1、数据校验概述
数据校验分为客户端校验和服务器端校验,客户端主要是通过过滤正常用户的误操作,是第一道防线,一般使用JavaScript代码实现。但是只有客户端校验是不够的,攻击者可以绕过客户端验证直接进行非法输入,这样可能会引起系统异常,为了确保数据的合法性,防止用户通过非正常手段提交错误信息,必须加上服务器端验证。
服务器端校验是整个应用阻止非法数据的最后一道防线,通过应用中的编程实现。服务器端验证对于系统的安全性、完整性、健壮性起到了至关重要的作用。在Spring MVC 框架中可以利用Spring自带的验证框架验证数据,也可以利用JSR303实现数据验证。
在Spring MVC 框架中有两种方法可以验证输入数据,一种是利用Spring自带的验证框架,另一种是利用JSR303实现验证,推荐使用JSR303验证。
2、JSR303验证
对于JSR303验证,目前有两个实现,一个是Hibernate Validator,一个是Apache BVal。本教程采用的是Hibernate Validator,它和Hibernate无关,只是使用它进行数据验证。
(1)下载与安装Hibernate Validator(maven项目忽略此步)
下载地址:https://sourceforge.net/projects/hibernate/files/hibernate-validator/
本教程使用的是hibernate-validator-5.4.0.Final-dist.zip
分别导入以下jar包:
dist目录下的 hibernate-validator-t.4.0.Final.jar
dist/lib/required目录下的 classmate-1.3.1.jar、javax.el-3.0.1-b08.jar、jboss-logging-3.3.0.Final.jar、validation-api-1.1.0.Final.jar
(2)maven项目配置
在pom.xml中引入
<dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId> <version>5.4.0.Final</version> </dependency>
(3)注册校验器
在springmvc.xml配置文件中,注册校验器
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.2.xsd"> <!--将AnnotationHandler自动扫描到IOC容器中--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.springmvc"></context:component-scan> <!--配置视图解析器--> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <!--配置前缀--> <property name="prefix" value="/"></property> <!--配置后缀--> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property> </bean> <!--注册校验器--> <bean id="validator" class="org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation.LocalValidatorFactoryBean"> <property name="providerClass" value="org.hibernate.validator.HibernateValidator"></property> </bean> <!--开启Valid功能--> <mvc:annotation-driven validator="validator"></mvc:annotation-driven> </beans>
(4)创建POJO实体类
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Length; import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.NotEmpty; import javax.validation.constraints.Pattern; public class User {
@NotEmpty(message = "用户名不能为空") @Length(min = 6,max = 12,message = "用户名的长度为{min}-{max}位") private String username;
@NotEmpty(message = "密码不能为空") @Length(min = 6,max = 8,message = "密码的长度为{min}-{max}位") private String password;
@NotEmpty(message = "手机号不能为空") @Pattern(regexp = "^1[34578]\d{9}$",message = "手机号格式不正确") private String phone; //getter和setter方法 }
(5)创建控制器类
@Controller public class ValidatorTestController { @RequestMapping("/userLogin") public String login(@Valid User user, BindingResult br, Model model){ int errorCount = br.getErrorCount(); if(errorCount>0){ FieldError username = br.getFieldError("username"); FieldError password = br.getFieldError("password"); FieldError phone = br.getFieldError("phone"); if (username!=null) { model.addAttribute("userNameMSG",username.getDefaultMessage()); } if (password!=null) { model.addAttribute("pwdMSG",password.getDefaultMessage()); } if (phone!=null) { model.addAttribute("phoneMSG",phone.getDefaultMessage()); } return "testValidator"; } return "success"; } }
(6)创建数据校验页面
创建testValid.jsp页面
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" isELIgnored="false" %> <html> <head> <title>数据校验</title> <style> span{ color: red;} </style> </head> <body> <form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/userLoginDemo" method="post"> <p> 用户名:<input type="text" name="username" value="${user.username}"> <span>${userNameMSG}</span> </p> <p> 密码:<input type="password" name="password" value="${user.password}"> <span>${pwdMSG}</span> </p> <p> 手机号:<input type="text" name="phone" value="${user.phone}"> <span>${phoneMSG}</span> </p> <p> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </p> </form> </body> </html>
效果展示:
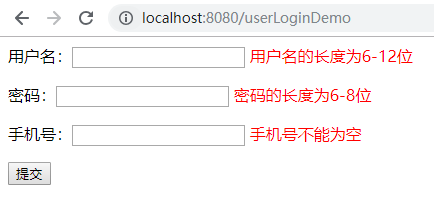
3、JSR303常用标注类型
(1)空检查
- @Null 验证对象是否为null
- @NotNull 验证对象是否不为null, 无法查检长度为0的字符串
- @NotBlank 检查约束字符串是不是Null还有被Trim的长度是否大于0,只对字符串,且会去掉前后空格.
- @NotEmpty 检查约束元素是否为NULL或者是EMPTY.
(2)Booelan检查
- @AssertTrue 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 true
- @AssertFalse 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 false
(3)长度检查
- @Size(min=, max=) 验证对象(Array,Collection,Map,String)长度是否在给定的范围之内
- @Length(min=, max=) Validates that the annotated string is between min and max included.
(4)日期检查
- @Past 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之前
- @Future 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之后
- @Pattern 验证 String 对象是否符合正则表达式的规则
(5)数值检查
建议使用在Stirng,Integer类型,不建议使用在int类型上,因为表单值为“”时无法转换为int,但可以转换为Stirng为"",Integer为null
- @Min 验证 Number 和 String 对象是否大等于指定的值
- @Max 验证 Number 和 String 对象是否小等于指定的值
- @DecimalMax 被标注的值必须不大于约束中指定的最大值. 这个约束的参数是一个通过BigDecimal定义的最大值的字符串表示.小数存在精度
- @DecimalMin 被标注的值必须不小于约束中指定的最小值. 这个约束的参数是一个通过BigDecimal定义的最小值的字符串表示.小数存在精度
- @Digits 验证 Number 和 String 的构成是否合法
- @Digits(integer=,fraction=) 验证字符串是否是符合指定格式的数字,interger指定整数精度,fraction指定小数精度。
- @Range(min=, max=) 检查数字是否介于min和max之间.
- @Range(min=10000,max=50000,message="range.bean.wage")
- private BigDecimal wage;
- @Valid 递归的对关联对象进行校验, 如果关联对象是个集合或者数组,那么对其中的元素进行递归校验,如果是一个map,则对其中的值部分进行校验.(是否进行递归验证)
- @CreditCardNumber信用卡验证
- @Email 验证是否是邮件地址,如果为null,不进行验证,算通过验证。
- @ScriptAssert(lang= ,script=, alias=)
- @URL(protocol=,host=, port=,regexp=, flags=)