Dijkstra算法用于解决单源最短路径问题,通过逐个收录顶点来确保已收录顶点的路径长度为最短。


图片来自陈越姥姥的数据结构课程:https://mooc.study.163.com/learn/1000033001?tid=1000044001#/learn/content?type=detail&id=1000112011&cid=1000126096
Dijkstra算法的时间复杂度,取决于“V=未收录顶点中dist最小者”的算法。这一步可以用线性查找实现,也可以用最小堆实现。
线性查找的算法就不用多说了。最小堆的算法有一个问题:最小堆是以未收录顶点的dist作为key来建立的,但是每一轮循环都会把部分顶点的dist值改变,也就会破坏最小堆的有序性,怎么解决?
显然应该在每一轮循环中把最小堆重新调整成有序。现在问题又来了:
1. 复杂度还合算吗?
建堆的时间复杂度是O(N),pop一个元素的时间复杂度是O(logN);线性查找的时间复杂度也是O(N)。建堆还额外使用了O(N)的空间。
看似一点都不合算。但我又想到每一轮循环中的建堆操作,很可能只需要调整少量元素,而对于其他元素,只需要进行访问。然而线性查找连调整都不需要,只有交换。再然而,循环过程中堆会变小,使建堆的时间复杂度中的常数变小。至于到底哪个更快,还得实践出真知。
所以只能从消除建堆操作入手。这样又是另一种算法了,参考资料[1]给出了详细说明,这种算法中每一轮的时间复杂度为O(logN),总时间复杂度为O(|E|log|V|)(V为顶点,E为边)。
2. 如何利用STL进行堆操作?
STL <algorithm> 头文件提供了 std::is_heap 、 std::is_heap_until (这两个需要C++11)、 std::make_heap 、 std::push_heap 、 std::pop_heap 和 std::sort_heap 等函数模板用于堆操作。
现有一道单源最短路径的题:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805523835109376,Dijkstra算法的变形而已。
以下为实现代码。三种算法用宏定义选择,已选择优先队列算法。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <limits> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <queue> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <utility> 7 #include <functional> 8 9 //#define LINEAR 10 //#define HEAP 11 #define QUEUE 12 13 struct Path 14 { 15 Path() = default; 16 Path(int _city, int _dist) 17 : city(_city), dist(_dist) 18 { 19 ; 20 } 21 int city; 22 int dist; 23 bool operator<(const Path& _rhs) const 24 { 25 return dist < _rhs.dist; 26 } 27 bool operator>(const Path& _rhs) const 28 { 29 return dist > _rhs.dist; 30 } 31 }; 32 33 struct City 34 { 35 std::vector<Path> paths; 36 int team; 37 int dist = std::numeric_limits<int>::max(); 38 bool collected = false; 39 int team_max = 0; 40 int dist_count = 0; 41 }; 42 43 #ifdef HEAP 44 class