1.Flink中exactly once实现原理分析
生产者从kafka拉取数据以及消费者往kafka写数据都需要保证exactly once。目前flink中支持exactly once的source不多,有kafka source;能实现exactly once的sink也不多,如kafka sink、streamingFileSink,其都要开启checkpoint才能实现exactly once。接下来以FlinkKafkaProducer为例,深入研究其源代码,从而理解flink中的exactly once(精准一次性语义)是怎么实现的。
1.1 大致流程图(也叫分两阶段提交原理)
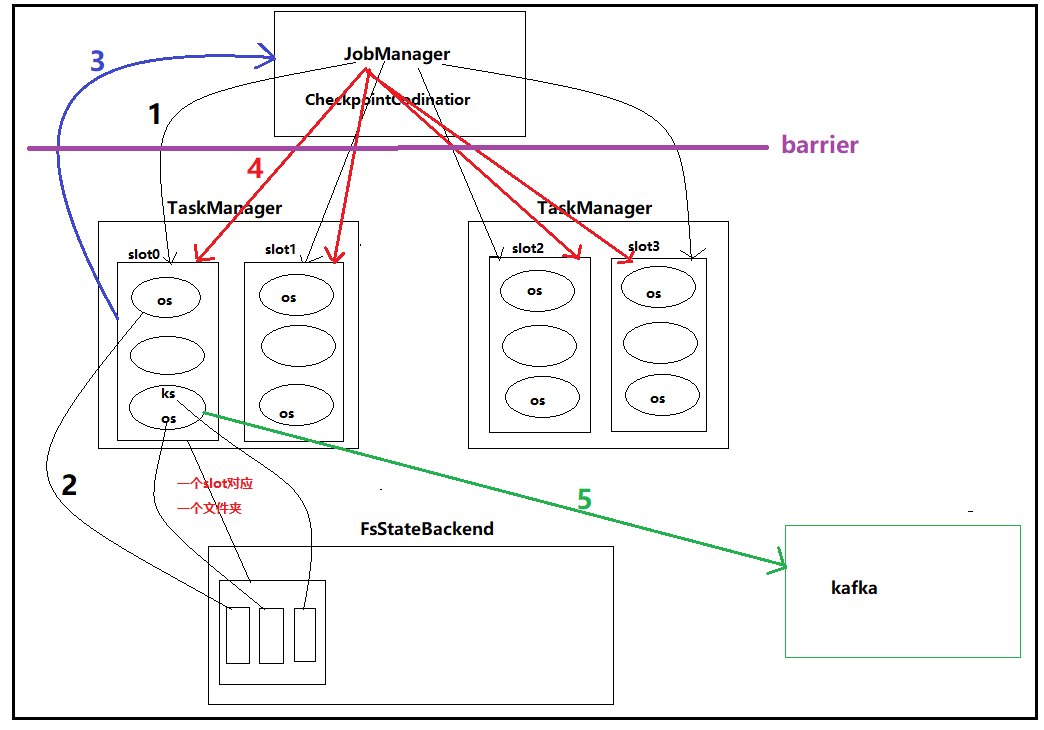
1. JobManager定期(通过CheckpointCodinator)向各个包含state的subTask发起checkpoint的请求
2. subTask将各自的state写入到相应的statebackend,一个资源槽对应一个文件,其中各个subTask的state写入这个文件中
3. 各个subTask向JobManager发送checkpoint成功的消息
4. 当所有subTask都发送了checkpoint成功的消息后,jobManager会向所有实现了checkpoint的subTask发送成功的消息
5. subTask往kafka写数据,并且向Kafka提交事务()
注意:为了保证一个流水线(pipeline)上的operrator state和keyedstate数据一致,flink引入了barrier机制,即在jobmanager和taskManager间设置一个barrier,相当于节流,保证在checkpoint时,source不能在读取数据
问题:kafka涉及到生产者往里面写数据一个事务,以及消费者读取数据一个事务,这两个事物间有什么联系?
1.2 源码解析
(1)首先看FlinkKafkaProducer类,可以发现其继承了TwoPhaseCommitSinkFunction

