volatile:
让变量每次在使用的时候,都从主存中取。
volatile具有synchronized关键字的“可见性”,但是没有synchronized关键字的“并发正确性”,也就是说不保证线程执行的有序性。
也就是说,volatile变量对于每次使用,线程都能得到当前volatile变量的最新值。但是volatile变量并不保证并发的正确性。
1. volatile的可见性:
案例:
public class TestVolatile { private static boolean status = false; public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { new Thread(() -> { while (!status) { } }).start(); Thread.sleep(100L); status = true; System.out.println("status is " + status); } }
运行结果:status 状态已经打印,但是线程还在继续执行中。

原因是:每一个线程都会创建自己的变量副本存在寄存器中。主线程将值修改了,其他线程是不知道的。
要让status值变了,能够让其他线程都知晓,可以使用volatile.
涉及线程知识:https://www.cnblogs.com/jssj/p/11432409.html
将上述代码修改一下:
下面的代码
private static boolean status = false;
改成
private volatile static boolean status = false;
再次运行程序:线程就停止了。
添加一个额外知识:(困扰我好久的疑问)
将上述代码进行修改:去掉volatile,再循环中加入一行:System.out.println("--------------");
public class TestVolatile { private static boolean status = false; public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { new Thread(() -> { while (!status) { System.out.println("--------------"); } }).start(); Thread.sleep(1L); status = true; System.out.println("status is " + status); } }
运行:

线程正常停止了。 为什么?
看了println源码:
public void println(String x) { synchronized (this) { print(x); newLine(); } }
发现关键字:synchronized。猜测和它有关。
验证:(在循环里面增加了一个synchronized锁,其他都不变)
public class TestVolatile { static TestVolatile testVolatile = new TestVolatile(); private static boolean status = false; public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { new Thread(() -> { while (!status) { synchronized (testVolatile){ } } }).start(); Thread.sleep(100L); status = true; System.out.println("status is " + status); } }
运行结果:

线程正常停止。
同时也证明了:synchronized 也有可见性。开心^-^!
2. volatile的非原子性:
public class Counter { private volatile int inc = 0; private void increase() { inc++; } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Counter counter = new Counter(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { new Thread(() -> { for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) { counter.increase(); } }).start(); } Thread.sleep(3000L); System.out.println(counter.inc); } }
运行结果:(每次运行结果不一样的)

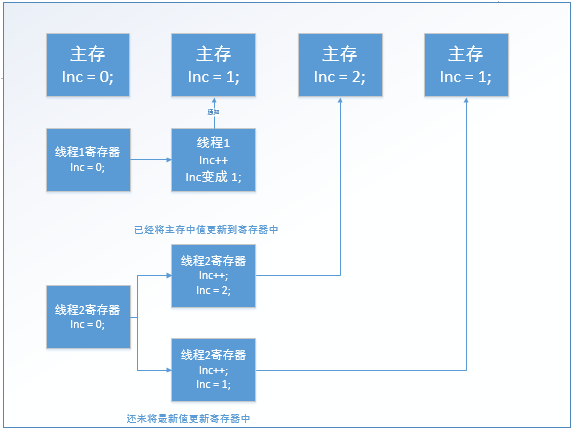
原因是:虽然volatile有可见性,但是主存中的变量值和每一个线程寄存器中的变量在某一时刻存在不一致的情况。
图解:(volatile的变量会去主存中获取值,但不一定是最新的),得到结论,volatile不会导致线程阻塞。
synchronized:
Java语言的关键字,当它采用修饰一个方法或一个代码块的时候,能够保证在同一时刻最多只有一个线程执行该段代码。
public class MyLockTest implements Runnable { private static int index = 1000; @Override public void run() { while(true) { if(index > 0){ try { //为了让效果更佳明显 Thread.sleep(1L); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } index--; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"; index = " + index); }else{ break; } } } public static void main(String[] args) { MyLockTest test = new MyLockTest(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { new Thread(test, "thread-" + i).start(); } System.out.println("index = "+index); } }
运行结果:

1. synchronized 原子性
public class MyLockTest implements Runnable { private static int index = 1000; @Override public void run() { while(true) { synchronized (this){ if(index > 0){ try { //为了让效果更佳明显 Thread.sleep(1L); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } index--; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"; index = " + index); }else{ break; } } } } public static void main(String[] args) { MyLockTest test = new MyLockTest(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { new Thread(test, "thread-" + i).start(); } System.out.println("index = "+index); } }
运行结果:

synchronized 代码块中的代码就变成一个原子不可分割,必须全部执行完,才能让下一个线程调用。
从中发现执行速度下降非常明显,执行变得异常慢。
2. 可见性上面已经验证过:
3. 无序性,哪个线程执行,资源靠抢(案列中一直被3这个线程占着,每次效果不一)。
下面看看ReentrantLock 锁,可以做到有序,公平,每一个线程先到先得,效率更低。
ReentrantLock 锁
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class MyLockTest implements Runnable { private static int index = 1000; private ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock(true); @Override public void run() { while(true) { reentrantLock.lock(); if(index > 0){ try { //为了让效果更佳明显 Thread.sleep(1L); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } index--; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"; index = " + index); }else{ break; } reentrantLock.unlock(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { MyLockTest test = new MyLockTest(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { new Thread(test, "thread-" + i).start(); } System.out.println("index = "+index); } }
运行结果:

总结:
可见性:volatile ,synchronized ,ReentrantLock
原子性:synchronized ,ReentrantLock
有序性:ReentrantLock
效率(高到低):volatile ,synchronized ,ReentrantLock
Java中还有其他锁,后续有机会补充。
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/wo541075754/article/details/82144223