Comparator 45 { 46 public: 47 Comparator(std::vector<City>& _cities) 48 : cities_(&_cities) 49 { 50 ; 51 } 52 bool operator()(int _lhs, int _rhs) 53 { 54 return (*cities_)[_lhs].dist > (*cities_)[_rhs].dist; 55 } 56 private: 57 std::vector<City>* cities_; 58 }; 59 #endif 60 61 int main() 62 { 63 int n, m, src, dst; 64 std::cin >> n >> m >> src >> dst; 65 std::vector<City> cities(n); 66 for (auto& city : cities) 67 std::cin >> city.team; 68 for (int cnt = 0; cnt != m; ++cnt) 69 { 70 int src, dst, dist; 71 std::cin >> src >> dst >> dist; 72 cities[src].paths.emplace_back(dst, dist); 73 cities[dst].paths.emplace_back(src, dist); 74 } 75 76 { 77 auto& city = cities[src]; 78 cities[src].collected = true; 79 cities[src].dist = 0; 80 cities[src].dist_count = 1; 81 cities[src].team_max = cities[src].team; 82 } 83 #ifdef QUEUE 84 std::priority_queue<Path, std::vector<Path>, std::greater<Path>> queue; 85 #endif 86 for (const auto& path : cities[src].paths) 87 { 88 cities[path.city].dist = path.dist; 89 cities[path.city].dist_count = 1; 90 cities[path.city].team_max = cities[src].team + cities[path.city].team; 91 #ifdef QUEUE 92 queue.emplace(path.city, path.dist); 93 #endif 94 } 95 96 #ifdef HEAP 97 std::vector<int> heap; 98 heap.reserve(n - 1); 99 for (int i = 0; i != n; ++i) 100 if (i != src) 101 heap.push_back(i); 102 Comparator comp(cities); 103 std::make_heap(heap.begin(), heap.end(), comp); 104 #endif 105 106 while (1) 107 { 108 #ifdef LINEAR 109 int min_dist = std::numeric_limits<int>::max(); 110 int index = -1; 111 for (int i = 0; i != n; ++i) 112 if (!cities[i].collected && cities[i].dist < min_dist) 113 min_dist = cities[i].dist, index = i; 114 if (index == -1) 115 break; 116 auto& city = cities[index]; 117 #endif 118 #ifdef HEAP 119 