Mike is a bartender at Rico's bar. At Rico's, they put beer glasses in a special shelf. There are n kinds of beer at Rico's numbered from 1to n. i-th kind of beer has ai milliliters of foam on it.

Maxim is Mike's boss. Today he told Mike to perform q queries. Initially the shelf is empty. In each request, Maxim gives him a number x. If beer number x is already in the shelf, then Mike should remove it from the shelf, otherwise he should put it in the shelf.
After each query, Mike should tell him the score of the shelf. Bears are geeks. So they think that the score of a shelf is the number of pairs (i, j) of glasses in the shelf such that i < j and 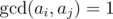 where
where 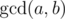 is the greatest common divisor of numbers aand b.
is the greatest common divisor of numbers aand b.
Mike is tired. So he asked you to help him in performing these requests.
The first line of input contains numbers n and q (1 ≤ n, q ≤ 2 × 105), the number of different kinds of beer and number of queries.
The next line contains n space separated integers, a1, a2, ... , an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 5 × 105), the height of foam in top of each kind of beer.
The next q lines contain the queries. Each query consists of a single integer integer x (1 ≤ x ≤ n), the index of a beer that should be added or removed from the shelf.
For each query, print the answer for that query in one line.
5 6
1 2 3 4 6
1
2
3
4
5
1
0
1
3
5
6
2
可以知道,一个500000范围内的数,不同的质因子的个数不会超过6个,因而可以考虑容斥原理解此题。
首先预处理出范围内的数所包含的不同质因子的个数及其中的质因子。设公约数包含某个质因子的对数为性质P,(P1,P2,P3,....),运用容斥原理则可解答此题了。其中,统计某个性质P的对数可以设一个数组预先把相应的对数的个数先存下来,这样可以简化计算。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#define LL long long
using namespace std;
const int N=500010;
int fac[N][10],cf[N];
LL mul[N];
int arr[N],cnum[500],c;
bool vis[N];
LL tot=0,ans=0,curans;
void initial(){
memset(cf,0,sizeof(cf));
for(int i=2;i<N;i++){
if(cf[i]) continue;
for(int j=i;j<N;j+=i){
fac[j][++cf[j]]=i;
}
}
}
void dfs(int num,int pos,int cnt,int val){
if(pos>cf[num]){
cnum[c++]=val;
if(cnt&1) curans-=mul[val];
else curans+=mul[val];
return ;
}
dfs(num,pos+1,cnt,val);
dfs(num,pos+1,cnt+1,val*fac[num][pos]);
}
void gao(int num){
c=0;
curans=0;
dfs(num,1,0,1);
}
int main(){
initial();
int n,q,x;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&q)!=EOF){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
vis[i]=false;
}
memset(mul,0,sizeof(mul));
for(int i=1;i<=q;i++){
scanf("%d",&x);
if(arr[x]==1){
if(!vis[x]){
vis[x]=true;
ans+=tot;
tot++;
mul[1]++;
}
else {
vis[x]=false;
ans-=tot-1;
tot--;
mul[1]--;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
continue;
}
// cout<<cf[arr[x]]<<endl;
if(!vis[x]){
vis[x]=true;
gao(arr[x]);
// cout<<curans<<endl;
ans+=curans;
tot++;
for(int i=0;i<c;i++)
mul[cnum[i]]++;
}
else{
vis[x]=false;
gao(arr[x]);
tot--;
ans-=curans;
for(int i=0;i<c;i++)
mul[cnum[i]]--;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}