前言
这个教程介绍了Thymeleaf与Spring框架的集成,特别是SpringMvc框架。
注意Thymeleaf支持同Spring框架的3.和4.版本的集成,但是这两个版本的支持是封装在thymeleaf-spring3和thymeleaf-spring4这两个独立的库中,项目中需要根据实际情况分别引用。
样例代码针对的是spring4.,但一般情况下,spring3.也可以无缝使用,所需要的仅仅是改变一下引用库。
1 Thymeleaf同Spring的整合
Thymeleaf与Spring进行整合后,可以在SpringMVC应用中完全替代JSP文件。
集成后你将:
- 就像控制JSP一样,使用SpringMvc的@Controller注解来映射Thymeleaf的模板文件。
- 在模板中使用SpringEL表达式来替换OGNL
- 在模板中创建的表单,完全支持Beans和结果的绑定,包括使用PropertyEditor,转换,和验证等。
- 可以通过Spring来管理国际化文件显示国际化信息。
注意,在使用本教程之前,您应该充分了解Thymeleaf的标准方言。
2 Spring标准方言
为了更加方便,更快捷的集成,Thymeleaf提供了一套能够与Spring正确工作的特有方言。
这套方言基于Thymeleaf标准方言实现,它在类org.thymeleaf.spring.dialect.SpringStandardDialect中,事实上,他继承于org.thymeleaf.standard.StandardDialect中。
除了已经出现在标准方言中的所有功能,Spring中还有以下特点:
- 不适用OGNL,而是SpringEL做完变量表达式,因此,所有的${...}和*{...}表达式将用Spring的表达式引擎进行处理。
- 访问应用context中的beans可以使用SpringEL语法:${@myBean.doSomething()}
- 基于表格处理的新属性:th:field,th:errors和th:errorclass,除此还有一个th:object的新实现,允许它使用表单命令选择器(??)。
- 一个新的表达式:#themes.code(...),相当于jsp自定义标签中的spring:theme。
- 在spring4.0集成中的一个新的表达式:#mvc.uri(...),相当于jsp自定义标签中的spring:mvcUrl(...)
注意,上述这些方言特性是不能再普通的TemplateEngine对象中使用的,应该配置一个org.thymeleaf.spring4.SpringTemplateEngine来执行。
一个配置的简单例子:
<bean id="templateResolver" class="org.thymeleaf.templateresolver.ServletContextTemplateResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/templates/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".html" />
</bean>
<bean id="templateEngine" class="org.thymeleaf.spring4.SpringTemplateEngine">
<property name="templateResolver" ref="templateResolver" />
</bean>
视图和视图解释器
SpringMvc中的视图和视图解释器
Spring有两个符合其模板系统核心的接口:
- org.springframework.web.servlet.View
- org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver
视图模型页面在应用中,让我修改和预定义他的行为的页面,可将其作为Bean来定义,视图是负责渲染实际的HTML,通常由一些模板引擎来负责,如JSP和Thymeleaf。
ViewResolvers是一个获取特定操作和语言的的视图对象的对象。通常,controller会向ViewResolvers要求转发到一个特定的视图(视图名为控制器返回的字符串)。然后在顺序执行应用中所有的视图解析器,直到有一个能够解析这个视图。在这种情况下,视图对象返回并控制传递给他的一个html渲染相。
注意,在一个应用中,并不是所有的页面都被定义为视图,但是只有那些行为我们希望以特定的方式进行非标准方式操作或者进行特定配置,例如,一些特殊的bean。如果一个ViewResolver请求一个view但没有响应的bean(这是一个常见的情况),一个新的视图对象将被临时创建并返回。
一个SpringMVC中Jsp+JSTL视图解释器的典型配置如下:
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="viewClass" value="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView" />
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsps/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
<property name="order" value="2" />
<property name="viewNames" value="*jsp" />
</bean>
根据他的属性就足够知道他是怎么配置的了:
- viewClass:建立视图实例的类,在JSP解析的时候所必须的,但是现在我们使用Thymeleaf,所以它是不需要的。
- prefix和suffix,和Thymeleaf的TemplateResolver对象的方式一直,设置前缀和后缀属性。
- order:设置在视图解析器查询链中的顺序
- viewNames:允许定义视图名称(可通过通配符),定义内的视图由视图解析器解析。
Thymeleaf中的视图和视图解析器
Thymeleaf和Spring类似,同样是对应两个接口:
- org.thymeleaf.spring4.view.ThymeleafView
- org.thymeleaf.spring4.view.ThymeleafViewResolver
这两个类将用于处理控制器返回Thymeleaf执行的结果。
Thymeleaf视图解析器的配置同样和JSP是非常相似的:
<bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring4.view.ThymeleafViewResolver">
<property name="templateEngine" ref="templateEngine" />
<property name="order" value="1" />
<property name="viewNames" value="*.html,*.xhtml" />
</bean>
它的templateEngin的值当然是前一章定义的SpringTemplateEngin对象,另外两个参数都是可选的,并且也之前的JSP 视图解析器配置的时候参数含义相同
需要注意一点,我们并不需要配置前缀和后缀,因为这些已经在模板解析器中指定,并会依次传递到模板引擎中。
如果我们想定义一个View的bean并设置一些静态变量该如何做呢?很简单:
<bean name="main" class="org.thymeleaf.spring4.view.ThymeleafView">
<property name="staticVariables">
<map>
<entry key="footer" value="foot信息" />
</map>
</property>
</bean>
模板配置
Spring基础配置
在与Spring配合使用的时候,Thymeleaf提供了ITemplateResolver和与之相关联的IResourceResolver的与Spring资源处理器相结合的实现,这些是:
org.thymeleaf.spring4.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver用于解析模板.org.thymeleaf.spring4.resourceresolver.SpringResourceResourceResolver主要供内部使用.