if (heap.empty()) 120 break; 121 auto& city = cities[heap[0]]; 122 #endif 123 #ifdef QUEUE 124 if (queue.empty()) 125 break; 126 Path temp; 127 while (1) 128 { 129 temp = queue.top(); 130 queue.pop(); 131 if (!cities[temp.city].collected) 132 break; 133 } 134 auto& city = cities[temp.city]; 135 #endif 136 city.collected = true; 137 for (const auto& path : city.paths) 138 { 139 if (!cities[path.city].collected) 140 { 141 auto& dest = cities[path.city]; 142 if (city.dist + path.dist < cities[path.city].dist) 143 { 144 dest.dist = city.dist + path.dist; 145 dest.dist_count = city.dist_count; 146 dest.team_max = city.team_max + dest.team; 147 } 148 else if (city.dist + path.dist == cities[path.city].dist) 149 { 150 dest.dist = city.dist + path.dist; 151 dest.dist_count += city.dist_count; 152 if (city.team_max + dest.team > dest.team_max) 153 dest.team_max = city.team_max + dest.team; 154 } 155 #ifdef QUEUE 156 queue.emplace(path.city, dest.dist); 157 #endif 158 } 159 } 160 #ifdef LINEAR 161 if (index == dst) 162 break; 163 #endif 164 #ifdef HEAP 165 if (heap[0] == dst) 166 break; 167 std::pop_heap(heap.begin(), heap.end(), comp); 168 heap.pop_back(); 169 std::make_heap(heap.begin(), heap.end(), comp); 170 #endif 171 #ifdef QUEUE 172 if (temp.city == dst) 173 break; 174 #endif 175 } 176 177 { 178 auto& city = cities[dst]; 179 std::cout << cities[dst].dist_count << ' ' << cities[dst].team_max; 180 } 181 182 return 0; 183 }
测试结果:
线性查找版

最小堆版
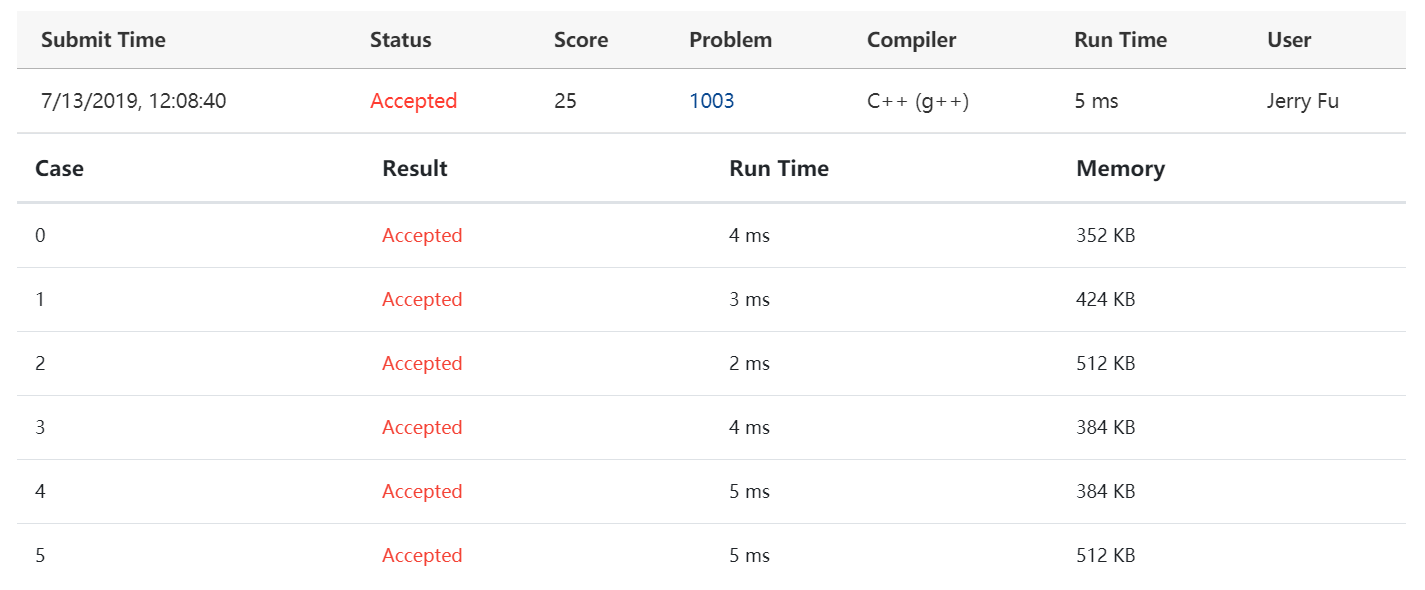
优先队列版
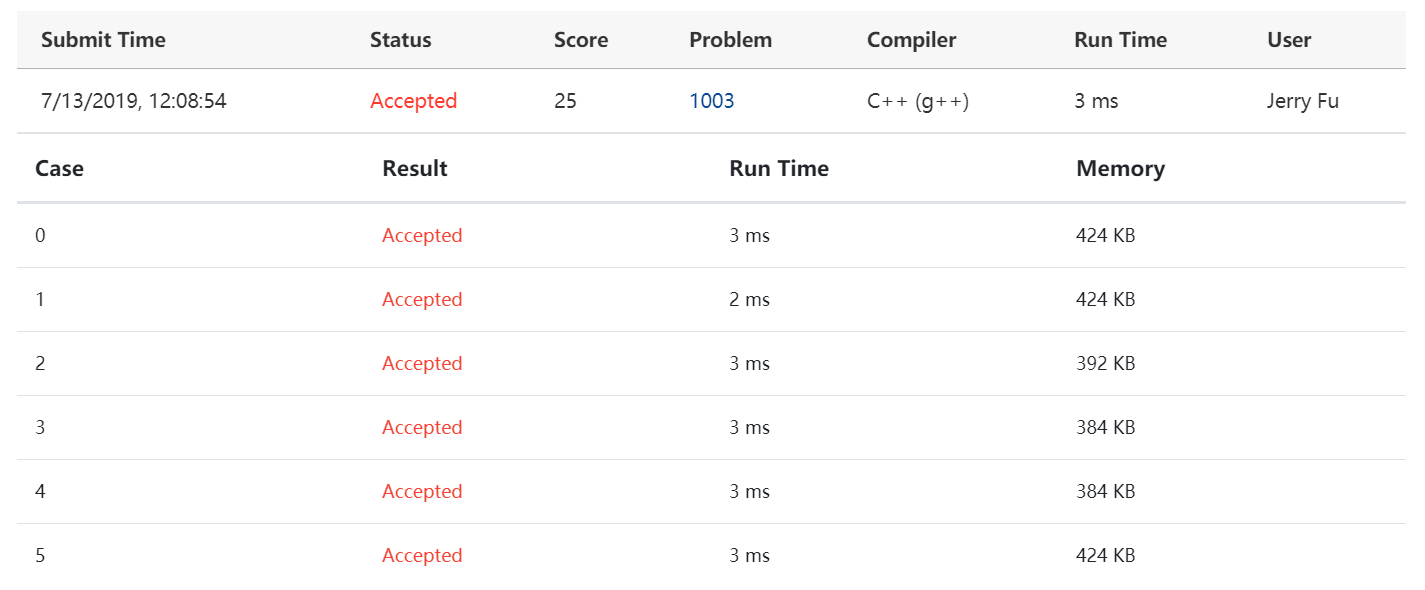
平台显示线性查找版的时间6ms,内存512KB;最小堆版的时间5ms,内存512KB;优先队列版的时间3ms,内存424KB。我认为时间都太短了,数据量不够大,不足以说明问题。
如果仅从理论上分析的话,我认为优先队列的算法是最优的。
参考资料:
[1] dijkstra + heap 优化 https://blog.csdn.net/sentimental_dog/article/details/51955765