(2)TwoPhaseCommitSinkFunction是所有要实现一次性语义的SinkFunction的一个比较推荐的基类,其实现了两个重要的接口,分别为:CheckpointedFunction, CheckpointListener
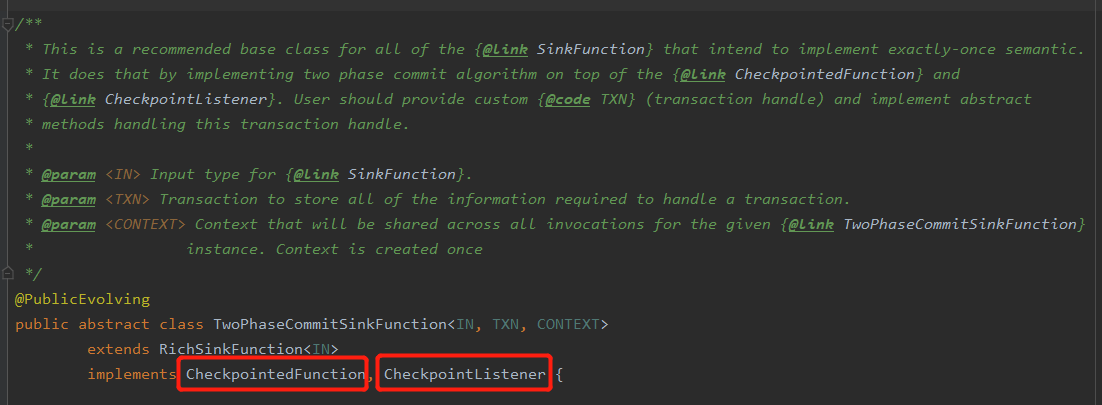
- CheckpointedFunction接口
此接口中包含两个方法,分别为snapshotState方法、initializeState方法,源代码如下

public interface CheckpointedFunction { /** * This method is called when a snapshot for a checkpoint is requested. This acts as a hook to the function to * ensure that all state is exposed by means previously offered through {@link FunctionInitializationContext} when * the Function was initialized, or offered now by {@link FunctionSnapshotContext} itself. * * @param context the context for drawing a snapshot of the operator * @throws Exception */ void snapshotState(FunctionSnapshotContext context) throws Exception; /** * This method is called when the parallel function instance is created during distributed * execution. Functions typically set up their state storing data structures in this method. * * @param context the context for initializing the operator * @throws Exception */ void initializeState(FunctionInitializationContext context) throws Exception; }
其中snapshotState方法是用checkpoint时,拍快照,其能将state持久化到statebackend。这里面存了一些transactionID、subTask编号、以及kafka的相关信息(用来写数据)。若是checkpoint成功了,但是subTask并没有成功将数据写入kafka,则会通过这个方法恢复原先最近的state进行恢复,然后继续
initializeState方法可以用来恢复state,解释可能以前将state持久化到了statebackend,但并没有将数据成功写入kafka,则可以ton过这个方法恢复最近的state,然后将数据继续往kafka写数据。
- CheckpointListener接口
此接口中包含一个notifyCheckpointComplete方法
源码如下

/** * This interface must be implemented by functions/operations that want to receive * a commit notification once a checkpoint has been completely acknowledged by all * participants. */ @PublicEvolving public interface CheckpointListener { /** * This method is called as a notification once a distributed checkpoint has been completed. * * Note that any exception during this method will not cause the checkpoint to * fail any more. * * @param checkpointId The ID of the checkpoint that has been completed. * @throws Exception */ void notifyCheckpointComplete(long checkpointId) throws Exception; }
notifyCheckpointComplete方法什么时候被调用呢?所有分区的subTask向JobManager相应checkpoint后才会被调用,即告知各个subTask,这次checkpoint成功了,可以进行下一步的操作了,该方法源码如下:

@Override public final void notifyCheckpointComplete(long checkpointId) throws Exception { // the following scenarios are possible here // // (1) there is exactly one transaction from the latest checkpoint that // was triggered and completed. That should be the common case. // Simply commit that transaction in that case. // // (2) there are multiple pending transactions because one previous // checkpoint was skipped. That is a rare case, but can happen // for example when: // // - the master cannot persist the metadata of the last // checkpoint (temporary outage in the storage system) but // could persist a successive checkpoint (the one notified here) // // - other tasks could not persist their status during // the previous checkpoint, but did not trigger a failure because they // could hold onto their state and could successfully persist it in // a successive checkpoint (the one notified here) // // In both cases, the prior checkpoint never reach a committed state, but // this checkpoint is always expected to subsume the prior one and cover all // changes since the last successful one. As a consequence, we need to commit // all pending transactions. // // (3) Multiple transactions are pending, but the checkpoint complete notification // relates not to the latest. That is possible, because notification messages // can be delayed (in an extreme case till arrive after a succeeding checkpoint // was triggered) and because there can be concurrent overlapping checkpoints // (a new one is started before the previous fully finished). // // ==> There should never be a case where we have no pending transaction here // Iterator<Map.Entry<Long, TransactionHolder<TXN>>> pendingTransactionIterator = pendingCommitTransactions.entrySet().iterator(); Throwable firstError = null; while (pendingTransactionIterator.hasNext()) { Map.Entry<Long, TransactionHolder<TXN>> entry = pendingTransactionIterator.next(); Long pendingTransactionCheckpointId = entry.getKey(); TransactionHolder<TXN> pendingTransaction = entry.getValue(); if (pendingTransactionCheckpointId > checkpointId) { continue; } LOG.info("{} - checkpoint {} complete, committing transaction {} from checkpoint {}", name(), checkpointId, pendingTransaction, pendingTransactionCheckpointId); logWarningIfTimeoutAlmostReached(pendingTransaction); try { commit(pendingTransaction.handle); } catch (Throwable t) { if (firstError == null) { firstError = t; } } LOG.debug("{} - committed checkpoint transaction {}", name(), pendingTransaction); pendingTransactionIterator.remove(); } if (firstError != null) { throw new FlinkRuntimeException("Committing one of transactions failed, logging first encountered failure", firstError); } }
注意,该方法除了提醒个subTask此次checkpoint成功了外,还会提交事务,具体见源码如下(为该方法源码的一部分):
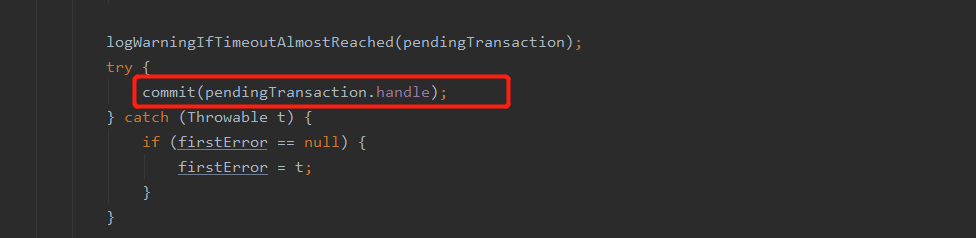
FlinkKafkaProducer中的commit方法

@Override protected void commit(FlinkKafkaProducer.KafkaTransactionState transaction) { if (transaction.isTransactional()) { try { transaction.producer.commitTransaction(); } finally { recycleTransactionalProducer(transaction.producer); } } }
若是事务提交失败后,该怎么办呢?没关系,事务提交失败后,会根据重启策略重启,并调用initializeState方法恢复先前最近的一个state,继续往kafka写数据,提交事务,再次提交事务时,就不是调用commit方法了,而是调用FlinkKafkaProducer中的recoverAndCommit方法(这块也可能是preCommit方法,自己还没完全看懂源码),先恢复数据再commit事务,源码如下

@Override protected void recoverAndCommit(FlinkKafkaProducer.KafkaTransactionState transaction) { if (transaction.isTransactional()) { try ( FlinkKafkaInternalProducer<byte[], byte[]> producer = initTransactionalProducer(transaction.transactionalId, false)) { producer.resumeTransaction(transaction.producerId, transaction.epoch); producer.commitTransaction(); } catch (InvalidTxnStateException | ProducerFencedException ex) { // That means we have committed this transaction before. LOG.warn("Encountered error {} while recovering transaction {}. " + "Presumably this transaction has been already committed before", ex, transaction); } } }
注意:这里可以保证checkpoint成功,以及事务提交成功,但是没法保证它俩在一起同时成功。但这也没关系,就算checkpoint成功了,事务没成功也没关系。事务没成功会回滚,它会从statebackend中恢复数据,然后再向kafka中写数据,提交事务。
2 自定义两阶段提交sink实例
自定义两阶段提交sink,其面向的存储系统一定要支持事务,比如mysq,0.11版以后的kafka。简单来说,自定义两阶段提交sink就是继承TwoPhaseCommitSinkFunction类,然后重写里面的方法,具体见下面的例子
MySQL分两阶段提交的Sink
druid连接池