这个模板解析器允许应用使用标准Spring资源解析语法来解析模板程序,它可以这样配置:
<bean id="templateResolver"
class="org.thymeleaf.spring4.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver">
<property name="suffix" value=".html" />
<property name="templateMode" value="HTML5" />
</bean>
然后就可以像这样使用视图:
@RequestMapping("/doit")
public String doIt() {
...
return "classpath:resources/templates/doit";
}
注意Spring基础的资源解析器不会被默认使用,它只是一个除了Thymeleaf核心所提供的模板资源解析器之外的模板资源解析器。
麝香生长管理系统
示例代码可以从此处下载下载
简介
有很多人都喜欢麝香,每年春天我们都会在小花盆里放上优良的土壤,还有麝香的种子,将它们放在阳光下,耐心的等待它们的生长。
但是今年我们受够了靠贴标签来知道每个花盆里种的是什么,所以我们决定使用Spring+Thymeleaf来制作一个应用,用于管理我们的一个培育目录,这个应用叫:春叶培育管理员系统。
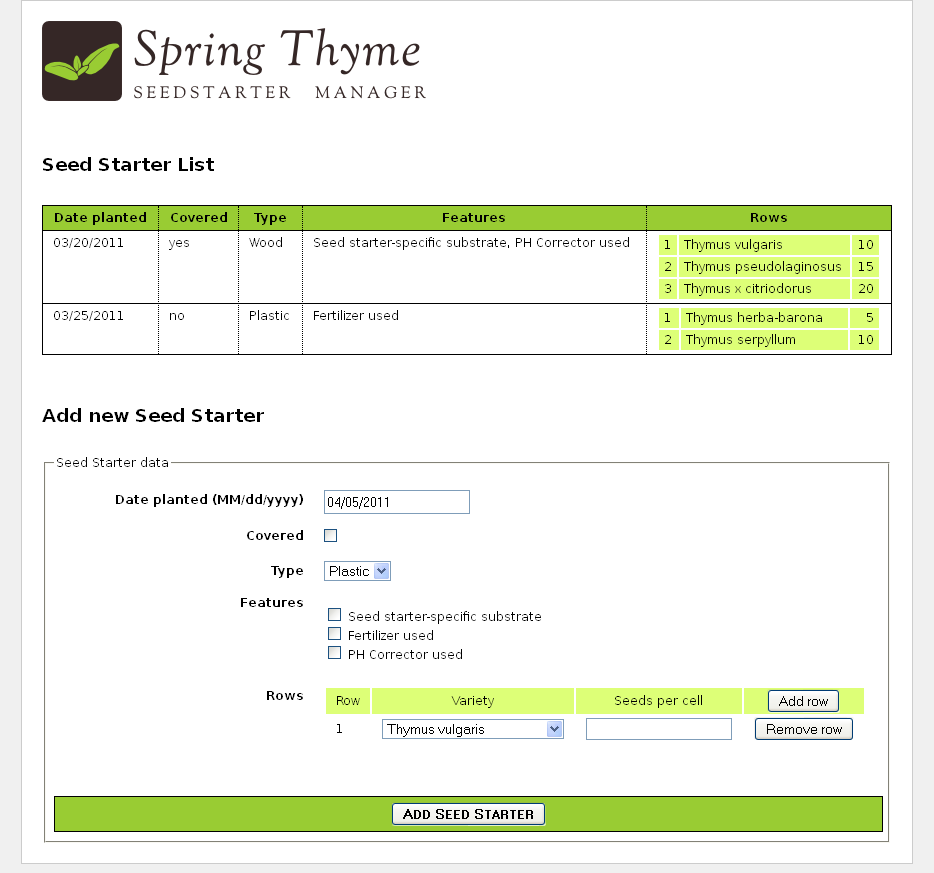
同Thymeleaf教程中的古泰虚拟商店一样,这个春叶培育管理系统将会设计到Spring+Thymeleaf的最重要的部分。
业务层
我们将为我们的应用配置一个简单的业务层,首先看看数据模型:
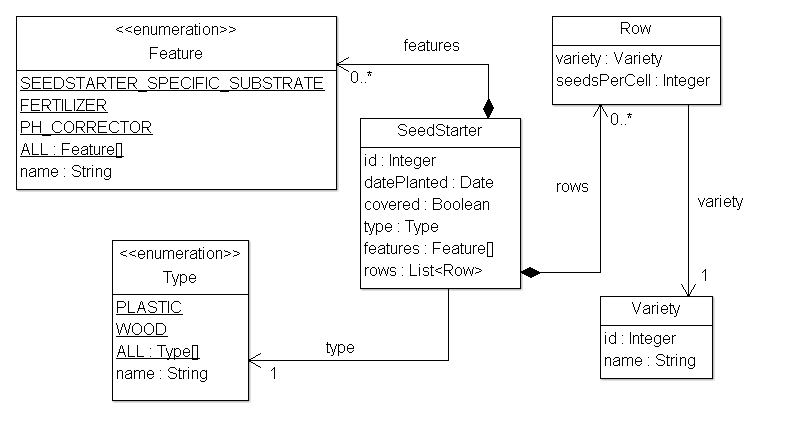
用几个简单的服务类提供所需的业务方法:
@Service
public class SeedStarterService {
@Autowired
private SeedStarterRepository seedstarterRepository;
public List<SeedStarter> findAll() {
return this.seedstarterRepository.findAll();
}
public void add(final SeedStarter seedStarter) {
this.seedstarterRepository.add(seedStarter);
}
}
和:
@Service
public class VarietyService {
@Autowired
private VarietyRepository varietyRepository;
public List<Variety> findAll() {
return this.varietyRepository.findAll();
}
public Variety findById(final Integer id) {
return this.varietyRepository.findById(id);
}
}
Spring MVC配置
接下来我们需要在应用中建立MVC配置文件,它将不仅包括SpringMvc的资源处理和注解扫描,还创建了模板引擎和视图解释器的实例。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<!-- **************************************************************** -->
<!-- RESOURCE FOLDERS CONFIGURATION -->
<!-- Dispatcher configuration for serving static resources -->
<!-- **************************************************************** -->
<mvc:resources location="/images/" mapping="/images/**" />
<mvc:resources location="/css/" mapping="/css/**" />
<!-- **************************************************************** -->
<!-- SPRING ANNOTATION PROCESSING -->
<!-- **************************************************************** -->
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService" />
<context:component-scan base-package="thymeleafexamples.stsm" />
<!-- **************************************************************** -->
<!-- MESSAGE EXTERNALIZATION/INTERNATIONALIZATION -->
<!-- Standard Spring MessageSource implementation -->
<!-- **************************************************************** -->
<bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource">
<property name="basename" value="Messages" />
</bean>
<!-- **************************************************************** -->
<!-- CONVERSION SERVICE -->
<!-- Standard Spring formatting-enabled implementation -->
<!-- **************************************************************** -->
<bean id="conversionService"
class="org.springframework.format.support.FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<property name="formatters">
<set>
<bean class="thymeleafexamples.stsm.web.conversion.VarietyFormatter" />
<bean class="thymeleafexamples.stsm.web.conversion.DateFormatter" />
</set>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- **************************************************************** -->
<!-- THYMELEAF-SPECIFIC ARTIFACTS -->
<!-- TemplateResolver <- TemplateEngine <- ViewResolver -->
<!-- **************************************************************** -->
<bean id="templateResolver"
class="org.thymeleaf.templateresolver.ServletContextTemplateResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/templates/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".html" />
<property name="templateMode" value="HTML5" />
</bean>
<bean id="templateEngine"
class="org.thymeleaf.spring4.SpringTemplateEngine">
<property name="templateResolver" ref="templateResolver" />
</bean>
<bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring4.view.ThymeleafViewResolver">
<property name="templateEngine" ref="templateEngine" />
</bean>
</beans>
注意:这里选择了HTML5作为模板模式。
控制器
当然,这个应用程序中还需要一个控制器,由于这个应用只有一个页面,用户种子的生长的查看和添加,所以只需要一个控制器就可以了:
@Controller
public class SeedStarterMngController {
@Autowired
private VarietyService varietyService;
@Autowired
private SeedStarterService seedStarterService;
...
}
现在看看在这个控制器中可以添加什么?
模型属性(ModelAttribute注解)
@ModelAttribute("allTypes")
public List<Type> populateTypes() {
return Arrays.asList(Type.ALL);
}
@ModelAttribute("allFeatures")
public List<Feature> populateFeatures() {
return Arrays.asList(Feature.ALL);
}
@ModelAttribute("allVarieties")
public List<Variety> populateVarieties() {
return this.varietyService.findAll();
}
@ModelAttribute("allSeedStarters")
public List<SeedStarter> populateSeedStarters() {
return this.seedStarterService.findAll();
