队列Queue
概述
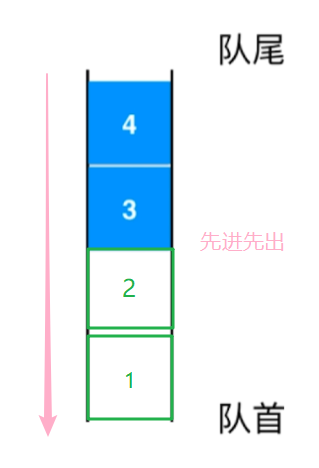
队列也是一种线性结构。(排成一列的成线性的)
相比数组,队列对应的操作是数组的子集
只能从一端(队尾)添加元素,只能从另一端(队首)取出元素
和我们生活当中的排队是一个意思
特性
是一种先进先出的数据结构。(先到先得)
First In First Out (FIFO)
队列的实现

Queue接口:
public interface Queue<E> {
int getSize();
boolean isEmpty();
void enqueue(E e);
E dequeue();
E getFront();
}
简单实现:
public class ArrayQueue<E> implements Queue<E> {
// 用自己写的数组
private Array<E> array;
public ArrayQueue(int capacity){
array = new Array<>(capacity);
}
public ArrayQueue(){
array = new Array<>();
}
@Override
public int getSize(){
return array.getSize();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty(){
return array.isEmpty();
}
public int getCapacity(){
return array.getCapacity();
}
@Override
public void enqueue(E e){
array.addLast(e);
}
@Override
public E dequeue(){
return array.removeFirst();
}
@Override
public E getFront(){
return array.getFirst();
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append("Queue: ");
res.append("front [");
for(int i = 0 ; i < array.getSize() ; i ++){
res.append(array.get(i));
if(i != array.getSize() - 1)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append("] tail");
return res.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayQueue<Integer> queue = new ArrayQueue<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++){