package cn._51doit.flink.day11; import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory; import javax.sql.DataSource; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.Properties; public class DruidConnectionPool { private transient static DataSource dataSource = null; private transient static Properties props = new Properties(); static { props.put("driverClassName", "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); props.put("url", "jdbc:mysql://172.16.200.101:3306/bigdata?characterEncoding=UTF-8"); props.put("username", "root"); props.put("password", "123456"); try { dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(props); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private DruidConnectionPool() { } public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { return dataSource.getConnection(); } }
MySqlTwoPhaseCommitSinkFunction

package cn._51doit.flink.day11; import org.apache.flink.api.common.ExecutionConfig; import org.apache.flink.api.common.typeutils.base.VoidSerializer; import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2; import org.apache.flink.api.java.typeutils.runtime.kryo.KryoSerializer; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.sink.TwoPhaseCommitSinkFunction; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.SQLException; public class MySqlTwoPhaseCommitSink extends TwoPhaseCommitSinkFunction<Tuple2<String, Integer>, MySqlTwoPhaseCommitSink.ConnectionState, Void> { public MySqlTwoPhaseCommitSink() { super(new KryoSerializer<>(MySqlTwoPhaseCommitSink.ConnectionState.class, new ExecutionConfig()), VoidSerializer.INSTANCE); } @Override protected MySqlTwoPhaseCommitSink.ConnectionState beginTransaction() throws Exception { System.out.println("=====> beginTransaction... "); //Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://172.16.200.101:3306/bigdata?characterEncoding=UTF-8", "root", "123456"); Connection connection = DruidConnectionPool.getConnection(); connection.setAutoCommit(false); return new ConnectionState(connection); } @Override protected void invoke(MySqlTwoPhaseCommitSink.ConnectionState connectionState, Tuple2<String, Integer> value, Context context) throws Exception { Connection connection = connectionState.connection; PreparedStatement pstm = connection.prepareStatement("INSERT INTO t_wordcount (word, counts) VALUES (?, ?) ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE counts = ?"); pstm.setString(1, value.f0); pstm.setInt(2, value.f1); pstm.setInt(3, value.f1); pstm.executeUpdate(); pstm.close(); } @Override protected void preCommit(MySqlTwoPhaseCommitSink.ConnectionState connectionState) throws Exception { System.out.println("=====> preCommit... " + connectionState); } @Override protected void commit(MySqlTwoPhaseCommitSink.ConnectionState connectionState) { System.out.println("=====> commit... "); Connection connection = connectionState.connection; try { connection.commit(); connection.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException("提交事物异常"); } } @Override protected void abort(MySqlTwoPhaseCommitSink.ConnectionState connectionState) { System.out.println("=====> abort... "); Connection connection = connectionState.connection; try { connection.rollback(); connection.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException("回滚事物异常"); } } static class ConnectionState { private final transient Connection connection; ConnectionState(Connection connection) { this.connection = connection; } } }
3 将数据写入Hbase
使用hbase的幂等性结合at least Once(flink中state能恢复,在两次checkpoint间可能会有重复读取数据的情况)实现精确一次性语义
HBaseUtil

package cn._51doit.flink.day11; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Connection; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.ConnectionFactory; /** * Hbase的工具类,用来创建Hbase的Connection */ public class HBaseUtil { /** * @param zkQuorum zookeeper地址,多个要用逗号分隔 * @param port zookeeper端口号 * @return */ public static Connection getConnection(String zkQuorum, int port) throws Exception { Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create(); conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", zkQuorum); conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.property.clientPort", port + ""); Connection connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(conf); return connection; } }
MyHbaseSink