}
方法映射
接下来是控制器最重要的一部分了,那就是方法映射(RequestMapping),一个表单页和一个新的种子对象添加页。
@RequestMapping({"/","/seedstartermng"})
public String showSeedstarters(final SeedStarter seedStarter) {
seedStarter.setDatePlanted(Calendar.getInstance().getTime());
return "seedstartermng";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/seedstartermng", params={"save"})
public String saveSeedstarter(
final SeedStarter seedStarter, final BindingResult bindingResult, final ModelMap model) {
if (bindingResult.hasErrors()) {
return "seedstartermng";
}
this.seedStarterService.add(seedStarter);
model.clear();
return "redirect:/seedstartermng";
}
配置转换服务##
为了在模板视图中更加方便的使用日期和我们自己定义的各种对象,我们注册的了一个转换服务在上下文中:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans ...>
...
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService" />
...
<!-- **************************************************************** -->
<!-- CONVERSION SERVICE -->
<!-- Standard Spring formatting-enabled implementation -->
<!-- **************************************************************** -->
<bean id="conversionService"
class="org.springframework.format.support.FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<property name="formatters">
<set>
<bean class="thymeleafexamples.stsm.web.conversion.VarietyFormatter" />
<bean class="thymeleafexamples.stsm.web.conversion.DateFormatter" />
</set>
</property>
</bean>
...
</beans>
转换服务允许我们注册两个org.springframework.format.Formatter接口的实现,关于Spring转换的更多信息,请查验文档
首先看一下DateFormatter,它的日期格式定义的字符串定义在Message.properties文件中,并且以date.format作为key.
public class DateFormatter implements Formatter<Date> {
@Autowired
private MessageSource messageSource;
public DateFormatter() {
super();
}
public Date parse(final String text, final Locale locale) throws ParseException {
final SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = createDateFormat(locale);
return dateFormat.parse(text);
}
public String print(final Date object, final Locale locale) {
final SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = createDateFormat(locale);
return dateFormat.format(object);
}
private SimpleDateFormat createDateFormat(final Locale locale) {
final String format = this.messageSource.getMessage("date.format", null, locale);
final SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat(format);
dateFormat.setLenient(false);
return dateFormat;
}
}
而VarietyFormatter可以自动转换我们的各种实体,将他们用在表单上(基本通过id)
public class VarietyFormatter implements Formatter<Variety> {
@Autowired
private VarietyService varietyService;
public VarietyFormatter() {
super();
}
public Variety parse(final String text, final Locale locale) throws ParseException {
final Integer varietyId = Integer.valueOf(text);
return this.varietyService.findById(varietyId);
}
public String print(final Variety object, final Locale locale) {
return (object != null ? object.getId().toString() : "");
}
}
在之后的内容,我们会学习更多的关于formatter的内容。
种子生长列表
首先,在/WEB-INF/templatesseedstartermng.html页将显示一个当前的已培育种子的列表,为此我们需要一些额外的信息,和通过表达式执行一些模型属性:
<div class="seedstarterlist" th:unless="${#lists.isEmpty(allSeedStarters)}">
<h2 th:text="#{title.list}">List of Seed Starters</h2>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th th:text="#{seedstarter.datePlanted}">Date Planted</th>
<th th:text="#{seedstarter.covered}">Covered</th>
<th th:text="#{seedstarter.type}">Type</th>
<th th:text="#{seedstarter.features}">Features</th>
<th th:text="#{seedstarter.rows}">Rows</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="sb : ${allSeedStarters}">
<td th:text="${{sb.datePlanted}}">13/01/2011</td>
<td th:text="${sb.covered}? #{bool.true} : #{bool.false}">yes</td>
<td th:text="#{${'seedstarter.type.' + sb.type}}">Wireframe</td>
<td th:text="${#strings.arrayJoin(
#messages.arrayMsg(
#strings.arrayPrepend(sb.features,'seedstarter.feature.')),
', ')}">Electric Heating, Turf</td>
<td>
<table>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="row,rowStat : ${sb.rows}">
<td th:text="${rowStat.count}">1</td>
<td th:text="${row.variety.name}">Thymus Thymi</td>
<td th:text="${row.seedsPerCell}">12</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
这里几乎是全部代码,现在分别查看每一个片段。
首先,这一部分将只在有种子在培育的时候显示,我们将使用th:unless属性来通过#lists.iEmpty(...)方法来实现这个目标。
<div class="seedstarterlist" th:unless="${#lists.isEmpty(allSeedStarters)}">
objects的工具类,比如#lists是SpringEL表达式,他就像在OGNL表达式中同样的方式使用。
接下来是一些国际化的文本:
<h2 th:text="#{title.list}">List of Seed Starters</h2>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th th:text="#{seedstarter.datePlanted}">Date Planted</th>
<th th:text="#{seedstarter.covered}">Covered</th>
<th th:text="#{seedstarter.type}">Type</th>
<th th:text="#{seedstarter.features}">Features</th>
<th th:text="#{seedstarter.rows}">Rows</th>
...
