Java中字符串是String类的实例,字符串也是对象,所以 Java将字符串作为对象进行管理
Java使用java.lang 包中的String类来创建字符串。
1.定义字符串:
使用 " " 定义,java中由""定义的多个字符都是字符串,不能作为其他类型使用,例如"30+70"绝不等于100
2.声明字符串变量
String str=null;
String str="";
空字符串和Null
空字符串 是由""定义的 是一个实例化后的字符串对象,但不包含任何字符
null 并不是字符串的实例对象,是一个常量 ,只是不包含任何东西而已
注意:一个Java对象(字符串也是对象)必须先初始化,然后才能使用,否则编辑器会报告 “使用的变量未初始化”错误
3.创建字符串
String str="jelo";
4.字符串连接
使用+符号进行字符串的连接
@1.与基本数据类型连接
int float double boolean long char short 等,直接将这些数据转变成字符串,然后进行连接。
@2.字符串与对象连接
Java中的所有类都是Object类的子类,他们直接或间接的继承了Object类的方法,包括toString()方法
toString()方法
将对象转换成字符串,在字符串连接对象时,将调用这个方法使对象转换成字符串,然后再执行连接操作
toString()方法分析
默认实现是输出创建该对象的类的全路径名称和内存地址,如果实例中的类不重构toString()方法,那么程序将输出以下结果
com.lzw.Apple@c17164
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Apple abl=new Apple("apple");
System.out.println("苹果类----"+abl);
}
}
class Apple{
private String name;
public Apple(String name) {
this.name=name;
}
public String toString(){
String str="我是一个大苹果---"+this.name;
return str;
}
}
没有重写toString类
苹果类----com.sgb.Apple@ad8659
5.字符串操作
(1).字符串比较
equals()方法和equalsignoreCase()方法
@1 equals()方法
比较两个字符串内容是否相等,字符串是对象类型,所以不能简单的用==判断是否相等,比较的是内存地址
boolean equals(String str)
str作比较的字符串对象
boolean 返回的值
equals()比较的是对象的内容(区分大小写格式),但==比较的是两个对象的内存地址(即使内容相同,不同对象的内存地址也是不同的)
@2 equalsignoreCase(str) 方法忽略大小写
忽略大小写的比较 其余功能和equals相同
String str1="abc";
String str2=new String("abc");
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2)); true
System.out.println(str1==str2); false
String str1="abc";
String str2="abc";
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2)); true
System.out.println(str1==str2); true
Java中字符串如果存在不会再开辟新的空间而是直接指向已存在字符串
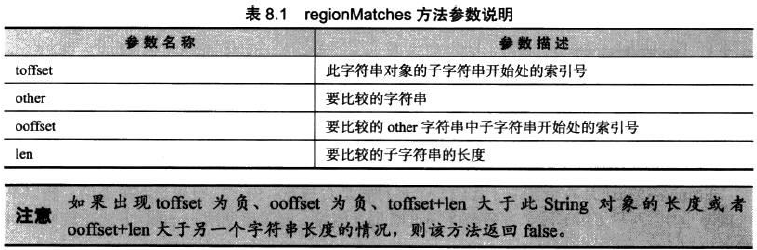
@3 regionMatches(toffset,other,ooffset,len)
将一个字符串中指定长度的子字符串和另一个字符串中的子字符串进行比较 区分大小写
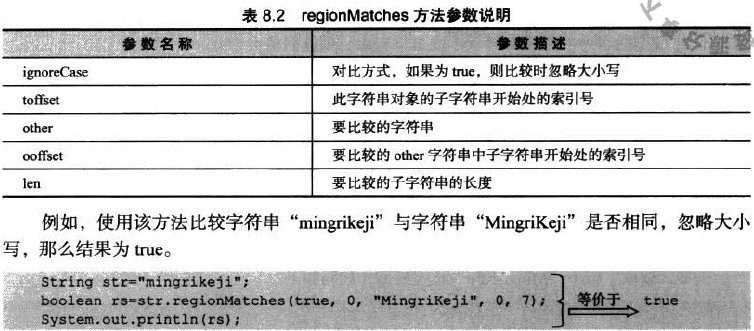
regionMatches(ignoreCase,toffset,other,ooffset,len)
忽略大小写
参数详解
@4.startsWith() endsWith()
判断字符串是否以指定的内容开始或结束 是返回true 否 返回false
"MingriLeji".startsWith("Ming"); true
"MingriLeji".endsWith("ji"); true
@5.compareTo() 比较
判断 一个字符串是大于等于还是小于另一个字符串,大小依据是根据他们在字典中的顺序决定
int compareTo(String str)
等于 返回0
小于 返回值小于0
大于 返回值 大于0
5.取得字符串的长度
str.leng();
6.字符串大小写转换
toLowerCase() 转小写 str.toLowerCase() 分配一个新字符串
toUpperCase() 转大写