queue.enqueue(i);
System.out.println(queue);
if(i % 3 == 2){
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
}
}
简单队列的复杂度分析

出队函数会存在O(n)级别
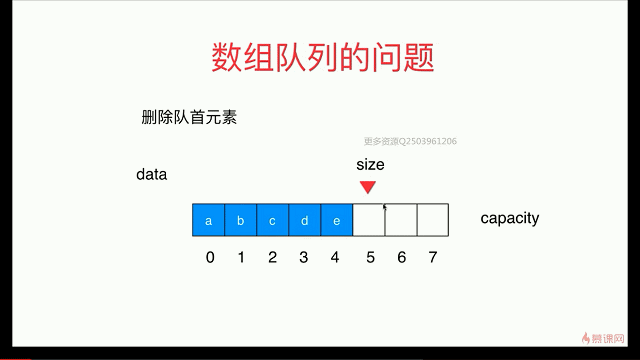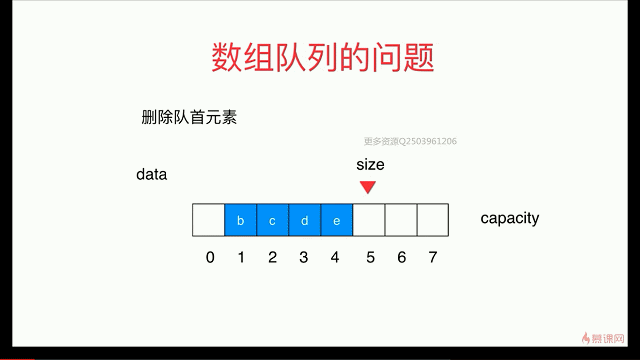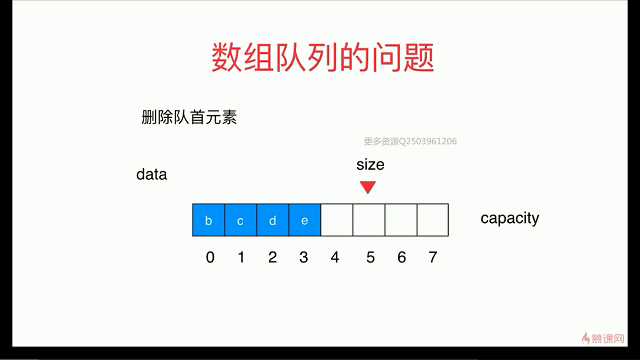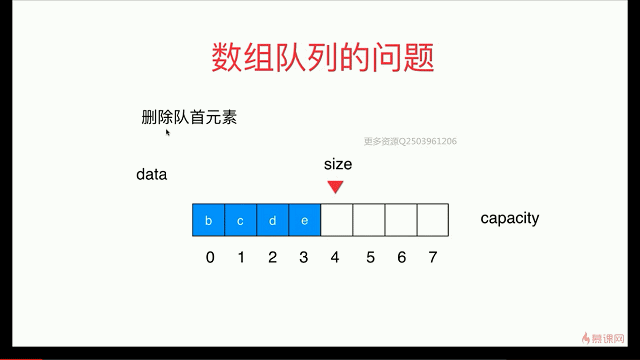
解决:用 循环队列
循环队列 Loop-Queue
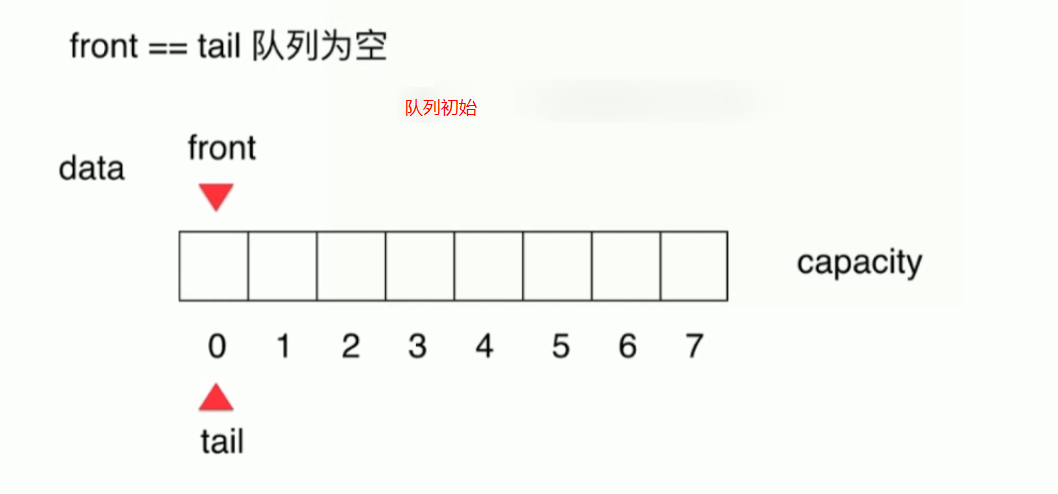
分析
队列初始 front==tail
入队:
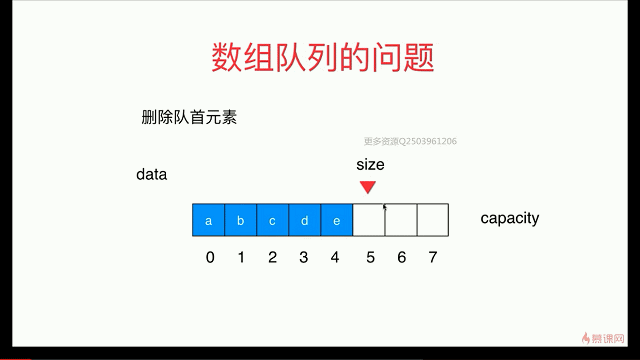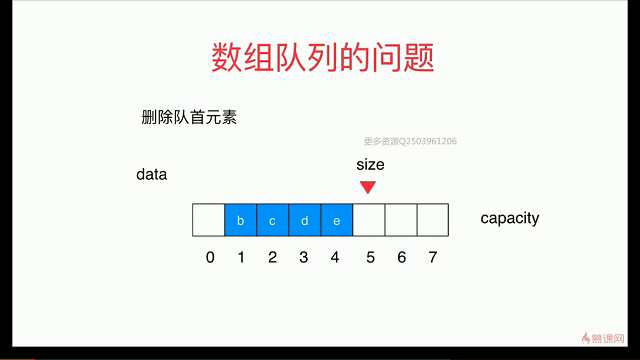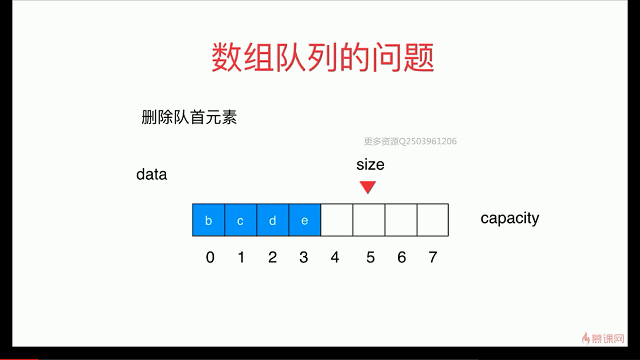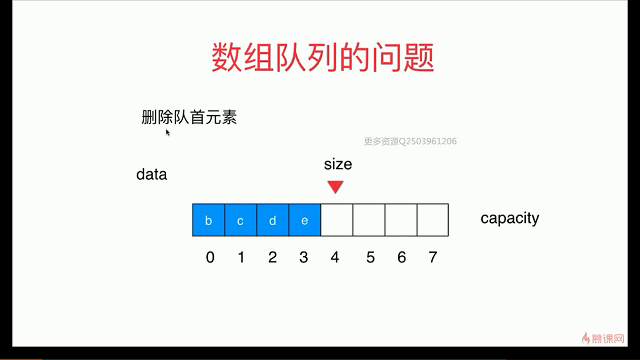
出队:
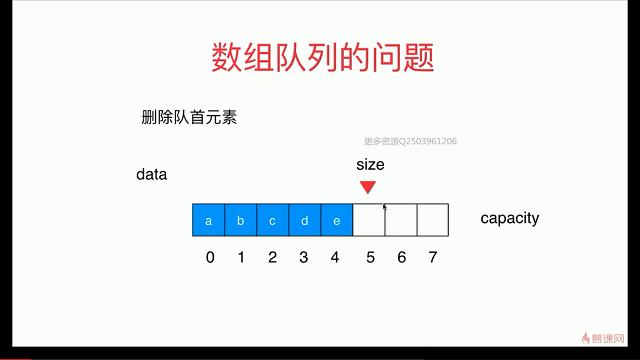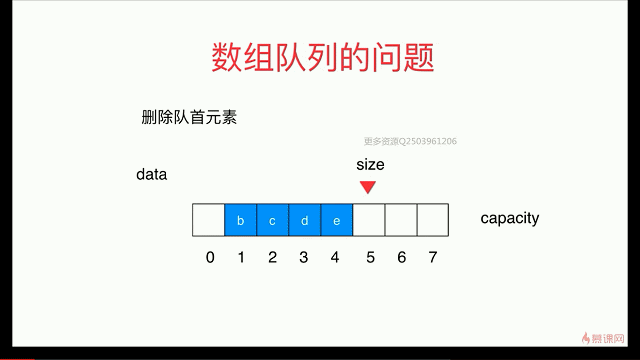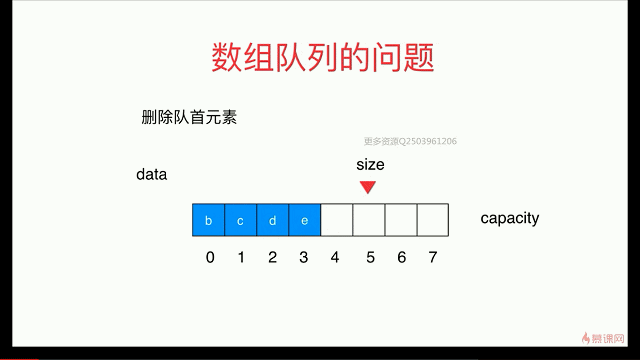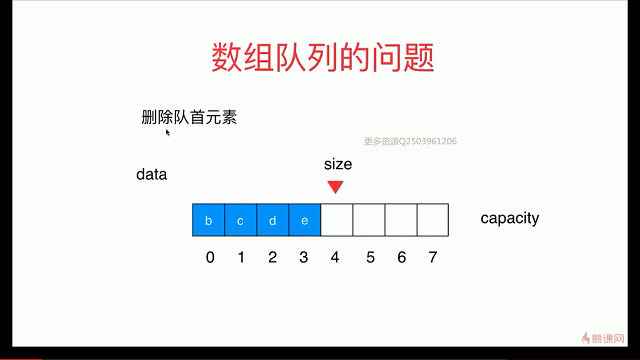
循环队列:



循环队列的实现
public class LoopQueue<E> implements Queue<E> {
private E[] data;
// 维护队首和队尾的指针
private int front, tail;
// 队列的大小
private int size; // 有兴趣的同学,在完成这一章后,可以思考一下:
// LoopQueue中不声明size,如何完成所有的逻辑?
// 这个问题可能会比大家想象的要难一点点:)
public LoopQueue(int capacity){
// 因为front 和 tail 维护队列时, 要有意识的浪费一个空间 所以capacity要加1
data = (E[])new Object[capacity + 1];
front = 0;
tail = 0;
size = 0;
}
public LoopQueue(){
this(10);
}