在这个SpringMVC应用程序中,我们通过一个bean定义了一个MessageSource在我们的spring的XML配置文件中:
<bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource">
<property name="basename" value="Messages" />
</bean>
basename表示我们将使用message打头的资源文件,如Message_en.properties或者Message_ZH_cn.properties,比如英文版如下:
title.list=Lista de semilleros
date.format=dd/MM/yyyy
bool.true=sí
bool.false=no
seedstarter.datePlanted=Fecha de plantación
seedstarter.covered=Cubierto
seedstarter.type=Tipo
seedstarter.features=Características
seedstarter.rows=Filas
seedstarter.type.WOOD=Madera
seedstarter.type.PLASTIC=Plástico
seedstarter.feature.SEEDSTARTER_SPECIFIC_SUBSTRATE=Sustrato específico para semilleros
seedstarter.feature.FERTILIZER=Fertilizante
seedstarter.feature.PH_CORRECTOR=Corrector de PH
在表格的第一列,将显示种子的培育开始时间,我们将通过定义的DateFormatter将它自动格式化显示,为了做到这一点,将使用${{}}语法,这个语法将自动应用Spring的转换服务。
<td th:text="${{sb.datePlanted}}">13/01/2011</td>
下面将显示花盆中是否有种子,通过改变bean的布尔值属性将布尔值转换为国际化的是和否。:
<td th:text="${sb.covered}? #{bool.true} : #{bool.false}">yes</td>
下一步将展示花盆的类型,它的类型是有两个值的枚举型(值分别为木制和塑料),这也是我为什么在配置文件中定义了seedstarter.type.WOOD和seedstarter.type.PLAStIC两个属性的原因。
但为了获取国际化之后的值,我们需要给实际值增加seedstarter.type的前缀,来生成Message 属性的key返回所需的值:
<td th:text="#{${'seedstarter.type.' + sb.type}}">Wireframe</td>
列表中最困难的部分就是功能列,因为在这里需要显示左右的功能,如"电加热,草皮",这里讲采用逗号分隔原有枚举数组的方式。
注意这样也是有些困难的,因为这些枚举需要根据他的类型进行具体化,需要:
- 给特征数组的所有元素规划响应的前缀,
- 获得从步骤1相对应的外部信息
- 把所有从步骤2获取的信息,用逗号分隔
为了实现这一点,我们创建了如下的代码:
<td th:text="${#strings.arrayJoin(
#messages.arrayMsg(
#strings.arrayPrepend(sb.features,'seedstarter.feature.')),
', ')}">Electric Heating, Turf</td>
列表的最有一列很简单,事实上,它有一个嵌套表,用于显示每一行的内容。
<td>
<table>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="row,rowStat : ${sb.rows}">
<td th:text="${rowStat.count}">1</td>
<td th:text="${row.variety.name}">Thymus Thymi</td>
<td th:text="${row.seedsPerCell}">12</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</td>
创建表单
处理命令对象
SpringMVC的表单支持bean就是命令对象,这个对象通过对象领域模型的方式提供get和set方法,在浏览器建立获取用户输入值的输入框架。
Thymeleaf需要你显示的在form标签内通过th:object属性指定命令对象:
<form action="#" th:action="@{/seedstartermng}" th:object="${seedStarter}" method="post">
...
