Exec source 适用于监控一个实时追加的文件,但不能保证数据不丢失;Spooldir Source 能够保证数据不丢失,且能够实现断点续传,但延迟较高,不能实时监控;而 Taildir Source 既能够实现断点续传,又可以保证数据不丢失,还能够进行实时监控。
一、创建配置文件 flume-taildir-hdfs.conf
https://flume.apache.org/FlumeUserGuide.html#taildir-source
监控 /tmp/upload/ 目录下以 COMPLETED 结尾的文件
a3.sources = r3 a3.sinks = k3 a3.channels = c3 # Describe/configure the source a3.sources.r3.type = TAILDIR a3.sources.r3.filegroups = f1 a3.sources.r3.filegroups.f1 = /tmp/upload/.*COMPLETED a3.sources.r3.positionFile = /opt/apache-flume-1.9.0-bin/tail_dir.json # Describe the sink a3.sinks.k3.type = hdfs a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.path = hdfs://h136:9000/flume/tailDir/%Y%m%d/%H # 上传文件的前缀 a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.filePrefix = upload- # 是否按照时间滚动文件夹 a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.round = true # 多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹 a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.roundValue = 1 # 重新定义时间单位 a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.roundUnit = hour # 是否使用本地时间戳 a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true # 积攒多少个 Event 才 flush 到 HDFS 一次 a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.batchSize = 100 # 设置文件类型,可支持压缩 a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.fileType = DataStream # 多久生成一个新的文件 a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.rollInterval = 60 # 设置每个文件的滚动大小大概是 128M a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700 # 文件的滚动与 Event 数量无关 a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.rollCount = 0 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a3.channels.c3.type = memory a3.channels.c3.capacity = 1000 a3.channels.c3.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a3.sources.r3.channels = c3 a3.sinks.k3.channel = c3
二、启动
cd /opt/apache-flume-1.9.0-bin/ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a3 --conf-file /tmp/flume-job/flume-taildir-hdfs.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console

三、改动监视文件
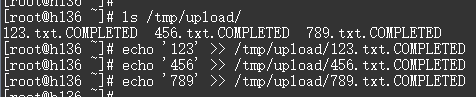
echo '123' >> /tmp/upload/123.txt.COMPLETED echo '456' >> /tmp/upload/456.txt.COMPLETED echo '789' >> /tmp/upload/789.txt.COMPLETED
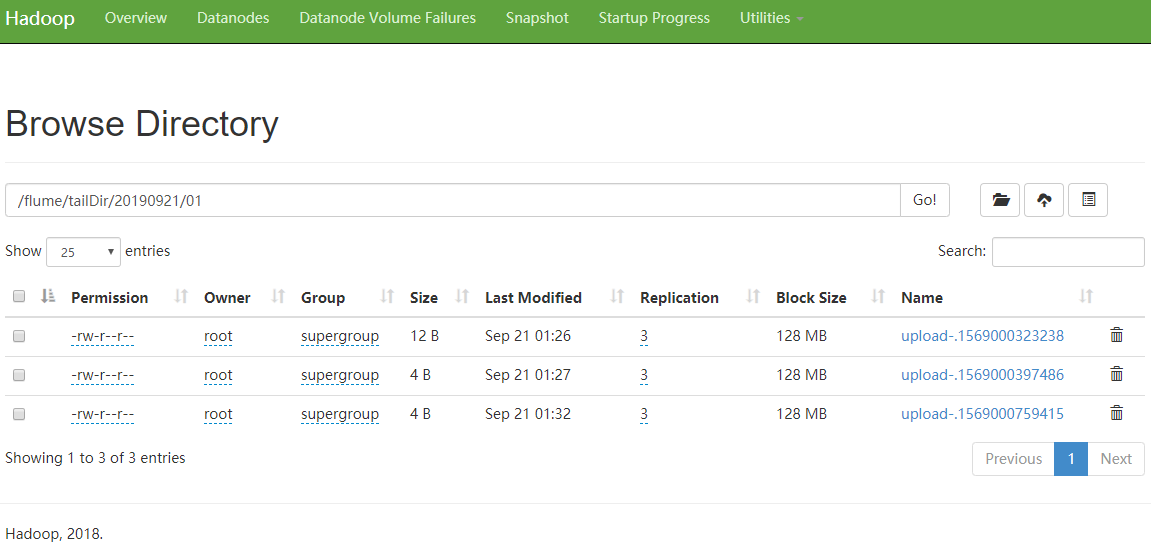
查看 HDFS 上的文件
Taildir 说明:Taildir Source 维护了一个 json 格式的 position File,其会定期的往 position File 中更新每个文件读取到的最新的位置,因此能够实现断点续传。Position File 的格式如下:

[
{"inode":1717446,"pos":8,"file":"/tmp/upload/456.txt.COMPLETED"},
{"inode":1717449,"pos":8,"file":"/tmp/upload/789.txt.COMPLETED"},
{"inode":1717442,"pos":12,"file":"/tmp/upload/123.txt.COMPLETED"}
]
Linux 中储存文件元数据的区域就叫做 inode,每个 inode 都有一个号码,操作系统用 inode 号码来识别不同的文件,Unix/Linux 系统内部不使用文件名,而使用 inode 号码来识别文件。