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length - 1;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty(){
return front == tail;
}
@Override
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
@Override
public void enqueue(E e){
if((tail + 1) % data.length == front)
resize(getCapacity() * 2);
data[tail] = e;
tail = (tail + 1) % data.length;
size ++;
}
@Override
public E dequeue(){
if(isEmpty())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot dequeue from an empty queue.");
E ret = data[front];
data[front] = null;
front = (front + 1) % data.length;
size --;
if(size == getCapacity() / 4 && getCapacity() / 2 != 0)
resize(getCapacity() / 2);
return ret;
}
@Override
public E getFront(){
if(isEmpty())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Queue is empty.");
return data[front];
}
private void resize(int newCapacity){
E[] newData = (E[])new Object[newCapacity + 1];
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++)
newData[i] = data[(i + front) % data.length];
data = newData;
front = 0;
tail = size;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Queue: size = %d , capacity = %d
", size, getCapacity()));
res.append("front [");
for(int i = front ; i != tail ; i = (i + 1) % data.length){
res.append(data[i]);
if((i + 1) % data.length != tail)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append("] tail");
return res.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
LoopQueue<Integer> queue = new LoopQueue<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++){
queue.enqueue(i);
System.out.println(queue);
if(i % 3 == 2){
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
}
}
循环队列的复杂度分析

测验:
import java.util.Random;
public class Main {
// 测试使用q运行opCount个enqueueu和dequeue操作所需要的时间,单位:秒
private static double testQueue(Queue<Integer> q, int opCount){
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
Random random = new Random();
for(int i = 0 ; i < opCount ; i ++)
q.enqueue(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
for(int i = 0 ; i < opCount ; i ++)
q.dequeue();
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
return (endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int opCount = 100000;
ArrayQueue<Integer> arrayQueue = new ArrayQueue<>();
double time1 = testQueue(arrayQueue, opCount);
System.out.println("ArrayQueue, time: " + time1 + " s");
LoopQueue<Integer> loopQueue = new LoopQueue<>();
double time2 = testQueue(loopQueue, opCount);
System.out.println("LoopQueue, time: " + time2 + " s");
}
}
运行结果:

性能提高了将近100多倍。
真正好的性能评估是:n次实验求平均值。