</form>
这个th:object与其他的的地方用途是一直的,但是事实上在这种特定情况下,为了与SpringMVC框架的正确整合增加了一些特定的限制:
- 在form标签中的th:object的值必须是变量表达式(${...}),只能指定属性模型属性的名字,而不能使用属性导航,这意味着,表达式${seedStarter}是正确的,而${seedStarter.data}则不是。
- 一个form标签内只能指定一个th:object属性,这与html中form标签不能嵌套的特性相一致。
input
下面是如何将一个input插入到表单中
<input type="text" th:field="*{datePlanted}" />
正象上边的代码所示,新增了一个th:field的属性,这是SpringMVC集成的一个重要特征,它帮你完成了表单bean和输入框之间的繁重的绑定工作。可以看出他在from中的路径属性和SpringMVC的jsp标签库一样。
th:field属性的不同行为取决于它所附加的不同标签,包括<input>,<select>或<textarea>(还包括标签的不同type属性类型),在这种情况下,时间上上面哪行代码会是这样的:
<input type="text" id="datePlanted" name="datePlanted" th:value="*{datePlanted}" />
事实上,可能比上边的代码还要多一些东西,因为th:fild还可能会注册一个Spring的转换服务,包括之前我们看到的DateFormatter(甚至这个表达式中没使用双大括号),因此,这个日期也将被正确的格式化。
th:field的值必须使用选择表达式,这样将在这个环境中使用表单bean,而不是上下文变量或SpringMVC的模型属性。
相反对于th:object这类,它的表达式可以使用属性导航(事实上在JSP的<form:input标签中,可以使用任何的路径属性表达式)
注意th:field属性也可以在HTML5的的新增类型中使用,如<input type="datetime">,<input type="color">等,有效的增加了对SpringMVC对HTML5支持的完整性。
复选框
th:field也可以用在checkbox中,比如如下代码:
<div>
<label th:for="${#ids.next('covered')}" th:text="#{seedstarter.covered}">已种植</label>
<input type="checkbox" th:field="*{covered}" />
</div>
注意这里有一些除了复选框之外的好东西,比如外部label和它使用的#ids.next("covered")方法,用于当改id的复选框执行的时候获取它的id值。
那么为什么我们需要这个字段的id属性动态生成呢?因为复选框可能是多值的,因此它会给id值添加一个序列号后缀(内部使用#ids.seq(...)函数)来保证同一属性的复选框有不同的id值。
我们可以看看多值的复选框:
<ul>
<li th:each="feat : ${allFeatures}">
<input type="checkbox" th:field="*{features}" th:value="${feat}" />
<label th:for="${#ids.prev('features')}"
th:text="#{${'seedstarter.feature.' + feat}}">Heating</label>
</li>
</ul>
注意这次我们增加了一个th:value属性,因为这次的特征属性不是一个布尔值,而是一个数组。
一般情况下,它的输出为:
<ul>
<li>
<input id="features1" name="features" type="checkbox" value="SEEDSTARTER_SPECIFIC_SUBSTRATE" />
<input name="_features" type="hidden" value="on" />
<label for="features1">Seed starter-specific substrate</label>
</li>
<li>
<input id="features2" name="features" type="checkbox" value="FERTILIZER" />
<input name="_features" type="hidden" value="on" />
<label for="features2">Fertilizer used</label>
</li>
<li>
<input id="features3" name="features" type="checkbox" value="PH_CORRECTOR" />
<input name="_features" type="hidden" value="on" />
<label for="features3">PH Corrector used</label>
</li>
</ul>
我们可以看到一个序列后缀增加在每一个id的属性中,#ids.prev(....)函数允许我们把检索最后一个序列值,生成的一个特定的id。
用不着担心那些隐藏域的名称为"_features":这是为了避免浏览器将未选中的复选框的值在表单提交是没有自动发送而故意添加的。
还应注意到,如果我们的表单bean中的feature属性已经包含了一些特定的值,那么th:field还将会自动在相应的标签中增加checked="checked"属性。
单选框
单选框的用法和一个非布尔值的多选框使用方式类似,只是他不是多选:
<ul>
<li th:each="ty : ${allTypes}">
<input type="radio" th:field="*{type}" th:value="${ty}" />
<label th:for="${#ids.prev('type')}" th:text="#{${'seedstarter.type.' + ty}}">Wireframe</label>
</li>
</ul>
下拉列表
下拉列表包含两个部分:<select>标签和它包含的<option>标签。在创建这种表单域的时候,只有<select>标签需要导入th:field属性,但th:value属性却在<option>标签中非常重要,因为他们提供了目前选选择框的选项(使用和非布尔复选框和单选框类似的手段)
使用类型作为下拉列表:
<select th:field="*{type}">
<option th:each="type : ${allTypes}"
th:value="${type}"
th:text="#{${'seedstarter.type.' + type}}">Wireframe</option>
</select>
这段代码理解起来很容易,只是注意属性优先级让我们可以在option标签内使用th:each属性。
动态域
由于SpringMVC的高级表单绑定功能,使得我们可以使用复杂的SpringEL表达式来绑定动态表单域到表单bean中。这将允许我们在SeedStarter bean中创建一个新的Row对象,并将这个row的域添加到用户请求的form中。
为了做到这一点,我们需要在控制器中提供一些新的映射方法,它将根据我们的特定请求的参数来决定添加或删除一行我们定义的SeedStarter.
@RequestMapping(value="/seedstartermng", params={"addRow"})
public String addRow(final SeedStarter seedStarter, final BindingResult bindingResult) {
seedStarter.getRows().add(new Row());
return "seedstartermng";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/seedstartermng", params={"removeRow"})
public String removeRow(
final SeedStarter seedStarter, final BindingResult bindingResult,
final HttpServletRequest req) {
final Integer rowId = Integer.valueOf(req.getParameter("removeRow"));
seedStarter.getRows().remove(rowId.intValue());
return "seedstartermng";
}
现在给form添加一个动态table
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th th:text="#{seedstarter.rows.head.rownum}">Row</th>
<th th:text="#{seedstarter.rows.head.variety}">Variety</th>
<th th:text="#{seedstarter.rows.head.seedsPerCell}">Seeds per cell</th>
<th>
<button type="submit" name="addRow" th:text="#{seedstarter.row.add}">Add row</button>
</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="row,rowStat : *{rows}">
<td th:text="${rowStat.count}">1</td>
<td>
<select th:field="*{rows[__${rowStat.index}__].variety}">
<option th:each="var : ${allVarieties}"
th:value="${var.id}"
th:text="${var.name}">Thymus Thymi</option>
</select>
</td>
<td>
<input type="text" th:field="*{rows[__${rowStat.index}__].seedsPerCell}" />
</td>
<td>
<button type="submit" name="removeRow"
th:value="${rowStat.index}" th:text="#{seedstarter.row.remove}">Remove row</button>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
这里出现了很多东西,但都不难理解,除了这一句:
<select th:field="*{rows[__${rowStat.index}__].variety}">
...