package cn._51doit.flink.day11; import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2; import org.apache.flink.api.java.utils.ParameterTool; import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.sink.RichSinkFunction; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.TableName; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Connection; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Table; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class MyHbaseSink extends RichSinkFunction<Tuple2<String, Double>> { private transient Connection connection; private transient Integer maxSize = 1000; private transient Long delayTime = 5000L; private transient Long lastInvokeTime; private transient List<Put> puts = new ArrayList<>(maxSize); public MyHbaseSink() {} public MyHbaseSink(Integer maxSize, Long delayTime) { this.maxSize = maxSize; this.delayTime = delayTime; } @Override public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception { super.open(parameters); ParameterTool params = (ParameterTool) getRuntimeContext() .getExecutionConfig().getGlobalJobParameters(); //创建一个Hbase的连接 connection = HBaseUtil.getConnection( params.getRequired("hbase.zookeeper.quorum"), params.getInt("hbase.zookeeper.property.clientPort", 2181) ); lastInvokeTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); } @Override public void invoke(Tuple2<String, Double> value, Context context) throws Exception { String rk = value.f0; Put put = new Put(rk.getBytes()); put.addColumn("data".getBytes(), "order".getBytes(), value.f1.toString().getBytes()); puts.add(put); //使用ProcessingTime long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //加到一个集合中 if(puts.size() == maxSize || currentTime - lastInvokeTime >= delayTime) { //获取一个HbaseTable Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("myorder")); table.put(puts); puts.clear(); lastInvokeTime = currentTime; table.close(); } } @Override public void close() throws Exception { connection.close(); } }
4 ProtoBuf
protoBuf是一种序列化机制,数据存储还是二进制,其特点是序列化、反序列化快,占用空间小(相比json而言,是它的1/3)、跨平台、跨语言。
4.1 protobuf的使用测试
(1)创建一个maven工程
(2)导入pom依赖,具体内容见下

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>org.example</groupId> <artifactId>protobuf-bean</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <properties> <maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target> <encoding>UTF-8</encoding> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.protobuf</groupId> <artifactId>protobuf-java</artifactId> <version>3.7.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.protobuf</groupId> <artifactId>protobuf-java-util</artifactId> <version>3.7.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId> <artifactId>kafka-clients</artifactId> <version>2.4.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <extensions> <extension> <groupId>kr.motd.maven</groupId> <artifactId>os-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>1.6.2</version> </extension> </extensions> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.xolstice.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>protobuf-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>0.6.1</version> <configuration> <protocArtifact> com.google.protobuf:protoc:3.7.1:exe:${os.detected.classifier} </protocArtifact> <pluginId>grpc-java</pluginId> </configuration> <executions> <execution> <goals> <goal>compile</goal> <goal>compile-custom</goal> </goals> </execution> </executions> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
(3)在main目录下创建一个proto文件夹,在这个文件夹下编辑相应的xxx.proto文件,具体如下

syntax = "proto3";
option java_package = "cn._51doit.proto";
option java_outer_classname = "OrderProto";
message Order {
int32 id = 1;
string time = 2;
double money = 3;
}
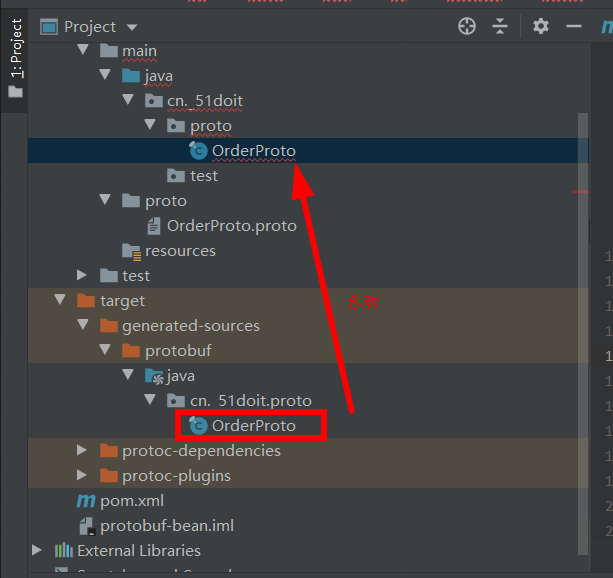
(4)在maven的plugins中会有个protobuf插件,点击里面的protobuf.compile,即可在项目中的target目录下生成相应的protobuf bean文件(支持多种语言的schema信息)
(5)将得到的proto bean移到自己想要的目录中即可
此测试就是将json数据转成protoBuf bean格式数据,然后在将其序列化输出,以及反序列化至bean输出
OrderProtoTest

