misc_list, list) { // 遍历整个misc_list链表,所有的杂项驱动设备都有一个miscdevice数据结构,这些杂项驱动设备通过一个全局的misc_list链表连在一起, 相当一个记录
if (c->minor == misc->minor) { // 如果misc_list中已经有了这个设备(minor相同),则解锁返回,这里c是遍历时的tmp miscdevice,指向当前遍历节点
mutex_unlock(&misc_mtx);
return -EBUSY;
}
}
if (misc->minor == MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR) { // 如果misc_list中没有该设备,判断minor是否准备动态分配,实验中如此设置
int i = find_first_zero_bit(misc_minors, DYNAMIC_MINORS); // misc_minors是杂项设备位图,总共有64个位DYNAMIC_MINORS=64,表示可以注册64个杂项设备,这句代码找到位图中的空闲位置(表示还能加新设备)
if (i >= DYNAMIC_MINORS) { // 如果超过总设备数,则解锁返回
mutex_unlock(&misc_mtx);
return -EBUSY;
}
misc->minor = DYNAMIC_MINORS - i - 1; // 计算子设备号,赋值到misc->minor
set_bit(i, misc_minors); // 对应的位图也置位
}
dev = MKDEV(MISC_MAJOR, misc->minor); // 生成设备号
// 在sysfs中创建并注册一个设备,可以在/dev下面看到misc->name
misc->this_device = device_create(misc_class, misc->parent, dev, misc, "%s", misc->name);
1480/**
1481 * device_create - creates a device and registers it with sysfs
1482 * @class: pointer to the struct class that this device should be registered to
1483 * @parent: pointer to the parent struct device of this new device, if any
1484 * @devt: the dev_t for the char device to be added
1485 * @drvdata: the data to be added to the device for callbacks
1486 * @fmt: string for the device's name
1487 *
1488 * This function can be used by char device classes. A struct device
1489 * will be created in sysfs, registered to the specified class.
1490 *
1491 * A "dev" file will be created, showing the dev_t for the device, if
1492 * the dev_t is not 0,0.
1493 * If a pointer to a parent struct device is passed in, the newly created
1494 * struct device will be a child of that device in sysfs.
1495 * The pointer to the struct device will be returned from the call.
1496 * Any further sysfs files that might be required can be created using this
1497 * pointer.
1498 *
1499 * Returns &struct device pointer on success, or ERR_PTR() on error.
1500 *
1501 * Note: the struct class passed to this function must have previously
1502 * been created with a call to class_create().
1503 */
1504struct device *device_create(struct class *class, struct device *parent, // 这个函数以后会详细看
1505 dev_t devt, void *drvdata, const char *fmt, ...)
1506{
1507 va_list vargs;
1508 struct device *dev;
1509
1510 va_start(vargs, fmt);
1511 dev = device_create_vargs(class, parent, devt, drvdata, fmt, vargs);
1512 va_end(vargs);
1513 return dev;
1514}
// this_device是在创建设备节点时指向函数device_create()返回的设备结构
if (IS_ERR(misc->this_device)) { // 如果创建节点出错,并且
int i = DYNAMIC_MINORS - misc->minor - 1; // 计算子设备号之前misc->minor的值
if (i < DYNAMIC_MINORS && i >= 0) // 计算位图位i,如果在0-64之间,说明在set_bit中置位了,则清楚位图,处理错误,准备返回
clear_bit(i, misc_minors);
err = PTR_ERR(misc->this_device);
goto out;
}
/*
* Add it to the front, so that later devices can "override"
* earlier defaults
*/
list_add(&misc->list, &misc_list); // 以上操作都没有问题后,将新设备加入misc_list链表,解锁返回
out:
mutex_unlock(&misc_mtx);
return err;
}
***************************************************************************
同样,对应misc_register函数,在exit中会调用misc_deregister函数
/**
* misc_deregister - unregister a miscellaneous device
* @misc: device to unregister
*
* Unregister a miscellaneous device that was previously
* successfully registered with misc_register(). Success
* is indicated by a zero return, a negative errno code
* indicates an error.
*/
int misc_deregister(struct miscdevice *misc)
{
int i = DYNAMIC_MINORS - misc->minor - 1;
if (WARN_ON(list_empty(&misc->list))) // 如果该misc->list的next指向自己,则出错返回
return -EINVAL;
mutex_lock(&misc_mtx); // 上锁
list_del(&misc->list); // 将misc从misc_list链表中删除
device_destroy(misc_class, MKDEV(MISC_MAJOR, misc->minor)); // 对应device_create!
1524/**
1525 * device_destroy - removes a device that was created with device_create()
1526 * @class: pointer to the struct class that this device was registered with
1527 * @devt: the dev_t of the device that was previously registered
1528 *
1529 * This call unregisters and cleans up a device that was created with a
1530 * call to device_create().
1531 */
1532void device_destroy(struct class *class, dev_t devt)
1533{
1534 struct device *dev;
1535
1536 dev = class_find_device(class, NULL, &devt, __match_devt);
1537 if (dev) {
1538 put_device(dev);
1539 device_unregister(dev);
1540 }
1541}
1542EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(device_destroy);
if (i < DYNAMIC_MINORS && i >= 0)
clear_bit(i, misc_minors); // 计算位图位i,如果在0-64之间,说明在set_bit中置位了,清楚位图
mutex_unlock(&misc_mtx); // 解锁返回
return 0;
}
***************************************************************************
总结杂项设备驱动的注册与卸载流程:
misc_register:找到空闲设备位图位置 -> 计算子设备号(如果动态的话),位图位置位 - > device_creat() -> miscdevice结构体加入misc_list链表中
misc_deregister: 将miscdevice结构体从misc_list链表中删除 -> device_destory() -> 位图位清零
***************************************************************************
与s3c24xx_gpiolib_init函数一样,misc也有一个初始化函数会在linux初始化时运行,下面来分析这个函数
static int __init misc_init(void)
{
int err;
#ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS //在proc文件系统下创建一个"misc"目录。 misc_proc_fops是该文件系统下文件的操作函数集
proc_create("misc", 0, NULL, &misc_proc_fops);
#endif
misc_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "misc"); // 前面device_create()中的misc_class就是在这里初始化的
err = PTR_ERR(misc_class);
if (IS_ERR(misc_class)) // 出错处理
goto fail_remove;
err = -EIO;
if (register_chrdev(MISC_MAJOR,"misc",&misc_fops)) //注册一个主设备号为MISC_MAJOR(10)的字符设备,设备操作函数集为misc_fops
goto fail_printk;
misc_class->devnode = misc_devnode;
return 0;
fail_printk: // 错误处理
printk("unable to get major %d for misc devices/n", MISC_MAJOR);
class_destroy(misc_class);
fail_remove:
remove_proc_entry("misc", NULL);
return err;
}
subsys_initcall(misc_init);
***************************************************************************
好,到这里基本把一些GPIO相关的基本函数和结构体都简单说明了,虽然还有不少不清楚的地方,但还是有些帮助,文中还有些不清楚的地方还有待以后能一一解决,我会不断补充!