</select>
如果你记得Thymeleaf教程,那么应该明白__${...}__是一种预处理表达式的语法。这是一个在处理整个表达式之前的内部表达式,但为什么用这种方式指定行的索引呢,下面这种方式不行么:
<select th:field="*{rows[rowStat.index].variety}">
...
</select>
嗯事实上,是不行的,他的问题是SpringEL表达式不执行数值中括号里边的表达式变量,索引执行上边的语句时,会得到一个错误的结果,就是字面形式的row[rowStat.index] (而不是row[0],row[1])而不是行集合中的正确位置,这就是为什么在这里需要预处理。
让我们看看产生的html后按"添加行"按钮几次:
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>1</td>
<td>
<select id="rows0.variety" name="rows[0].variety">
<option selected="selected" value="1">Thymus vulgaris</option>
<option value="2">Thymus x citriodorus</option>
<option value="3">Thymus herba-barona</option>
<option value="4">Thymus pseudolaginosus</option>
<option value="5">Thymus serpyllum</option>
</select>
</td>
<td>
<input id="rows0.seedsPerCell" name="rows[0].seedsPerCell" type="text" value="" />
</td>
<td>
<button name="removeRow" type="submit" value="0">Remove row</button>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>2</td>
<td>
<select id="rows1.variety" name="rows[1].variety">
<option selected="selected" value="1">Thymus vulgaris</option>
<option value="2">Thymus x citriodorus</option>
<option value="3">Thymus herba-barona</option>
<option value="4">Thymus pseudolaginosus</option>
<option value="5">Thymus serpyllum</option>
</select>
</td>
<td>
<input id="rows1.seedsPerCell" name="rows[1].seedsPerCell" type="text" value="" />
</td>
<td>
<button name="removeRow" type="submit" value="1">Remove row</button>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
验证和错误信息
让我们看看当有错误的时候如何给一个表单域一个CSS类:
<input type="text" th:field="*{datePlanted}"
th:class="${#fields.hasErrors('datePlanted')}? fieldError" />
可以看到,#fields.hasErrors(...)函数接受一个表达式参数(datePlanted),返回一个布尔值告诉field该字段是否有验证错误。
我们可以根据他们各自的field获取所有的错误:
<ul>
<li th:each="err : ${#fields.errors('datePlanted')}" th:text="${err}" />
</ul>
通过迭代,我们可以使用th:errors,一个专门用于创建一个通过制定选择器筛选的错误列表的属性,通过
分隔。
<input type="text" th:field="*{datePlanted}" />
<p th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('datePlanted')}" th:errors="*{datePlanted}">Incorrect date</p>
简单错误基础css样式,th:errorclass
在上边的例子中,如果字段有错误,将为表单的input域设置一个css类,因为这种方式很常见,Thymeleaf提供了一个特定的属性为 th:errorclass
应用于form域的标签(input,select,textarea等),它将从现有的name属性或th:field属性字段的名词相同的属性,如果发生错误,则将制定的css类追加到标签中。
<input type="text" th:field="*{datePlanted}" class="small" th:errorclass="fieldError" />
如果datePlanted发生错误,则:
<input type="text" id="datePlanted" name="datePlanted" value="2013-01-01" class="small fieldError" />
全部错误
如果我们想要在form中显示所有的错误呢?我们只需要通过'*'或'all'(等价)来查询#field.hasErrors(...)方法和#field.errors(...)方法:
<ul th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('*')}">
<li th:each="err : ${#fields.errors('*')}" th:text="${err}">Input is incorrect</li>
</ul>
在上边的例子中,我们得到所有的错误并迭代他们:
<ul>
<li th:each="err : ${#fields.errors('*')}" th:text="${err}" />
</ul>
建立一个以
分隔的列表:
<p th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('all')}" th:errors="*{all}">Incorrect date</p>
最后,注意#field.hasErrors("")等效的属性#fields.hasAnyErrors()和#fields.errors()的等效的#fields.allErrors(),可以使用喜欢的任何语法。
<div th:if="${#fields.hasAnyErrors()}">
<p th:each="err : ${#fields.allErrors()}" th:text="${err}">...</p>
</div>
全局错误
Spring表单还有一种错误,全局错误,都是些不与窗体的任何特定字段关联的错误。
Thymeleaf提供了一个global的常量来访问这些错误。
<ul th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('global')}">
<li th:each="err : ${#fields.errors('global')}" th:text="${err}">Input is incorrect</li>
</ul>
<p th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('global')}" th:errors="*{global}">Incorrect date</p>
以及等效的#field.hasGlobalErrors()和#field.globalErrors()方法。
<div th:if="${#fields.hasGlobalErrors()}">
<p th:each="err : ${#fields.globalErrors()}" th:text="${err}">...</p>
</div>
在表单外部显示错误
表单验证错误也可以在表单外部显示,方法是通过变量(即${...})的内部选择变量(*{...})增加表单bean的名字作为前缀的方式。
<div th:errors="${myForm}">...</div>
<div th:errors="${myForm.date}">...</div>
<div th:errors="${myForm.*}">...</div>
<div th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('${myForm}')}">...</div>
<div th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('${myForm.date}')}">...</div>
<div th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('${myForm.*}')}">...</div>
<form th:object="${myForm}">
...