package cn._51doit.test; import cn._51doit.proto.OrderProto; import com.google.protobuf.InvalidProtocolBufferException; import com.google.protobuf.util.JsonFormat; public class OrderProtoTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws InvalidProtocolBufferException { String json = "{"id": 100, "time": "2020-07-01", "money": 66.66}"; //使用工具类生成一个类 OrderProto.Order.Builder bean = OrderProto.Order.newBuilder(); //将数据拷贝的bean中 JsonFormat.parser().merge(json, bean); bean.setId(666); bean.setTime("2019-10-18"); bean.setMoney(888.88); //序列化转成二进制 //bean -> byte数组 byte[] bytes = bean.build().toByteArray(); System.out.println("二进制:" + bytes); //反序列化 //二进制数组转成bean OrderProto.Order order = OrderProto.Order.parseFrom(bytes); System.out.println("对象格式:" + order); } }
4.2 将数据以ProtoBuf的二进制形式发送到Kafka
DataToKafka

package cn._51doit.test; import cn._51doit.proto.DataBeanProto; import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer; import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerRecord; import java.util.Properties; public class DataToKafka { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1 配置参数 Properties props = new Properties(); //连接kafka节点 props.setProperty("bootstrap.servers", "feng05:9092,feng06:9092,feng07:9092"); props.setProperty("key.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer"); props.setProperty("value.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.ByteArraySerializer"); String topic = "dataproto"; // 2 kafka的生产者 KafkaProducer<String, byte[]> producer = new KafkaProducer<String, byte[]>(props); DataBeanProto.DataBean.Builder bean = DataBeanProto.DataBean.newBuilder(); DataBeanProto.DataBeans.Builder list = DataBeanProto.DataBeans.newBuilder(); for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { //往bean中设置属性 bean.setId(i); bean.setTitle("doit-" + i); bean.setUrl("www.51doit.cn"); //将bean追加到list中 list.addDataBean(bean); //清空原来分组的数据 bean.clear(); if(list.getDataBeanCount() == 10) { //将beans的集合转成protobuf的二进制 byte[] bytes = list.build().toByteArray(); ProducerRecord<String, byte[]> record = new ProducerRecord<>(topic, bytes); producer.send(record); //一次发送10条 producer.flush(); list.clear(); } } System.out.println("message send success"); // 释放资源 producer.close(); } }
4.3 Flume的KafkaChannel整合kafka序列化器
需求:(1)在kafka中定义序列化器,在数据写入kafka前,将之转成对应的二进制存入kafka
(2)Flink从Kafka中拉取刚存入相应格式的二进制数据,转成ProtoBuf的Bean

(1)kafka序列化器的实现
大致思路就是首先获取一个protoBuf bean,然后定义一个序列化器,实现一个Serializer接口,在里面重写serialize方法,具体逻辑见下面代码。将该代码打包,放到flume的lib文件夹中,注意需要将flume的lib中protobuf-java-2.5.0.jar注释或者删除掉。
KafkaProtoBufSerializer

package cn._51doit.test; import cn._51doit.proto.UserProto; import com.google.protobuf.InvalidProtocolBufferException; import com.google.protobuf.util.JsonFormat; import org.apache.kafka.common.header.Headers; import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.Serializer; import java.util.Map; public class KafkaProtoBufSerializer implements Serializer<byte[]> { @Override public void configure(Map<String, ?> configs, boolean isKey) { } @Override public byte[] serialize(String topic, byte[] data) { // 将source传给channel的数据转成ProtoBuf的二进制 //line是一个json String line = new String(data); UserProto.User.Builder bean = UserProto.User.newBuilder(); //使用工具类将JSON的数据的数据set到bean中 try { JsonFormat.parser().merge(line, bean); } catch (InvalidProtocolBufferException e) { return null; } return bean.build().toByteArray(); //返回的是ProtoBuf的二进制 } @Override public byte[] serialize(String topic, Headers headers, byte[] data) { return new byte[0]; } @Override public void close() { } }
(2)Flink的Kafka反序列化器的实现
注意,此处除了要设置反序列化,即将kafka中确定topic中的protoBuf格式的二进制数据序列化成protoBuf的bean,还要指定bean的序列化规则(注册自定义的序列化类),这样flink处理该数据时才能进行网络传输
DataBeanProto(bean,跨语言)
使用4.1方法生成
DataBeansDeserializer反序列化器