</form>
富错误对象
Thymeleaf提供了以bean的形式(代替单纯的String)提供错误信息的能力,包括fieldName(String),message(String),和global(String)属性的错误。
这些错误可以通过工具方法#fields.datailedErrors()来实现:
<ul>
<li th:each="e : ${#fields.detailedErrors()}" th:class="${e.global}? globalerr : fielderr">
<span th:text="${e.global}? '*' : ${e.fieldName}">The field name</span> |
<span th:text="${e.message}">The error message</span>
</li>
</ul>
它仍然是一个原型
现在程序已经好了,现在看一下创建的html模板页面。
使用Thymeleaf框架的一大好处就是,所有这些功能加入到网页后,网页仍然可作为原型使用(所以我们说他是天然模板),打开浏览器,不执行程序直接运行seedstartermng.html:
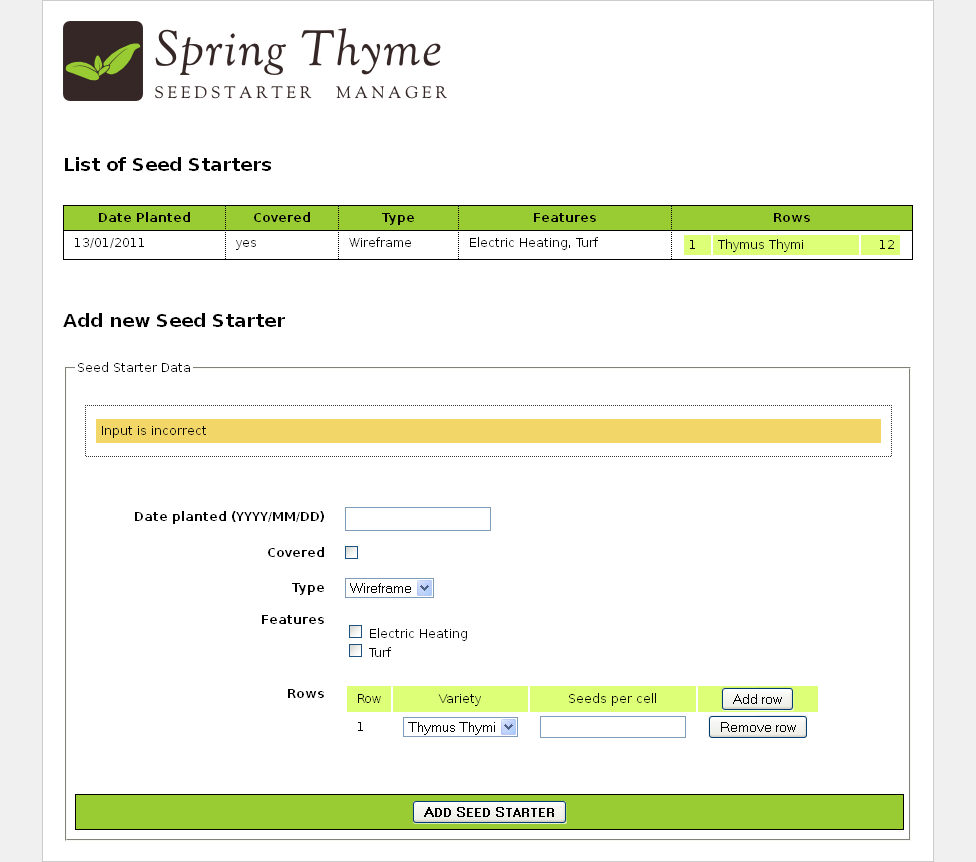
可以看到,虽然他没有运行起来,不是一个有效的数据,但它是一个完全有效的,可以直接显示的原型,试想一下,如果是jsp的话,那会怎样呢?
转换服务
配置
就像前文所说,Thymeleaf可以在上下文中注册一个转换服务,再次看一下他的配置信息
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans ...>
...
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService" />
...
<!-- **************************************************************** -->
<!-- CONVERSION SERVICE -->
<!-- Standard Spring formatting-enabled implementation -->
<!-- **************************************************************** -->
<bean id="conversionService"
class="org.springframework.format.support.FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<property name="formatters">
<set>
<bean class="thymeleafexamples.stsm.web.conversion.VarietyFormatter" />
<bean class="thymeleafexamples.stsm.web.conversion.DateFormatter" />
</set>
</property>
</bean>
...
</beans>
${{...}}语法
转换服务可以通过${{...}}语法很轻松的实现对象到字符串的转换或格式化:
- 变量语法${{...}}
- 选择变量语法*{{...}}
例如,将一个Integer型转换为字符串类型,并通过逗号来分隔:
<p th:text="${val}">...</p>
<p th:text="${{val}}">...</p>
返回结果为:
<p>1234567890</p>
<p>1,234,567,890</p>
表单中使用
我们之前看到的每一个th:field属性都将始终使用转换服务:
<input type="text" th:field="*{datePlanted}" />
等效于:
<input type="text" th:field="*{{datePlanted}}" />
注意这是唯一一种在表达式中使用单大括号的转换服务。
#conversions工具对象
conversions工具对象表达式允许手动执行转换服务:
<p th:text="${'Val: ' + #conversions.convert(val,'String')}">...</p>
工具对象表达式的语法为:
-
conversions.convert(Object,Class):将对象转换为指定的类
-
conversions.convert(Object,String):和上边相同,但是指定的目标为String类(java.lang包名可以省略)
渲染片段模板
Thymeleaf提供了将一个模板只渲染一部分,并作为一个片段返回的能力。
这是一个非常有用的组件化工具,比如,它可以用于执行AJAX的Controller的调用,用于在已经加载的浏览器中返回一个片段标签(如用于更新选择,启用禁用按钮等)。
片段渲染可以使用Thymeleaf的片段规范:一个实现了org.thymeleaf.fragment.IFragmentSpec接口的对象。
最常用的一个实现是org.thymeleaf.standard.fragment.StandardDOMSelectorFragmentSpec类,它允许一个片段规范包括之前说过的th:insert,th:replace使用DOM选择器。
在视图bean中指定片段
视图bean是在应用程序上下文中声明的org.thymeleaf.spring4.view.ThymeleafView的bean,它允许这样定义一个片段:
<bean name="content-part" class="org.thymeleaf.spring4.view.ThymeleafView">
<property name="templateName" value="index" />
<property name="fragmentSpec">
<bean class="org.thymeleaf.standard.fragment.StandardDOMSelectorFragmentSpec"
c:selectorExpression="content" />
</property>
</bean>
通过上边的bean的定义,如果controller返回一个content-part(bean的名字),
@RequestMapping("/showContentPart")
public String showContentPart() {
...
return "content-part";
}
Thymeleaf将只返回index模板的content片段。一旦前缀后缀都设置并匹配,那么它可能为/WEB-INF/templates/index.html,
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
...