package cn._51doit.flink.day11; import org.apache.flink.api.common.serialization.DeserializationSchema; import org.apache.flink.api.common.typeinfo.TypeInformation; import java.io.IOException; /** * 自定义的Flink反序列化器 */ public class DataBeansDeserializer implements DeserializationSchema<DataBeanProto.DataBeans> { //反序列化 @Override public DataBeanProto.DataBeans deserialize(byte[] message) throws IOException { return DataBeanProto.DataBeans.parseFrom(message); } @Override public boolean isEndOfStream(DataBeanProto.DataBeans nextElement) { return false; } @Override public TypeInformation<DataBeanProto.DataBeans> getProducedType() { return TypeInformation.of(DataBeanProto.DataBeans.class); } }
PBSerializer序列化器

package cn._51doit.flink.day11; import com.esotericsoftware.kryo.Kryo; import com.esotericsoftware.kryo.Serializer; import com.esotericsoftware.kryo.io.Input; import com.esotericsoftware.kryo.io.Output; import com.google.protobuf.Message; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.HashMap; public class PBSerializer extends Serializer<Message> { /* This cache never clears, but only scales like the number of * classes in play, which should not be very large. * We can replace with a LRU if we start to see any issues. */ final protected HashMap<Class, Method> methodCache = new HashMap<Class, Method>(); /** * This is slow, so we should cache to avoid killing perf: * See: http://www.jguru.com/faq/view.jsp?EID=246569 */ protected Method getParse(Class cls) throws Exception { Method meth = methodCache.get(cls); if (null == meth) { meth = cls.getMethod("parseFrom", new Class[]{ byte[].class }); methodCache.put(cls, meth); } return meth; } //序列化 @Override public void write(Kryo kryo, Output output, Message mes) { byte[] ser = mes.toByteArray(); output.writeInt(ser.length, true); output.writeBytes(ser); } //反序列化 @Override public Message read(Kryo kryo, Input input, Class<Message> pbClass) { try { int size = input.readInt(true); byte[] barr = new byte[size]; input.readBytes(barr); return (Message)getParse(pbClass).invoke(null, barr); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException("Could not create " + pbClass, e); } } }
测试类
ProtoBufDemo

package cn._51doit.flink.day11; import cn._51doit.flink.day10.FlinkUtilsV2; import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.FlatMapFunction; import org.apache.flink.api.java.utils.ParameterTool; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStream; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator; import org.apache.flink.util.Collector; public class ProtoBufDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ ParameterTool parameters = ParameterTool.fromPropertiesFile(args[0]); DataStream<DataBeanProto.DataBeans> dataBeansStream = FlinkUtilsV2.createKafkaDataStream(parameters, "dataproto", "gid", DataBeansDeserializer.class); //注册自定义的序列化类 FlinkUtilsV2.getEnv().getConfig().registerTypeWithKryoSerializer(DataBeanProto.DataBeans.class, PBSerializer.class); FlinkUtilsV2.getEnv().getConfig().registerTypeWithKryoSerializer(DataBeanProto.DataBean.class, PBSerializer.class); SingleOutputStreamOperator<DataBeanProto.DataBean> dataBeanStream = dataBeansStream.flatMap( new FlatMapFunction<DataBeanProto.DataBeans, DataBeanProto.DataBean>() { @Override public void flatMap(DataBeanProto.DataBeans list, Collector<DataBeanProto.DataBean> out) throws Exception { for (DataBeanProto.DataBean dataBean : list.getDataBeanList()) { out.collect(dataBean); } } }); dataBeanStream.print(); FlinkUtilsV2.getEnv().execute(); } }