<body>
...
<div th:fragment="content">
只有这里渲染!!
</div>
...
</body>
</html>
另外应该注意到,因为Thymeleaf可以使用DOM选择器,所有我们可以不用任何th:fragment属性,而只用id属性来选择一个片段,如:
<bean name="content-part" class="org.thymeleaf.spring4.view.ThymeleafView">
<property name="fragmentSpec">
<bean class="org.thymeleaf.standard.fragment.StandardDOMSelectorFragmentSpec"
c:selectorExpression="#content" />
</property>
<property name="templateName" value="index" />
</bean>
同样完美的适用:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
...
<body>
...
<div id="content">
只有这里渲染!!
</div>
...
</body>
</html>
通过控制权的返回值指定片段
不声明一个视图bean,可以从控制器自己就可以使用与片段相同的语法,类似于th:insert,th:rplace属性等,如:
@RequestMapping("/showContentPart")
public String showContentPart() {
...
return "index :: content";
}
当然,同样可以使用基于DOM选择器的功能,所有我们也可以是选择使用基于标准的HTML属性,如id="content"
@RequestMapping("/showContentPart")
public String showContentPart() {
...
return "index :: #content";
}
也可以使用参数:
@RequestMapping("/showContentPart")
public String showContentPart() {
...
return "index :: #content ('myvalue')";
}
先进的集成功能
与RequestDataValueProcessor集成
现在Thymeleaf无缝的与Spring的RequestDataValueProcessor接口集成,这个接口允许拦截链接URLS,表达URLS和表达域的值,以及为了启用安全,如抵御CSRF而自动透明的添加一些隐藏域。
在应用的上下文中可以简单的配置RequestDataValueProcessor:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.1.xsd">
...
<bean name="requestDataValueProcessor"
class="net.example.requestdata.processor.MyRequestDataValueProcessor" />
</beans>
Thymeleaf将通过这种方式使用它:
- 在渲染URL之前,th:href和th:src将会调用RequestDataValueProcessor.processUrl(...)
- 在渲染表单的action属性之前,th:action会调用RequestDataValueProcessor.processAction(...),另外他会检查之前执行RequstDataValueProcessor.getExtraHiddenFields(...)用来新增返回的hidden域。
- 在渲染value属性之前,th:value会调用RequestDataProcessor.processFormFieldValue(...),除非在这个标签中存在了th:field(这时候th:field属性起作用)
- 当存在th:field的时候,在渲染value属性之前会调用RequestDataValueProcessor.processFormFieldValue(...)处理这个属性值(
<textarea>处理内容值)
此功能只有Spring3.x以后使用
绑定地址到Controller
在Spring4.1之后的版本中,Spring允许通过注解直接从从视图链接到控制器,而不需要知道这些控制器映射的URI.
在Thymeleaf中可以通过#mvc.url(...)表达式方法调用Controller中符合驼峰命名规则的方法(get,set),调用的方式为方法的名字,即相当于jsp的spring:mvcUrl(...)自定义方法。
比如
public class ExampleController {
@RequestMapping("/data")
public String getData(Model model) { ... return "template" }
@RequestMapping("/data")
public String getDataParam(@RequestParam String type) { ... return "template" }
}
下边是一个链接到它的方法:
<a th:href="${(#mvc.url('EC#getData')).build()}">获取Data参数</a>
<a th:href="${(#mvc.url('EC#getDataParam').arg(0,'internal')).build()}">获取Data参数</a>
查阅更多这种机制可以查看这里
Spring WebFlow的集成
基础配置
Thymeleaf-spring4集成包包括与Spring WebFlow 2.3.x的集成
WebFlow包括当特定的事件(过渡)被触发时渲染页面片段的一些Ajax的功能,未来让Thymeleaf参加这些Ajax请求,我们将使用一个不通过的视图解析器的实现,它这样配置:
<bean id="thymeleafViewResolver" class="org.thymeleaf.spring4.view.AjaxThymeleafViewResolver">
<property name="viewClass" value="org.thymeleaf.spring4.view.FlowAjaxThymeleafView" />
<property name="templateEngine" ref="templateEngine" />
</bean>
然后在ViewResolver中配置WebFlow的ViewFactoryCreator.
<bean id="mvcViewFactoryCreator"
class="org.springframework.webflow.mvc.builder.MvcViewFactoryCreator">
<property name="viewResolvers" ref="thymeleafViewResolver"/>
</bean>
在这里可以指定模板的视图状态
<view-state id="detail" view="bookingDetail">
...
</view-state>
在上边的实例中,bookingDetail是Thymeleaf模板通常使用的一个方式,是模板引擎内任何模板解析器都可以懂的
Ajax片段
WebFlow的片段规范允许片段通过
<view-state id="detail" view="bookingDetail">
<transition on="updateData">
<render fragments="hoteldata"/>
</transition>
</view-state>
这些片段(即hoteldata)可以是逗号分隔的列表标记在th:fragment标签中。
<div id="data" th:fragment="hoteldata">
这里内容替换
</div>
永远记住,指定的片段必须有一个id属性,这样浏览器运行的Spring
JavaScript库才能对标签进行替换。
<view-state id="detail" view="bookingDetail">
<transition on="updateData">
<render fragments="[//div[@id='data']]"/>
</transition>
</view-state>
这将意味着th:fragment不在需要:
<div id="data">
This is a content to be changed
</div>
而出发updateData后转换的代码:
<script type="text/javascript" th:src="@{/resources/dojo/dojo.js}"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" th:src="@{/resources/spring/Spring.js}"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" th:src="@{/resources/spring/Spring-Dojo.js}"></script>
...
<form id="triggerform" method="post" action="">
<input type="submit" id="doUpdate" name="_eventId_updateData" value="Update now!" />
</form>
<script type="text/javascript">
Spring.addDecoration(
new Spring.AjaxEventDecoration({formId:'triggerform',elementId:'doUpdate',event:'onclick'}));
</script>